J Korean Soc Radiol.
2015 May;72(5):335-343. 10.3348/jksr.2015.72.5.335.
Comparison of the Effectiveness of Preoperative Portal Vein Embolization in Patients with Chronic Liver Disease: Gelfoam versus Gelfoam-Coil Combination
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology and Cardiac and Vascular Center, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Radiology, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. raddrsu@kuh.ac.kr
- KMID: 1793890
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2015.72.5.335
Abstract
- PURPOSE
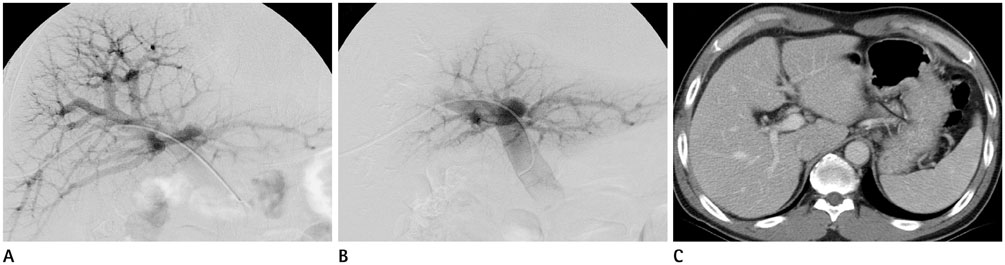
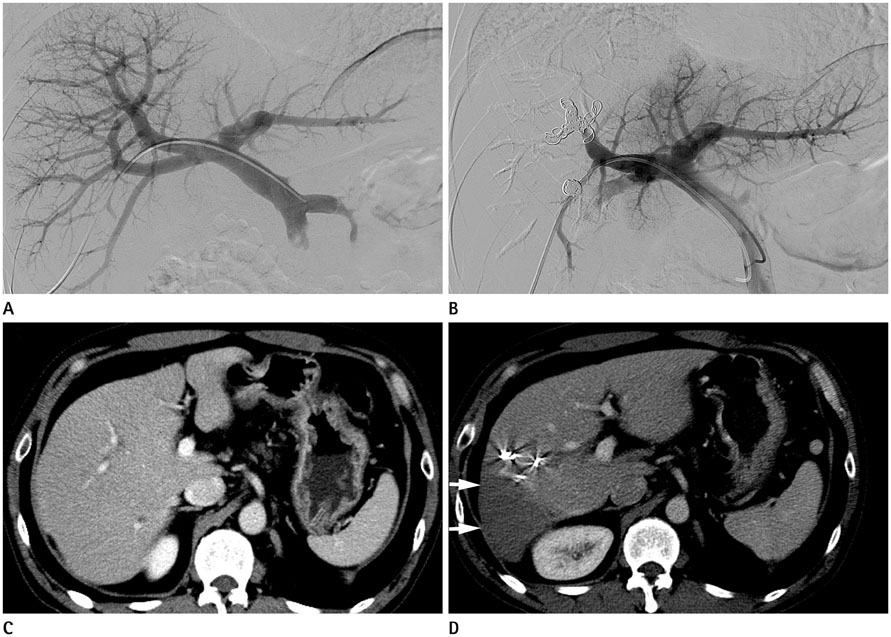
To compare the effectiveness of portal vein embolization (PVE) performed using gelfoam or a gelfoam-coil combination before major hepatic resection in patients with chronic liver disease.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
PVE using gelfoam or a gelfoam-coil combination was performed in 37 patients. From April 2003 to September 2007, PVE was performed using gelfoam (n = 17) and a gelfoam-coil combination (n = 20) to induce hypertrophy. Computed tomography volumetry was performed 2-4 weeks after PVE to assess the changes in liver volume.
RESULTS
The mean percentage increase in future liver remnant volume was 23.7 +/- 23.7% in the gelfoam group and 36.7 +/- 18.5% in the gelfoam-coil group (p = 0.02). Recanalization was found in 15 gelfoam group patients and 8 gelfoam-coil group patients (p = 0.003). The mean tumor size increased from 4.5 +/- 2.9 cm before PVE to 5.0 +/- 3.5 cm after PVE in the gelfoam group and from 4.3 +/- 2.2 cm before PVE to 4.7 +/- 2.5 cm after PVE in the gelfoam-coil group (p = 0.80).
