J Korean Med Sci.
2013 Aug;28(8):1145-1153. 10.3346/jkms.2013.28.8.1145.
Serum Level of Interleukin-33 and Soluble ST2 and Their Association with Disease Activity in Patients with Behcet's Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. seungki73@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Immune Tolerance Research Center, Convergent Research Consortium for Immunologic Disease, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1793018
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2013.28.8.1145
Abstract
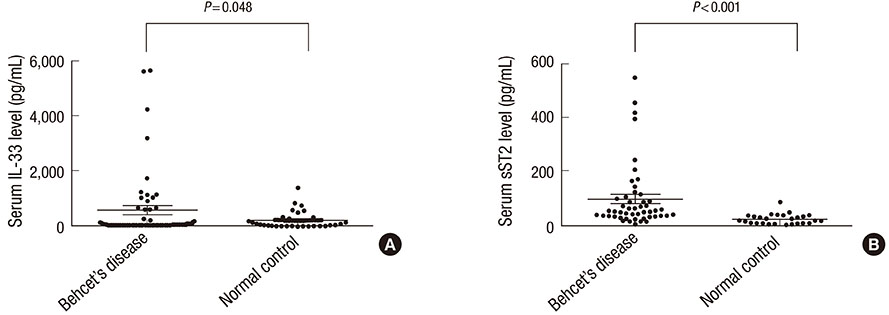
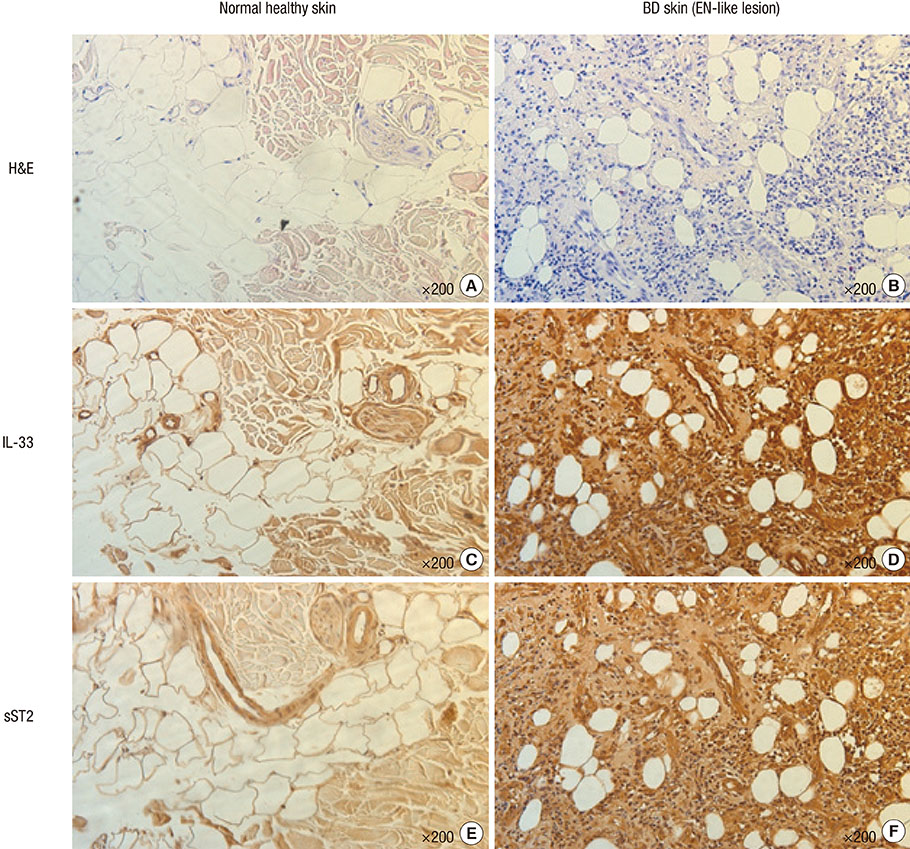
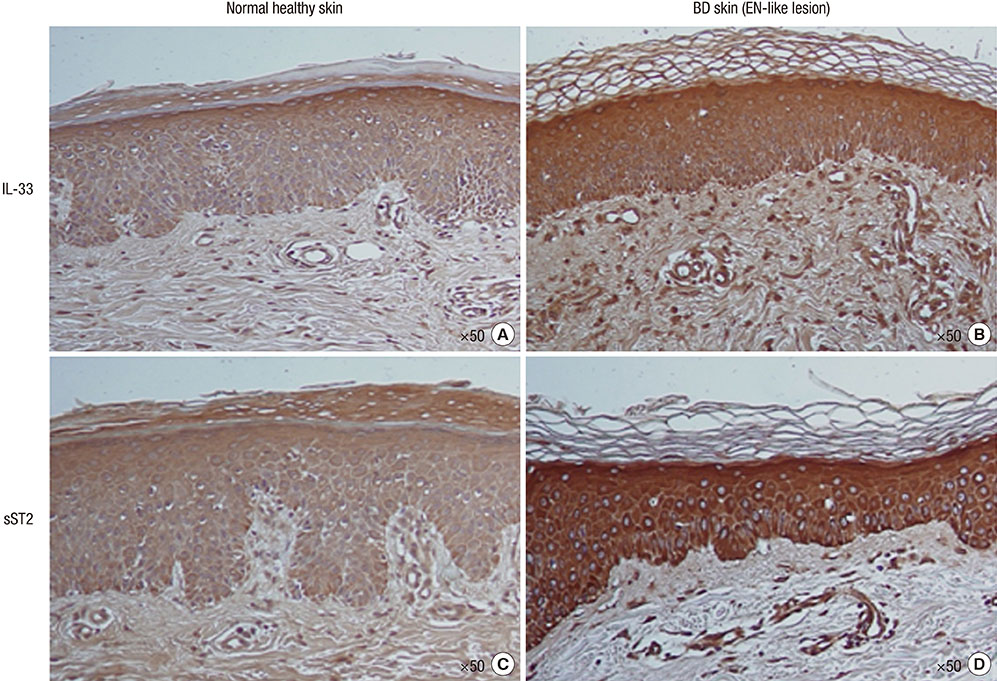
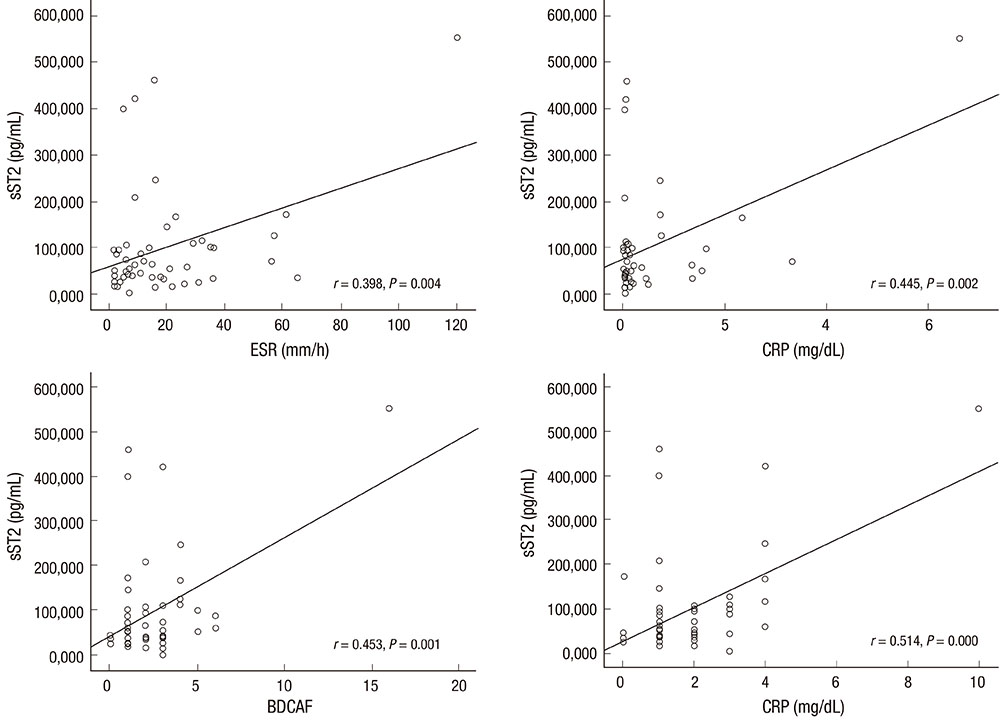
- Interleukin (IL)-33 is an important mediator of innate immunity. Behcet's disease (BD) is an autoinflammatory disorder characterized by hyperactivity of the innate immune response. We measured serum levels of IL-33 and its receptor soluble ST2 (sST2) in patients with BD to investigate their association with disease activity. Serum levels of both IL-33 and sST2 were higher in patients with BD compared with those in normal controls (IL-33: 594.48+/-175.04 pg/mL in BD and 224.23+/-56.64 pg/mL in normal controls [P=0.048], sST2: 99.01+/-15.92 pg/mL in BD and 23.56+/-3.25 pg/mL in normal controls [P<0.001]). IL-33 and sST2 expression in skin tissue, as shown by immunohistochemistry, was higher in patients with BD compared with that in the normal controls. Serum sST2 level correlated significantly with the BD currently active form (BDCAF), Iranian BD dynamic activity measure (IBDDAM), erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein. Multiple linear regression showed that serum sST2 was an independent factor associated with IBBDAM (regression coefficient, 0.374; P=0.004), and BDCAF (regression coefficient, 0.236; P=0.047). These results demonstrate that IL-33 and sST2 are highly expressed in patients with BD and that serum sST2 is an independent factor associated with IBDDAM and BDCAF, suggesting a potential role for sST2 as a surrogate marker of disease activity in patients with BD.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Behcet Syndrome/blood/*pathology
