Prevalence and Trends of Dementia in Korea: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1National Institute of Dementia, Seongnam, Korea. kwkimmd@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Neuropsychiatry, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 3Department of Psychiatry, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Brain and Cognitive Science, Seoul National University College of Natural Sciences, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1789948
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2014.29.7.903
Abstract
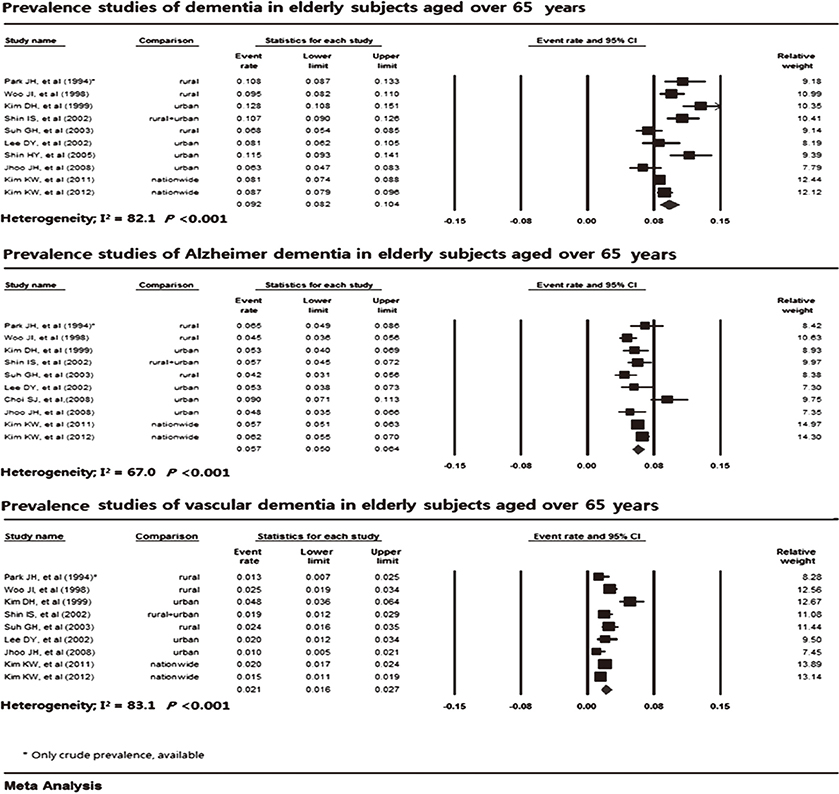
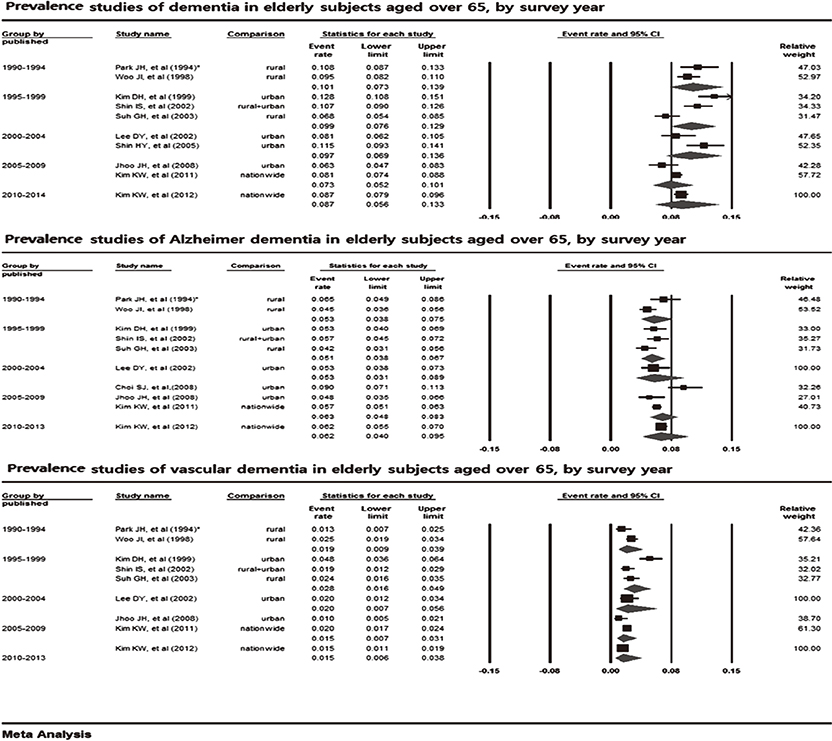
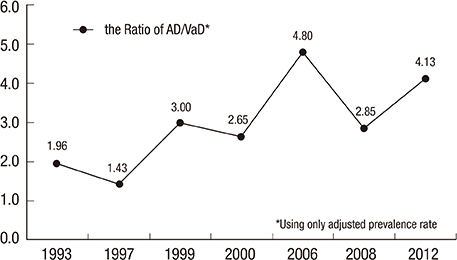
- Through a systematic review and meta-analysis of epidemiological studies on dementia, we assessed the prevalence of dementia and its subtypes-Alzheimer' disease (AD) and vascular dementia (VaD)-in Korea. We searched for epidemiological studies on dementia published in 1990-2013 using PubMed, Scopus, EMBASE, KoreaMed, KISS, and RiCH. Dementia prevalence in elderly patients (aged> or =65 yr) was 9.2% (95% confidence interval [CI], 8.2%-10.4%) from 11 studies, which was higher than those from Western and other Asian countries. AD was the most prevalent dementia type, with a prevalence of 5.7% (95% CI, 5.0%-6.4%) from 10 studies compared with 2.1% (95% CI, 1.6%-2.7%) for VaD from 9 studies. The age-specific prevalence of dementia approximately doubled with each 5.8-yr increase of age. Although a significant increasing trend of dementia prevalence was not observed, it increased slightly from 7.3% to 8.7% after 2005; AD prevalence increased after 1995 and VaD prevalence decreased after the early 2000s. The AD/VaD ratio increased from 1.96 in the early 1990s to 4.13 in the 2010s, similar to the worldwide ratio. Owing to this high prevalence in the aging population, dementia will impose significant economic burdens to Korean society.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 10 articles
-
Oldest Old Patients Should be Recruited More in Clinical Trials of Dementia
Young Ho Park
J Korean Med Sci. 2018;33(19):. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2018.33.e146.Incidence and Risk Factors for Dementia in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Nationwide Population-Based Study in Korea