CONCLUSION
The gelfoam-coil combination was more effective than gelfoam alone for induction of compensatory hypertrophy by PVE in patients with chronic liver disease.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Estimating the world cancer burden: Globocan 2000. Int J Cancer. 2001; 94:153–156.2. Forner A, Reig ME, de Lope CR, Bruix J. Current strategy for staging and treatment: the BCLC update and future prospects. Semin Liver Dis. 2010; 30:61–74.3. Tanaka H, Hirohashi K, Kubo S, Shuto T, Higaki I, Kinoshita H. Preoperative portal vein embolization improves prognosis after right hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with impaired hepatic function. Br J Surg. 2000; 87:879–882.4. Denys A, Lacombe C, Schneider F, Madoff DC, Doenz F, Qanadli SD, et al. Portal vein embolization with N-butyl cyanoacrylate before partial hepatectomy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and underlying cirrhosis or advanced fibrosis. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2005; 16:1667–1674.5. Kubota K, Makuuchi M, Kusaka K, Kobayashi T, Miki K, Hasegawa K, et al. Measurement of liver volume and hepatic functional reserve as a guide to decision-making in resectional surgery for hepatic tumors. Hepatology. 1997; 26:1176–1181.6. Lee KC, Kinoshita H, Hirohashi K, Kubo S, Iwasa R. Extension of surgical indications for hepatocellular carcinoma by portal vein embolization. World J Surg. 1993; 17:109–115.7. Madoff DC, Hicks ME, Vauthey JN, Charnsangavej C, Morello FA Jr, Ahrar K, et al. Transhepatic portal vein embolization: anatomy, indications, and technical considerations. Radiographics. 2002; 22:1063–1076.8. Abulkhir A, Limongelli P, Healey AJ, Damrah O, Tait P, Jackson J, et al. Preoperative portal vein embolization for major liver resection: a meta-analysis. Ann Surg. 2008; 247:49–57.9. de Baere T, Denys A, Paradis V. Comparison of four embolic materials for portal vein embolization: experimental study in pigs. Eur Radiol. 2009; 19:1435–1442.10. Huang JY, Yang WZ, Li JJ, Jiang N, Zheng QB. Portal vein embolization induces compensatory hypertrophy of remnant liver. World J Gastroenterol. 2006; 12:408–414.11. Wakabayashi H, Okada S, Maeba T, Maeta H. Effect of preoperative portal vein embolization on major hepatectomy for advanced-stage hepatocellular carcinomas in injured livers: a preliminary report. Surg Today. 1997; 27:403–410.12. Wakabayashi H, Ishimura K, Okano K, Karasawa Y, Goda F, Maeba T, et al. Application of preoperative portal vein embolization before major hepatic resection in patients with normal or abnormal liver parenchyma. Surgery. 2002; 131:26–33.13. Kokudo N, Tada K, Seki M, Ohta H, Azekura K, Ueno M, et al. Proliferative activity of intrahepatic colorectal metastases after preoperative hemihepatic portal vein embolization. Hepatology. 2001; 34:267–272.14. Bruix J, Sherman M. American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: an update. Hepatology. 2011; 53:1020–1022.15. Omary RA, Bettmann MA, Cardella JF, Bakal CW, Schwartzberg MS, Sacks D, et al. Quality improvement guidelines for the reporting and archiving of interventional radiology procedures. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2002; 13(9 Pt 1):879–881.16. Makuuchi M, Takayasu K, Takuma T, Yamazaki S, Hasegawa H, Nishiura S, et al. Preoperative transcatheter embolization of the portal venous branch for patients receiving extended lobectomy due to the bile duct carcinoma. J Jpn Soc Clin Surg. 1984; 45:1558–1564.17. Lin TY, Chen CC. Metabolic function and regeneration of cirrhotic and non-cirrhotic livers after hepatic lobectomy in man. Ann Surg. 1965; 162:959–972.18. Farges O, Belghiti J, Kianmanesh R, Regimbeau JM, Santoro R, Vilgrain V, et al. Portal vein embolization before right hepatectomy: prospective clinical trial. Ann Surg. 2003; 237:208–217.19. Vauthey JN, Chaoui A, Do KA, Bilimoria MM, Fenstermacher MJ, Charnsangavej C, et al. Standardized measurement of the future liver remnant prior to extended liver resection: methodology and clinical associations. Surgery. 2000; 127:512–519.20. Kim MJ, Choo SW, Do YS, Park KB, Han YH, Choo IW, et al. Use of double-occlusion balloon catheter: preoperative portal vein embolization for induction of future remnant liver hypertrophy. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2004; 27:16–20.21. de Baere T, Roche A, Vavasseur D, Therasse E, Indushekar S, Elias D, et al. Portal vein embolization: utility for inducing left hepatic lobe hypertrophy before surgery. Radiology. 1993; 188:73–77.22. de Baere T, Roche A, Elias D, Lasser P, Lagrange C, Bousson V. Preoperative portal vein embolization for extension of hepatectomy indications. Hepatology. 1996; 24:1386–1391.23. Lainas P, Boudechiche L, Osorio A, Coulomb A, Weber A, Pariente D, et al. Liver regeneration and recanalization time course following reversible portal vein embolization. J Hepatol. 2008; 49:354–362.24. Elias D, De Baere T, Roche A, Mducreux , Leclere J, Lasser P. During liver regeneration following right portal embolization the growth rate of liver metastases is more rapid than that of the liver parenchyma. Br J Surg. 1999; 86:784–788.25. van Gulik TM, van den Esschert JW, de Graaf W, van Lienden KP, Busch OR, Heger M, et al. Controversies in the use of portal vein embolization. Dig Surg. 2008; 25:436–444.26. Hayashi S, Baba Y, Ueno K, Nakajo M, Kubo F, Ueno S, et al. Acceleration of primary liver tumor growth rate in embolized hepatic lobe after portal vein embolization. Acta Radiol. 2007; 48:721–727.27. de Graaf W, van den Esschert JW, van Lienden KP, van Gulik TM. Induction of tumor growth after preoperative portal vein embolization: is it a real problem? Ann Surg Oncol. 2009; 16:423–430.28. Fischer L, Cardenas C, Thorn M, Benner A, Grenacher L, Vetter M, et al. Limits of Couinaud's liver segment classification: a quantitative computer-based three-dimensional analysis. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2002; 26:962–967.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Transcatheter transarterial gelfoam embolization
- Gelfoam Embolization Technique to Prevent Bone Cement Leakage during Percutaneous Vertebroplasty: Comparative Study of Gelfoam only vs. Gelfoam with Venography
- Hemoperitoneum due to Ruptured Paraumbilical Vein in a Cirrhotic Patient with Portal Hypertension: Treatment by means of Coil Embolization
- A Comparative Study on Transcatheter Renal Arterial Embolization (TRAE) in Rabbits with Absolute Ethanol and Gelfoam Particles
- Transarterial chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma: one year survival rate of 193 cases