Yonsei Med J.
2013 Sep;54(5):1137-1142. 10.3349/ymj.2013.54.5.1137.
Effect of 45degrees Reclining Sitting Posture on Swallowing in Patients with Dysphagia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Institute for Medical Sciences, Chonbuk National University Medical School and Research Institute of Clinical Medicine, Chonbuk National University Hospital, Jeonju, Korea. vivaseo@jbnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1793160
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2013.54.5.1137
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To determine the effect of a 45degrees reclining sitting posture on swallowing in patients with dysphagia.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Thirty-four patients with dysphagia were evaluated. Videofluoroscopic swallowing study was performed for each patient in 90degrees upright and in 45degrees reclining sitting posture. Patients swallowed 5 types of boluses twice: sequentially 2 mL thin liquid, 5 mL thin liquid, thick liquid, yogurt, and cooked rice. Data such as the penetration-aspiration scale (PAS), oral transit time (OTT), pharyngeal delay time (PDT), pharyngeal transit time (PTT), residue in valleculae and pyriform sinuses, premature bolus loss, and nasal penetration were obtained.
RESULTS
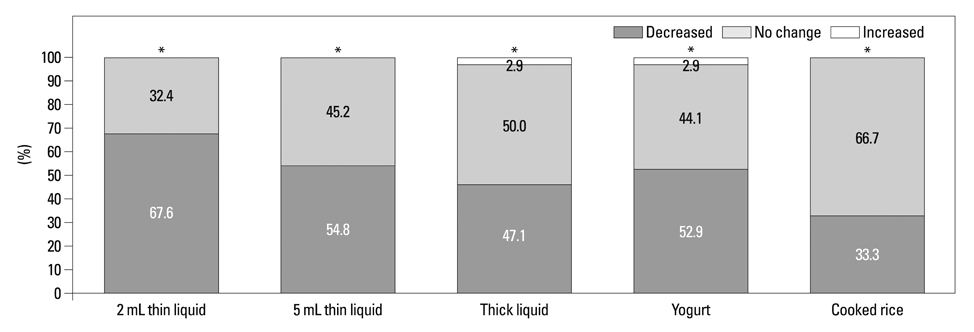
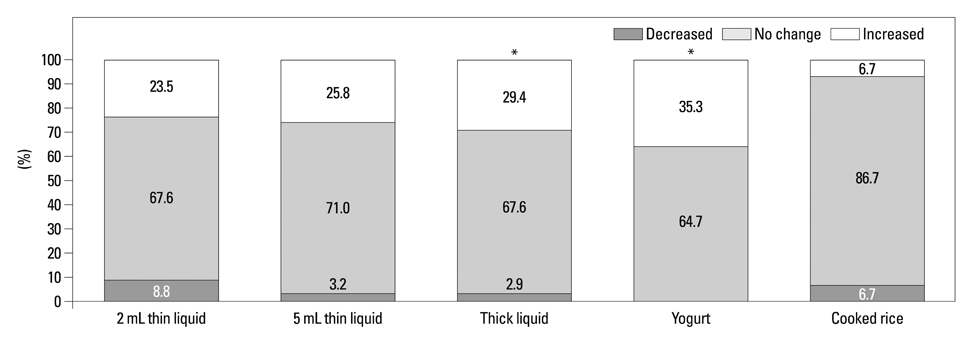
The mean PAS on the 2 mL thin liquid decreased significantly in the 45degrees reclining sitting posture (p=0.007). The mean PAS on 5 mL thin liquid in the 45degrees reclining sitting posture showed decreasing tendency. The residue in valleculae decreased significantly for all boluses in the 45degrees reclining sitting posture (p<0.001, p=0.002, p=0.003, p<0.001, p=0.020, respectively). The residue in pyriform sinuses increased significantly on 5 mL thin liquid, thick liquid, and yogurt (p=0.031, p=0.020, p=0.002, respectively). There were no significant differences in OTT, PDT, PTT, premature bolus loss, and nasal penetration between both postures.
CONCLUSION
PAS on 2 mL thin liquid and residue in valleculae on all types of boluses were decreased in a 45degrees reclining sitting posture. Therefore, we believe that the 45degrees reclining sitting posture on swallowing is beneficial for the patients with penetration or aspiration on small amounts of thin liquid and large amounts of residue in valleculae.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Han TR, Paik NJ, Park JW. The clinical functional scale for dysphagia in stroke patients. Korean J Stroke. 2001; 3:153–157.2. Park YH, Kim HS. Clinical Evaluation of the Swallowing. J Korean Dysphagia Soc. 2011; 1:19–24.3. Han TR, Paik NJ, Park JW. Quantifying swallowing function after stroke: a functional dysphagia scale based on videofluoroscopic studies. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2001; 82:677–682.
Article4. Han TR, Paik NJ, Kim IS. Dysphagia. In : Han TR, Bang MS, editors. Rehabilitation medicine. 3rd ed. Seoul: Koonja Press;2008. p. 369–391.5. Logemann JA. Evaluation and treatment of swallowing disorders. 2nd ed. Austin: pro-ed;1998.6. Rosenbek JC, Roecker EB, Wood JL, Robbins J. Thermal application reduces the duration of stage transition in dysphagia after stroke. Dysphagia. 1996; 11:225–233.
Article7. Rasley A, Logemann JA, Kahrilas PJ, Rademaker AW, Pauloski BR, Dodds WJ. Prevention of barium aspiration during videofluoroscopic swallowing studies: value of change in posture. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1993; 160:1005–1009.
Article8. Larnert G, Ekberg O. Positioning improves the oral and pharyngeal swallowing function in children with cerebral palsy. Acta Paediatr. 1995; 84:689–692.
Article9. Ha JS, Park SO, An HM, Park IS. The usefulness of supine position on swallowing of liquid diet in neurogenic dysphagia: comparison with sitting position. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2001; 25:916–922.10. Rosenbek JC, Robbins JA, Roecker EB, Coyle JL, Wood JL. A penetration-aspiration scale. Dysphagia. 1996; 11:93–98.
Article11. Tsubahara A. Principles and practice of dysphagia management. Seoul: Koonja Press;2011.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Usefulness of Supine Position on Swallowing of Liquid Diet in Neurogenic Dysphagia: Comparison with Sitting Position
- Effects of Head Lift Exercise on Oropharyngeal Swallowing Function and Dropout Rate According to Reclining Angle in Patients with Dysphagia after Stroke: A Randomized Trial
- Rehabilitation Techniques for Dysphagia
- Instrumental Assessment of Swallowing
- Influence of the Swallowing Posture and Liquid Thickness on the Ease of Pill Swallowing in Healthy Adults