Comparison of Preoperative and Postoperative Ocular Biometry in Eyes with Phakic Intraocular Lens Implantations
- Affiliations
-
- 1The Institute of Vision Research, Department of Ophthalmology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. tikim@yuhs.ac
- 2Yonsei Plus Eye Center, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 1793177
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2013.54.5.1259
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To compare preoperative and postoperative ocular biometry in patients with iris-fixated phakic intraocular lens (pIOLs): Artisan and Artiflex.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This study included 40 eyes with Artisan and 36 eyes with Artiflex pIOL implants. Anterior chamber depth (ACD) and axial length (AL) were measured by applanation ultrasonography (A-scan) and partial coherence interferometry (IOLMaster) preoperatively and 3 months after pIOL implantation.
RESULTS
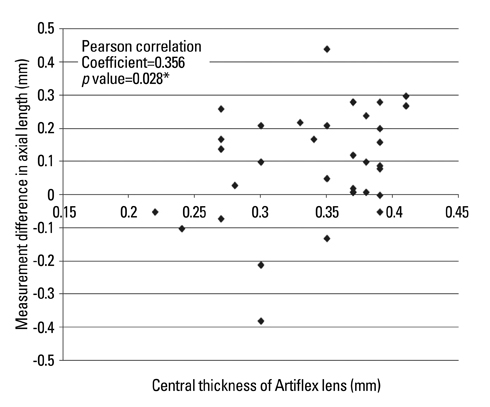
ACD measurements after Artisan or Artiflex pIOL implantation were smaller than preoperative measurements. Specifically, the difference after Artisan pIOL implantation was -1.07+/-0.17 mm by A-scan and -0.08+/-0.08 mm by IOLMaster. The difference after Artiflex pIOL implantation was -1.31+/-0.15 mm by A-scan and -0.05+/-0.07 mm by IOLMaster. After Artisan pIOL implantation, differences in AL measurements by A-scan were insignificant (difference: -0.03+/-0.15 mm), whereas postoperative AL measurements by IOLMaster were significantly longer than preoperative measurements (difference: 0.12+/-0.07 mm). After Artiflex pIOL implantation, AL measurements by both A-scan and IOLMaster were significantly longer than preoperative measurements (difference: 0.09+/-0.16 mm by A-scan and 0.07+/-0.10 mm by IOLMaster). In the Artiflex group, differences in AL measurements by A-scan correlated with the central thickness of the Artiflex pIOL.
CONCLUSION
ACD and AL measurements were influenced by iris-fixated phakic IOL implantation.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Evaluation of Optical Quality Parameters and Ocular Aberrations in Multifocal Intraocular Lens Implanted Eyes
Hun Lee, Kwanghyun Lee, Ji Min Ahn, Eung Kweon Kim, Bradford Sgrignoli, Tae-im Kim
Yonsei Med J. 2014;55(5):1413-1420. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2014.55.5.1413.Changes in Ocular Biometrics Measured after Implantation of a Phakic Intraocular Lens
Jung Hoo Lee, Gyu Won Ryu, Byung Gun Park
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2018;59(3):223-229. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2018.59.3.223.Changes in Ocular Biometrics Measured after Implantation of a Phakic Intraocular Lens
Jung Hoo Lee, Gyu Won Ryu, Byung Gun Park
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2018;59(3):223-229. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2018.59.3.223.Refractory Outcomes after Cataract Surgery in Acute Primary Angle-closure Glaucoma Patients Treated with Laser Iridotomy
Hye Seong Hwang, Dong Yoon Kim, Hyun Tae Kim, Ju Byung Chae, Sungmin Hyung
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2019;60(5):447-454. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2019.60.5.447.
Reference
-
1. Huang D, Schallhorn SC, Sugar A, Farjo AA, Majmudar PA, Trattler WB, et al. Phakic intraocular lens implantation for the correction of myopia: a report by the American Academy of Ophthalmology. Ophthalmology. 2009; 116:2244–2258.
Article2. Stulting RD, John ME, Maloney RK, Assil KK, Arrowsmith PN, Thompson VM. U.S. Verisyse Study Group. Three-year results of Artisan/Verisyse phakic intraocular lens implantation. Results of the United States Food And Drug Administration clinical trial. Ophthalmology. 2008; 115:464–472.e1.