Ji Hee Yu, Kyungdo Han, Sanghyun Park, Hanna Cho, Da Young Lee, Jin-Wook Kim, Ji A Seo, Sin Gon Kim, Sei Hyun Baik, Yong Gyu Park, Kyung Mook Choi, Seon Mee Kim, Nan Hee Kim
Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(1):113-124. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2018.0216.The Effect of Cataract Surgery on Cognitive Function in Elderly Adults
So Young Park, Sangkyung Choi
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2019;60(1):25-31. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2019.60.1.25.A Provincial Population-Based Survey on Attitudes towards Wills of Individuals with Dementia and Related Issues
Jung-Young Kim, Nam-Ju Sung, Soo-Jung Choi, Tae-Young Hwang
J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 2016;55(3):245-255. doi: 10.4306/jknpa.2016.55.3.245.National dementia research and development project
So-Hee Park, Jae-Hong Lee
J Korean Med Assoc. 2018;61(5):304-308. doi: 10.5124/jkma.2018.61.5.304.Risks and benefits of menopausal hormone therapy
Byung-Koo Yoon
J Korean Med Assoc. 2019;62(3):150-159. doi: 10.5124/jkma.2019.62.3.150.A retrospective analysis of outpatient anesthesia management for dental treatment of patients with severe Alzheimer's disease
Eunsun So, Hyun Jeong Kim, Myong-Hwan Karm, Kwang-Suk Seo, Juhea Chang, Joo Hyung Lee
J Dent Anesth Pain Med. 2017;17(4):271-280. doi: 10.17245/jdapm.2017.17.4.271.Dementia Epidemiology Fact Sheet 2022
Joon-Ho Shin
Ann Rehabil Med. 2022;46(2):53-59. doi: 10.5535/arm.22027.Cumulative Exposure to Metabolic Syndrome Components and the Risk of Dementia: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Yunjung Cho, Kyungdo Han, Da Hye Kim, Yong-Moon Park, Kun-Ho Yoon, Mee Kyoung Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee
Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(2):424-435. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2020.935.Association of diet quality score with the risk of mild cognitive impairment in the elderly
Eunbin Kim, Bo Youl Choi, Mi Kyung Kim, Yoon Jung Yang
Nutr Res Pract. 2022;16(5):673-684. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2022.16.5.673.
