J Korean Med Sci.
2014 Feb;29(2):248-253. 10.3346/jkms.2014.29.2.248.
Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Acute Hepatitis A in Korea: A Nationwide Multicenter Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym Univesity College of Medicine, Hallym Univesity Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Korea University Guro Hospital, Seoul, Korea. kwsbyun@unitel.co.kr
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 5Department of Internal Medicine, Gachon University Graduate School of Medicine, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea.
- 6Department of Internal Medicine, Inha University School of Medicine, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea.
- 7Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Cheonan Hospital, Cheonan, Korea.
- 8Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Korea University Anam Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 9Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Bucheon, Korea.
- 10Department of Internal Medicine, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Hanyang University Guri Hospital, Guri, Korea.
- 11Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Korea University Ansan Hospital, Ansan, Korea.
- 12Department of Internal Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea School of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea St. Mary's Hosptial, Seoul, Korea.
- 13Department of Internal Medicine, Kyungpook National University College of Medicine, Kyungpook National University Hospital, Daegu, Korea.
- 14Department of Internal Medicine, Ajou University School of Medicine, Ajou University Hospital, Suwon, Korea.
- 15Department of Internal Medicine, Wonkwang University School of Medicine, Wonkwang University Hospital, Iksan, Korea.
- 16Department of Internal Medicine, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Yeungnam University Medical Center, Daegu, Korea.
- 17Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Yonsei University Wonju Christian Hospital, Wonju, Korea.
- 18Department of Biostatistics, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1789983
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2014.29.2.248
Abstract
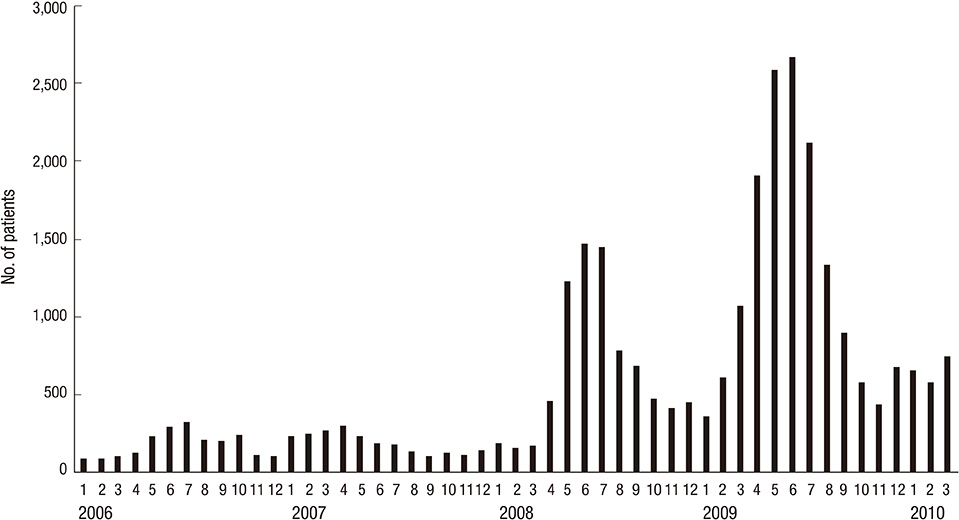
- The aim of this study was to investigate the clinical characteristics of acute hepatitis A during a recent outbreak in Korea. Data of patients diagnosed with acute hepatitis A from 2007 to 2009 were collected from 21 tertiary hospitals retrospectively. Their demographic, clinical, and serological characteristics and their clinical outcomes were analyzed. A total of 4,218 patients (mean age 33.3 yr) were included. The median duration of admission was 9 days. The mean of the highest ALT level was 2,963 IU/L, total bilirubin was 7.3 mg/dL, prothrombin time INR was 1.3. HBsAg was positive in 3.7%, and anti-HCV positive in 0.7%. Renal insufficiency occurred in 2.7%, hepatic failure in 0.9%, relapsing hepatitis in 0.7%, and cholestatic hepatitis in 1.9% of the patients. Nineteen patients (0.45%) died or were transplanted. Complications of renal failure or prolonged cholestasis were more frequent in patients older than 30 yr. In conclusion, most patients with acute hepatitis A recover uneventfully, however, complication rates are higher in patients older than 30 yr than younger patients. Preventive strategies including universal vaccination in infants and active immunization of hepatitis A to adult population should be considered for prevention of community-wide outbreaks of hepatitis A in Korea.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Acute Disease
Adolescent
Adult
Age Factors
Aged
Child
Child, Preschool
Cholestasis/epidemiology/etiology
Demography
Hepatitis A/complications/*diagnosis/mortality
Humans
Kidney Failure, Chronic/epidemiology/etiology
Liver Transplantation
Middle Aged
Morbidity
Republic of Korea
Retrospective Studies
Tertiary Care Centers
Young Adult
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Acute Pancreatitis associated with Acute Hepatitis A in an Old Aged Patient
Keepyung Hong, Chang-Nyol Paik, Ik Hyun Jo, Dae Bum Kim
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2020;76(4):211-214. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2020.76.4.211.Assay Sensitivity Difference Can Induce Anti-Hepatitis A Virus IgM Non-Reactive But Total (IgM and IgG) Reactive Results in Early Acute Hepatitis A
Soo-Kyung Kim, Kwon Yoo, Jungwon Huh
J Korean Med Sci. 2022;37(37):e287. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e287.