Blood Sedimentation
C-Reactive Protein/analysis
Female
Humans
Immunohistochemistry
Interleukins/*blood/metabolism
Male
Middle Aged
Receptors, Cell Surface/*blood/metabolism
Severity of Illness Index
Skin/metabolism/pathology
C-Reactive Protein
Interleukins
Receptors, Cell Surface
Figure
Reference
-
1. Schmitz J, Owyang A, Oldham E, Song Y, Murphy E, McClanahan TK, Zurawski G, Moshrefi M, Qin J, Li X, et al. IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1 receptor-related protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated cytokines. Immunity. 2005; 23:479–490.2. Moussion C, Ortega N, Girard JP. The IL-1-like cytokine IL-33 is constitutively expressed in the nucleus of endothelial cells and epithelial cells in vivo: a novel 'alarmin'? PLoS One. 2008; 3:e3331.3. Bergers G, Reikerstorfer A, Braselmann S, Graninger P, Busslinger M. Alternative promoter usage of the Fos-responsive gene Fit-1 generates mRNA isoforms coding for either secreted or membrane-bound proteins related to the IL-1 receptor. EMBO J. 1994; 13:1176–1188.4. Bhakta BB, Brennan P, James TE, Chamberlain MA, Noble BA, Silman AJ. Behçet's disease: evaluation of a new instrument to measure clinical activity. Rheumatology (Oxford). 1999; 38:728–733.5. Shahram F, Khabbazi A, Nadji A, Ziaie N, Banihashemi AT, Davatchi F. Comparison of existing disease activity indices in the follow-up of patients with Behçet's disease. Mod Rheumatol. 2009; 19:536–541.6. Verri WA Jr, Souto FO, Vieira SM, Almeida SC, Fukada SY, Xu D, Alves-Filho JC, Cunha TM, Guerrero AT, Mattos-Guimaraes RB, et al. IL-33 induces neutrophil migration in rheumatoid arthritis and is a target of anti-TNF therapy. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010; 69:1697–1703.7. Han GW, Zeng LW, Liang CX, Cheng BL, Yu BS, Li HM, Zeng FF, Liu SY. Serum levels of IL-33 is increased in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Rheumatol. 2011; 30:1583–1588.8. Mok MY, Huang FP, Ip WK, Lo Y, Wong FY, Chan EY, Lam KF, Xu D. Serum levels of IL-33 and soluble ST2 and their association with disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010; 49:520–527.9. Kuroiwa K, Arai T, Okazaki H, Minota S, Tominaga S. Identification of human ST2 protein in the sera of patients with autoimmune diseases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001; 284:1104–1108.10. Yang Z, Liang Y, Xi W, Li C, Zhong R. Association of increased serum IL-33 levels with clinical and laboratory characteristics of systemic lupus erythematosus in Chinese population. Clin Exp Med. 2011; 11:75–80.11. Oboki K, Ohno T, Kajiwara N, Saito H, Nakae S. IL-33 and IL-33 receptors in host defense and diseases. Allergol Int. 2010; 59:143–160.12. Oboki K, Ohno T, Kajiwara N, Arae K, Morita H, Ishii A, Nambu A, Abe T, Kiyonari H, Matsumoto K, et al. IL-33 is a crucial amplifier of innate rather than acquired immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010; 107:18581–18586.13. Hong YS, Moon SJ, Joo YB, Jeon CH, Cho ML, Ju JH, Oh HJ, Heo YJ, Park SH, Kim HY, et al. Measurement of interleukin-33 (IL-33) and IL-33 receptors (sST2 and ST2L) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Korean Med Sci. 2011; 26:1132–1139.14. Kageyama Y, Torikai E, Tsujimura K, Kobayashi M. Involvement of IL-33 in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis: the effect of etanercept on the serum levels of IL-33. Mod Rheumatol. 2012; 22:89–93.15. Mu R, Huang HQ, Li YH, Li C, Ye H, Li ZG. Elevated serum interleukin 33 is associated with autoantibody production in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2010; 37:2006–2013.16. Kunisch E, Chakilam S, Gandesiri M, Kinne RW. IL-33 regulates TNF-α dependent effects in synovial fibroblasts. Int J Mol Med. 2012; 29:530–540.17. Chen T, Jia RZ, Guo ZP, Cao N, Li MM, Jiao XY. Elevated serum interleukin-33 levels in patients with Henoch-Schönlein purpura. Arch Dermatol Res. 2013; 305:173–177.18. Ciccia F, Alessandro R, Rizzo A, Raimondo S, Giardina A, Raiata F, Boiardi L, Cavazza A, Guggino G, De Leo G, et al. IL-33 is overexpressed in the inflamed arteries of patients with giant cell arteritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013; 72:258–264.19. Carriere V, Roussel L, Ortega N, Lacorre DA, Americh L, Aguilar L, Bouche G, Girard JP. IL-33, the IL-1-like cytokine ligand for ST2 receptor, is a chromatin-associated nuclear factor in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007; 104:282–287.20. Sayinalp N, Ozcebe OI, Ozdemir O, Haznedaroğlu IC, Dündar S, Kirazli S. Cytokines in Behçet's disease. J Rheumatol. 1996; 23:321–322.21. Mildner M, Storka A, Lichtenauer M, Mlitz V, Ghannadan M, Hoetzenecker K, Nickl S, Dome B, Tschachler E, Ankersmit HJ. Primary sources and immunological prerequisites for sST2 secretion in humans. Cardiovasc Res. 2010; 87:769–777.22. Oshikawa K, Yanagisawa K, Tominaga Si, Sugiyama Y. ST2 protein induced by inflammatory stimuli can modulate acute lung inflammation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002; 299:18–24.23. Leung BP, Xu D, Culshaw S, McInnes IB, Liew FY. A novel therapy of murine collagen-induced arthritis with soluble T1/ST2. J Immunol. 2004; 173:145–150.24. Yin H, Huang BJ, Yang H, Huang YF, Xiong P, Zheng F, Chen XP, Chen YF, Gong FL. Pretreatment with soluble ST2 reduces warm hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006; 351:940–946.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Elevated levels of soluble ST2 but not galectin-3 are associated with increased risk of mortality in hemodialysis patients
- Levels of Soluble Interleukin-2 Receptors in Serum of Patients with Behçet's Disease
- Elevated Serum Levels of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Behcet's Syndrome
- Serum interleukin-6 in Kawasaki disease
- The soluble interleukin 2 receptor levels in Kawasaki disease