Reference
-
1. Ferri CP, Prince M, Brayne C, Brodaty H, Fratiglioni L, Ganguli M, Hall K, Hasegawa K, Hendrie H, Huang Y, et al. Global prevalence of dementia: a Delphi consensus study. Lancet. 2005; 366:2112–2117.2. Population Projections: general and processed statistics, statistics on population. accessed on 20 December 2013. Available at http://www.kosis.kr.3. Korea National Statistical Office. Report on the population and housing census. Seoul: Korea National Statistical Office;2005.4. World Population Prospects. The 2012 revision: population division, department of economic and social affairs. New York: United Nations;2012. accessed on 20 December 2013. Available at http://esa.un.org/unpd/wpp.5. Kim KW, Park JH, Kim MH, Kim MD, Kim BJ, Kim SK, Kim JL, Moon SW, Bae JN, Woo JI, et al. A nationwide survey on the prevalence of dementia and mild cognitive impairment in South Korea. J Alzheimers Dis. 2011; 23:281–291.6. Park J, Ko HJ, Park YN, Jung CH. Dementia among the elderly in a rural Korean community. Br J Psychiatry. 1994; 164:796–801.7. Kim DH, Na DL, Yeon BG, Kang Y, Min KB, Lee SH, Lee SS, Lee MR, Pyo OJ, Park CB, et al. Prevalence of dementia in the elderly of an urban community in Korea. Korean J Prev Med. 1999; 32:306–316.8. Woo JI, Lee JH, Yoo KY, Kim CY, Kim YI, Shin YS. Prevalence estimation of dementia in a rural area of Korea. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1998; 46:983–987.9. Lee DY, Lee JH, Ju YS, Lee KU, Kim KW, Jhoo JH, Yoon JC, Ha J, Woo JI. The prevalence of dementia in older people in an urban population of Korea: the Seoul Study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2002; 50:1233–1239.10. Shin IS, Kim JM, Yoon JS, Kim SJ, Yang SJ, Kim WJ, Lee SH, Kang SA, Kwak JY, Lee HY. Prevalence rate and risk factors of dementia compared between urban and rural communities of the Metropolitan Kwangju area. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 2002; 41:1165–1173.11. Suh GH, Kim JK, Cho MJ. Community study of dementia in the older Korean rural population. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2003; 37:606–612.12. Shin HY, Chung EK, Rhee JA, Yoon JS, Kim JM. Prevalence and related factors of dementia in an urban elderly population using a new screening method. J Prev Med Public Health. 2005; 38:351–358.13. Choi SJ, Jung SS, You YS, Shin BS, Kim JE, Yoon SW, Jeon DW, Baek JH, Park SW, Lee JG, et al. Prevalence of Alzheimer's dementia and its risk factors in community-dwelling elderly Koreans. Psychiatry Investig. 2008; 5:78–85.14. Jhoo JH, Kim KW, Huh Y, Lee SB, Park JH, Lee JJ, Choi EA, Han C, Choo IH, Youn JC, et al. Prevalence of dementia and its subtypes in an elderly urban Korean population: results from the Korean Longitudinal Study on Health and Aging (KLoSHA). Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2008; 26:270–276.15. Kim J, Jeon IS, Chun JH, Lee SI. The prevalence of dementia in a metropolitan city of South Korea. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2003; 18:617–622.16. Kwak DI, Choi YK, Jung IK, Lee MS. Epidemiological study of dementia in a Korea urban area. J Korean Geriatr Psychiatry. 1999; 3:44–52.17. Park NH, Lee YM, E LR. Prevalence and risk factors of dementia in the community elderly. J Korean Acad Community Health Nurs. 2008; 19:36–45.18. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009; 6:e1000097.19. Alzheimer's Disease International. World Alzheimer's report 2009. London: Alzheimer's Disease International;2009.20. Langa KM, Larson EB, Karlawish JH, Cutler DM, Kabeto MU, Kim SY, Rosen AB. Trends in the prevalence and mortality of cognitive impairment in the United States: is there evidence of a compression of cognitive morbidity? Alzheimers Dement. 2008; 4:134–144.21. George-Carey R, Adeloye D, Chan KY, Paul A, Kolčić I, Campbell H, Rudan I. An estimate of the prevalence of dementia in Africa: a systematic analysis. J Glob Health. 2012; 2:020401.22. Llibre Rodriguez JJ, Ferri CP, Acosta D, Guerra M, Huang Y, Jacob KS, Krishnamoorthy ES, Salas A, Sosa AL, Acosta I, et al. Prevalence of dementia in Latin America, India, and China: a population-based cross-sectional survey. Lancet. 2008; 372:464–474.23. Kasai M, Nakamura K, Meguro K. Alzheimer's disease in Japan and other countries: review of epidemiological studies in the last 10 years. Brain Nerve. 2010; 62:667–678.24. Suh GH, Shah A. A review of the epidemiological transition in dementia: cross-national comparisons of the indices related to Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2001; 104:4–11.25. Shibayama H, Kasahara Y, Kobayashi H. Prevalence of dementia in a Japanese elderly population. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1986; 74:144–151.26. Ueda K, Kawano H, Hasuo Y, Fujishima M. Prevalence and etiology of dementia in a Japanese community. Stroke. 