Article3. Dick HB, Budo C, Malecaze F, Güell JL, Marinho AA, Nuijts RM, et al. Foldable Artiflex phakic intraocular lens for the correction of myopia: two-year follow-up results of a prospective European multicenter study. Ophthalmology. 2009; 116:671–677.
Article4. Saxena R, Boekhoorn SS, Mulder PG, Noordzij B, van Rij G, Luyten GP. Long-term follow-up of endothelial cell change after Artisan phakic intraocular lens implantation. Ophthalmology. 2008; 115:608–613.e1.
Article5. Georgalas I, Petrou P, Papaconstantinou D, Koutsandrea C, Ladas I. Bilateral giant tear-associated retinal detachment following Artisan phakic intraocular lens implantation for correction of moderate myopia. Acta Ophthalmol. 2010; 88:e143–e144.
Article6. Lee SJ. Traumatic aniridia and aphakia after Artisan intraocular lens implantation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007; 33:1341–1342.
Article7. Chen LJ, Chang YJ, Kuo JC, Rajagopal R, Azar DT. Metaanalysis of cataract development after phakic intraocular lens surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008; 34:1181–1200.
Article8. Moshirfar M, Mifflin M, Wong G, Chang JC. Cataract surgery following phakic intraocular lens implantation. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2010; 21:39–44.
Article9. Kohnen T, Kook D, Morral M, Güell JL. Phakic intraocular lenses: part 2: results and complications. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010; 36:2168–2194.10. Hoffer KJ. Ultrasound axial length measurement in biphakic eyes. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003; 29:961–965.
Article11. Sanders DR, Bernitsky DA, Harton PJ Jr, Rivera RR. The Visian myopic implantable collamer lens does not significantly affect axial length measurement with the IOLMaster. J Refract Surg. 2008; 24:957–959.
Article12. Khokhar SK, Agarwal T, Dave V. Comparison of preoperative and postoperative axial length measurement with immersion A-scan in ICL cases. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009; 35:2168–2169.
Article13. Pitault G, Leboeuf C, Leroux les Jardins S, Auclin F, Chong-Sit D, Baudouin C. [Optical biometry of eyes corrected by phakic intraocular lenses]. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2005; 28:1052–1057.14. de Vries NE, Tahzib NG, Budo CJ, Webers CA, de Boer R, Hendrikse F, et al. Results of cataract surgery after implantation of an iris-fixated phakic intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009; 35:121–126.
Article15. Vetrugno M, Cardascia N, Cardia L. Anterior chamber depth measured by two methods in myopic and hyperopic phakic IOL implant. Br J Ophthalmol. 2000; 84:1113–1116.
Article16. Sheng H, Bottjer CA, Bullimore MA. Ocular component measurement using the Zeiss IOLMaster. Optom Vis Sci. 2004; 81:27–34.
Article17. Holladay JT. Standardizing constants for ultrasonic biometry, keratometry, and intraocular lens power calculations. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1997; 23:1356–1370.
Article18. Hong JP, Nam SM, Kim TI, Seo KY, Lee SY, Meduri A, et al. Reliability of RTVue, Visante, and slit-lamp adapted ultrasonic pachymetry for central corneal thickness measurement. Yonsei Med J. 2012; 53:634–641.
Article19. Eleftheriadis H. IOLMaster biometry: refractive results of 100 consecutive cases. Br J Ophthalmol. 2003; 87:960–963.
Article20. Rose LT, Moshegov CN. Comparison of the Zeiss IOLMaster and applanation A-scan ultrasound: biometry for intraocular lens calculation. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 2003; 31:121–124.
Article21. Parravano M, Oddone F, Sampalmieri M, Gazzaniga D. Reliability of the IOLMaster in axial length evaluation in silicone oil-filled eyes. Eye (Lond). 2007; 21:909–911.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Anterior Chamber Phakic Intraocular lens in Patients with high Myopia
- Aberration Change in Pseudophakia with Three Types of Acryl Intraocular Lens
- Two-year Endothalial Changes after Iris Fixed Phakic Intraocular Lens Implantation in Korean
- Visual Improvement in High Myopic Amblyopic Adult Eyes following Phakic Anterior Chamber Intraocular Lens Implantation
- Long Term Corneal Endothelial Cell Density Loss after Iris-fixed Phakic Intraocular Lens Implantation