Reference
-
1. Hong WS, Kim CY. Seroepidemiology of type A and type B hepatitis in Seoul area. Korean J Intern Med. 1982; 25:19–26.2. Kim TW, Lee KJ. Antibody to hepatitis A antigen in children and adolescents in Korea. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1982; 25:36–40.3. Lee JI, Kim JY, Kim ST, Yoon SY, Jeong SM, Kim YK, Lee BH. Epidemiologic study of antibody to hepatitis A antigen in Choong-chung area. Korean J Gastroenterol. 1982; 14:319–323.4. Sohn YM, Rho HO, Park MS, Park JH, Choi BY, Ki M, Jang WI. The changing epidemiology of hepatitis A in children and the consideration of active immunization in Korea. Yonsei Med J. 2000; 41:34–39.5. Yang DW, Lee YA, Shim JY, Park JY, Jung HL, Park MS, Keum DH. A seroepidemiologic study on hepatitis A in Seoul, Korea. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1999; 42:180–185.6. Lee SG, Lee JH, Paik SW, Koh KC, Choi MS, Rhee PL, Kim JJ. Clinical features of hepatitis A in Korean adults. Korean J Med. 1999; 56:685–690.7. Kwon YO, Choi IJ, Jung JW, Park JH. An epidemiologic study on the seropositive rate of hepatitis A virus among a selected group of children and adults in Busan. Korean J Pediatr. 2007; 50:262–267.8. Park CH, Cho YK, Park JH, Jun JS, Park ES, Seo JH, Lim JY, Woo HO, Youn HS, Ko GH, et al. Changes in the age-specific prevalence of hepatitis A virus antibodies: a 10-year cohort study in Jinju, South Korea. Clin Infect Dis. 2006; 42:1148–1150.9. Choi HK, Song YG, Kim CO, Shin SY, Chin BS, Han SH, Jin SJ, Chae YT, Baek JH, Kim SB, et al. Clinical features of re-emerging hepatitis A: an analysis of patients hospitalized during an urban epidemic in Korea. Yonsei Med J. 2011; 52:686–691.10. Jeong SH, Lee HS. Hepatitis A: clinical manifestations and management. Intervirology. 2010; 53:15–19.11. Lednar WM, Lemon SM, Kirkpatrick JW, Redfield RR, Fields ML, Kelley PW. Frequency of illness associated with epidemic hepatitis A virus infections in adults. Am J Epidemiol. 1985; 122:226–233.12. Lee D, Cho YA, Park Y, Hwang JH, Kim JW, Kim NY, Lee DH, Lee W, Jeong SH. Hepatitis A in Korea: epidemiological shift and call for vaccine strategy. Intervirology. 2008; 51:70–74.13. Jung YM, Park SJ, Kim JS, Jang JH, Lee SH, Kim JW, Park YM, Hwang SG, Rim KS, Kang SK, et al. Atypical manifestations of hepatitis A infection: a prospective, multicenter study in Korea. J Med Virol. 2010; 82:1318–1326.14. Sjogren MH, Tanno H, Fay O, Sileoni S, Cohen BD, Burke DS, Feighny RJ. Hepatitis A virus in stool during clinical relapse. Ann Intern Med. 1987; 106:221–226.15. Eng C, Chopra S. Acute renal failure in nonfulminant hepatitis A. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1990; 12:717–718.16. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Statistics of surveillance of hepatitis A. accessed on 1 October 2010. Available at http://stat.cdc.go.kr.17. Hoste EA, Kellum JA. Acute kidney injury: epidemiology and diagnostic criteria. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2006; 12:531–537.18. Williams R. Classification, etiology, and considerations of outcome in acute liver failure. Semin Liver Dis. 1996; 16:343–348.19. Gordon SC, Reddy KR, Schiff L, Schiff ER. Prolonged intrahepatic cholestasis secondary to acute hepatitis A. Ann Intern Med. 1984; 101:635–637.20. Choi HJ, Lee SY, Ma SH, Kim JH, Hur JK, Kang JH. Age related prevalence of antibodies to hepatitis A virus performed in Korea in 2005. Korean J Pediatr Infect Dis. 2005; 12:186–194.21. Kim JH. Recent epidemiological status and vaccination of hepatitis A in Korea. J Korean Med Assoc. 2008; 51:110–118.22. Barzaga BN. Hepatitis A shifting epidemiology in South-East Asia and China. Vaccine. 2000; 18:S61–S64.23. Lee CH, Chung KW, Moon YM. An outbreak of hepatitis A in Korean young adults in 1998. Korean J Gastroenterol. 1998; 32:105A.24. Choi HJ, Ko SY, Choe WH, Seo YS, Kim JH, Byun KS, Kim YS, Kim SU, Baik SK, Cheong JY, et al. Clinical features of acute viral hepatitis B in Korea: a multi-center study. Korean J Hepatol. 2011; 17:307–312.25. Song MH, Lim YS, Song TJ, Choi JM, Kim JI, Jun JB, Kim MY, Pyun DK, Lee HC, Jung YH, et al. The etiology of acute viral hepatitis for the last 3 years. Korean J Med. 2005; 68:256–260.26. Heo NY, Lim YS, Kang JM, Oh SI, Park CS, Jung SW, Lee YS, Kim KM, Lee HC, Chung YH, et al. Clinical features of fulminant hepatic failure in a tertiary hospital with a liver transplant center in Korea. Korean J Hepatol. 2006; 12:82–92.27. Gingrich GA, Hadler SC, Elder HA, Ash KO. Serologic investigation of an outbreak of hepatitis A in a rural day-care center. Am J Public Health. 1983; 73:1190–1193.28. Hadler SC, Webster HM, Erben JJ, Swanson JE, Maynard JE. Hepatitis A in day-care centers: a community-wide assessment. N Engl J Med. 1980; 302:1222–1227.29. Keeffe EB. Is hepatitis A more severe in patients with chronic hepatitis B and other chronic liver diseases? Am J Gastroenterol. 1995; 90:201–205.30. Kim DY, Ahn SH, Lee HW, Kim SU, Kim JK, Paik YH, Lee KS, Han KH, Chon CY. Anti-hepatitis A virus seroprevalence among patients with chronic viral liver disease in Korea. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007; 19:923–926.31. Song HJ, Kim TH, Song JH, Oh HJ, Ryu KH, Yeom HJ, Kim SE, Jung HK, Shim KN, Jung SA, et al. Emerging need for vaccination against hepatitis A virus in patients with chronic liver disease in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2007; 22:218–222.32. Chu CM, Liaw YF. Increased incidence of fulminant hepatic failure in previously unrecognized HBsAg carriers with acute hepatitis independent of etiology. Infection. 2005; 33:136–139.33. Kim KM, Eo SJ, Gwak GY, Choi MS, Lee JH, Koh KC, Yoo BC, Paik SW. Comparison of the clinical features of hepatitis A between HBsAg-positive and HBsAg-negative patients. Gut and Liver. 2011; 5:500–505.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prevention of Viral Hepatitis and Vaccination
- Clinical characteristics of patients with acute hepatitis A in Gwangju-Chonnam province for recent 10 years
- Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 5,628 patients with coronavirus disease 2019 in South Korea: A nationwide multicenter study
- Viral Hepatitis: Focus on Clinical Manifestations of Hepatitis A, B and C
- Should physicians go out of the way to differentiatebetween acute hepatitis B and acute exacerbation ofchronic hepatitis B?