1992; 23:798–803.27. Kiyohara Y, Yoshitake T, Kato I, Ohmura T, Kawano H, Ueda K, Fujishima M. Changing patterns in the prevalence of dementia in a Japanese community: the Hisayama Study. Gerontology. 1994; 40:29–35.28. Skoog I. Status of risk factors for vascular dementia. Neuroepidemiology. 1998; 17:2–9.29. De Leeuw FE, de Groot JC, Achten E, Oudkerk M, Ramos LM, Heijboer R, Hofman A, Jolles J, van Gijn J, Breteler MM. Prevalence of cerebral white matter lesions in elderly people: a population based magnetic resonance imaging study: the Rotterdam Scan Study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2001; 70:9–14.30. Kim KW, Gwak KP, Kim BJ, Kim SY, Kim SK, Kim JL, Kim TH, Moon SW, Park JH, Bae JN, et al. 2012 national study on the prevalence of dementia in Korean elders. Seongnam: Seoul National University Bundang Hospital; Ministry of Health & Welfare;2012.31. Park JH, Kwon YC. Modification of the mini-mental state examination for use in the elderly in a non-western society: Part I. development of Korean version of mini-mental state examination. Int J Geriat Psychiatr. 1990; 5:381–387.32. Kang Y, Na DL, Hahn SH. A validity study on the Korean Mini-Mental State Examination (K-MMSE) in dementia patients. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 1997; 15:300–308.33. Lee JH, Lee KU, Lee DY, Kim KW, Jhoo JH, Kim JH, Lee KH, Kim SY, Han SH, Woo JI. Development of the Korean version of the consortium to establish a registry for Alzheimer's disease assessment packet (CERAD-K): clinical and neuropsychological assessment batteries. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci. 2002; 57:P47–P53.34. Roth M, Tym E, Mountjoy CQ, Huppert FA, Hendrie H. CAMDEX: the Cambridge examination for mental disorders of the elderly (CAMDEX). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press;1988.35. Chun YS, Seo BY, Lee CY. Korean Wechsler Intelligence Scale-manual. Seoul: Chung-Ang Educational Research Center;1963.36. Mattis S. Mental Status Examination for organic mental syndrome in the elderly patient. In : Bellak L, Karasu TB, editors. Geriatric psychiatry: a handbook for psychiatrists and primary care physicians. New York: Grune & Stratton;1976. p. 77–121.37. Rosen WG, Terry RD, Fuld PA, Katzman R, Peck A. Pathological verification of ischemic score in differentiation of dementias. Ann Neurol. 1980; 7:486–488.38. Jung IK, Kwak DI, Joe SH, Lee HS. A study of standardization of Korean form of geriatric depression scale (KGDS). J Korean Geriatr Psychiatry. 1997; 1:61–72.39. Morris JC. The clinical dementia rating (CDR): current version and scoring rules. Neurology. 1993; 43:2412–2414.40. Park JH, Cho SW, Shon HS. Reliability of functional status measurements in elderly people. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 1995; 34:475–481.41. Kim JM, Kim SW, Shin IS, Zheng TJ, Yoon JS. Development of Korean version of community screening interview for dementia (CSID-K). J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 2004; 43:445–451.42. Kim JM, Stewart R, Prince M, Shin IS, Yoon JS. Diagnosing dementia in a developing nation: an evaluation of the GMS-AGECAT algorithm in an older Korean population. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2003; 18:331–336.43. Bae JN, Cho MJ. Development of the Korean version of the geriatric depression scale and its short form among elderly psychiatric patients. J Psychosom Res. 2004; 57:297–305.44. American Psychiatric Association. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-III-R. 3rd ed. Washington, D.C.: American Psychiatric Association;1987.45. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-IV. 4th ed. Washington, D.C.: American Psychiatric Association;1994.46. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic criteria from DSM-IV-TR. Washington, D.C.: American Psychiatric Association;2000.47. McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology. 1984; 34:939–944.48. Hachinski V, Iadecola C, Petersen RC, Breteler MM, Nyenhuis DL, Black SE, Powers WJ, DeCarli C, Merino JG, Kalaria RN, et al. National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke - Canadian Stroke Network vascular cognitive impairment harmonization standards. Stroke. 2006; 37:2220–2241.49. Copeland JR, Dewey ME, Griffiths-Jones HM. A computerized psychiatric diagnostic system and case nomenclature for elderly subjects: GMS and AGECAT. Psychol Med. 1986; 16:89–99.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Trends of Meta-analysis in Upper Gastrointestinal Diseases
- A Systematic Review of Nonpharmacological Interventions for Moderate to Severe Dementia: A Study Protocol for a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Proton-pump Inhibitors and the Risk of Dementia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- Factors Related to Dementia Attitudes Among Dementia Care Providers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- An Introduction of the Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis