J Korean Med Sci.
2008 Jun;23(3):484-491. 10.3346/jkms.2008.23.3.484.
Erythropoietin Attenuates Brain Injury, Subventricular Zone Expansion, and Sensorimotor Deficits in Hypoxic-Ischemic Neonatal Rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Bucheon Hospital, Buchoen, Korea.
- 2Department of Molecular Cell Biology, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine/Clinical Trial Center, Clinical Research Institute, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Samsung Biomedical Research Institute, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Pediatrics, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Pediatrics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yschang@skku.edu
- KMID: 1786889
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2008.23.3.484
Abstract
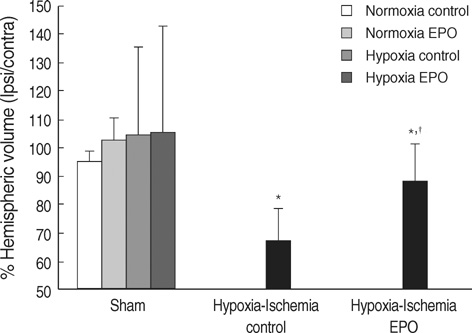
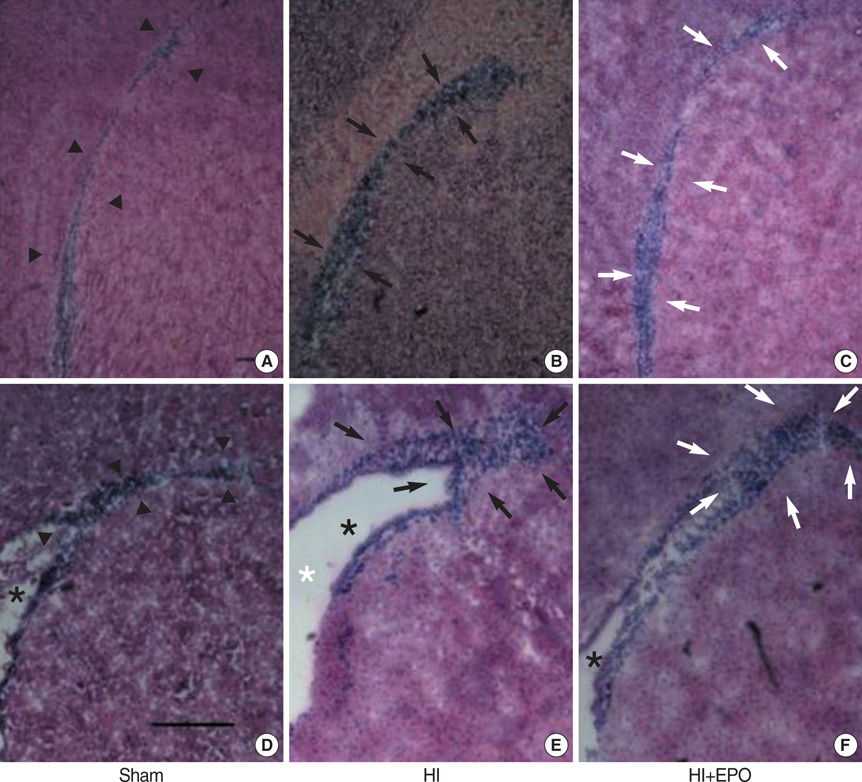
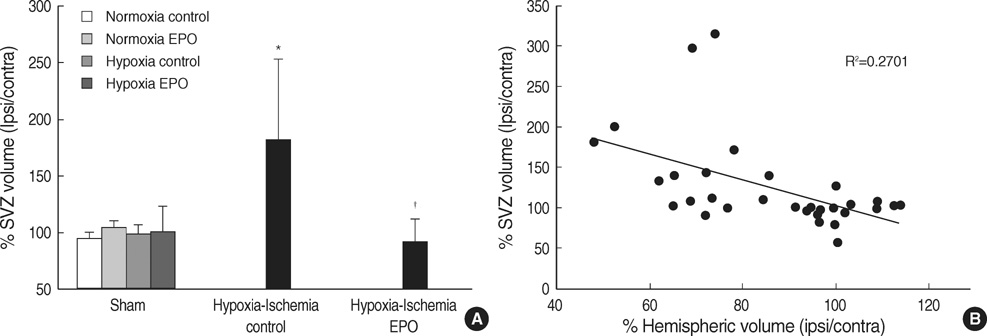
- The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of erythropoietin (EPO) on histological brain injury, subventricular zone (SVZ) expansion, and sensorimotor function deficits induced by hypoxia-ischemia (HI) in newborn rat pups. Seven-day-old male rat pups were divided into six groups: normoxia control, normoxia EPO, hypoxia control, hypoxia EPO, HI control, and HI EPO group. Sham surgery or HI was performed in all animals. HI was induced by ligation of the right common carotid artery followed by 90 min of hypoxia with 8% oxygen. Recombinant human EPO 3 U/g or saline was administered intraperitoneally, immediately, at 24- and 48-hr after insult. At two weeks after insult, animals were challenged with cylinder-rearing test for evaluating forelimb asymmetry to determine sensorimotor function. All animals were then sacrificed for volumetric analysis of the cerebral hemispheres and the SVZ. The saline-treated HI rats showed marked asymmetry by preferential use of the non-impaired, ipsilateral paw in the cylinder-rearing test. Volumetric analysis of brains revealed significantly decreased preserved ipsilateral hemispheric volume and increased ipsilateral SVZ volume compared with the sham-operated animals. Treatment of EPO significantly improved forelimb asymmetry and preserved ipsilateral hemispheric volume along with decreased expansion of ipsilateral SVZ following HI compared to the saline-treated HI rats. These results support the use of EPO as a candidate drug for treatment of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Vannucci RC. Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Am J Perinatol. 2000. 17:113–120.
Article2. Agnello D, Bigini P, Villa P, Mennini T, Cerami A, Brines ML, Ghezzi P. Erythropoietin exerts an anti-inflammatory effect on the CNS in a model of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Brain Res. 2002. 952:128–134.
Article3. Digicaylioglu M, Lipton SA. Erythropoietin-mediated neuroprotection involves cross-talk between Jak2 and NF-kappaB signalling cascades. Nature. 2001. 412:641–647.4. Shingo T, Sorokan ST, Shimazaki T, Weiss S. Erythropoietin regulates the in vitro and in vivo production of neuronal progenitors by mammalian forebrain neural stem cells. J Neurosci. 2001. 21:9733–9743.5. Aydin A, Genc K, Akhisaroglu M, Yorukoglu K, Gokmen N, Gonullu E. Erythropoietin exerts neuroprotective effect in neonatal rat model of hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Brain Dev. 2003. 25:494–498.
Article6. Kumral A, Ozer E, Yilmaz O, Akhisaroglu M, Gokmen N, Duman N, Ulukus C, Genc S, Ozkan H. Neuroprotective effect of erythropoietin on hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats. Biol Neonate. 2003. 83:224–228.
Article7. Sun Y, Zhou C, Polk P, Nanda A, Zhang JH. Mechanisms of erythropoietin-induced brain protection in neonatal hypoxia-ischemia rat model. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2004. 24:259–270.
Article8. Kumral A, Uysal N, Tugyan K, Sonmez A, Yilmaz O, Gokmen N, Kiray M, Genc S, Duman N, Koroglu TF, Ozkan H, Genc K. Erythropoietin improves long-term spatial memory deficits and brain injury following neonatal hypoxia-ischemia in rats. Behav Brain Res. 2004. 153:77–86.
Article9. Spandou E, Soubasi V, Papoutsopoulou S, Karkavelas G, Simeonidou C, Kaiki-Astara A, Guiba-Tziampiri O. Erythropoietin prevents hypoxia/ischemia-induced DNA fragmentation in an experimental model of perinatal asphyxia. Neurosci Lett. 2004. 366:24–28.
Article10. Spandou E, Papadopoulou Z, Soubasi V, Karkavelas G, Simeonidou C, Pazaiti A, Guiba-Tziampiri O. Erythropoietin prevents long-term sensorimotor deficits and brain injury following neonatal hypoxia-ischemia in rats. Brain Res. 2005. 1045:22–30.
Article11. Lois C, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Alvarez-Buylla A. Chain migration of neuronal precursors. Science. 1996. 271:978–981.
Article12. Arvidsson A, Collin T, Kirik D, Kokaia Z, Lindvall O. Neuronal replacement from endogenous precursors in the adult brain after stroke. Nat Med. 2002. 8:963–970.
Article13. Parent JM, Vexler ZS, Gong C, Derugin N, Ferriero DM. Rat forebrain neurogenesis and striatal neuron replacement after focal stroke. Ann Neurol. 2002. 52:802–813.
Article14. Plane JM, Liu R, Wang TW, Silverstein FS, Parent JM. Neonatal hypoxic-ischemic injury increases forebrain subventricular zone neurogenesis in the mouse. Neurobiol Dis. 2004. 16:585–595.
Article15. Chang YS, Mu D, Wendland M, Sheldon RA, Vexler ZS, McQuillen PS, Ferriero DM. Erythropoietin improves functional and histological outcome in neonatal stroke. Pediatr Res. 2005. 58:106–111.
Article16. Yang Z, Levison SW. Hypoxia/ischemia expands the regenerative capacity of progenitors in the perinatal subventricular zone. Neuroscience. 2006. 139:555–564.
Article17. Ong J, Plane JM, Parent JM, Silverstein FS. Hypoxic-ischemic injury stimulates subventricular zone proliferation and neurogenesis in the neonatal rat. Pediatr Res. 2005. 58:600–606.
Article18. Wang L, Zhang Z, Wang Y, Zhang R, Chopp M. Treatment of stroke with erythropoietin enhances neurogenesis and angiogenesis and improves neurological function in rats. Stroke. 2004. 35:1732–1737.
Article19. Zhu C, Xu F, Wang X, Shibata M, Uchiyama Y, Blomgren K, Hagberg H. Different apoptotic mechanisms are activated in male and female brains after neonatal hypoxia-ischaemia. J Neurochem. 2006. 96:1016–1027.
Article20. Rice JE 3rd, Vannucci RC, Brierley JB. The influence of immaturity on hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in the rat. Ann Neurol. 1981. 9:131–141.
Article21. Park WS, Sung DK, Kang S, Koo SH, Kim YJ, Lee JH, Chang YS, Lee M. Neuroprotective effect of cycloheximide on hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats. J Korean Med Sci. 2006. 21:337–341.
Article22. Park WS, Sung DK, Kang S, Koo SH, Kim YJ, Lee JH, Chang YS, Lee M. Therapeutic window for cycloheximide treatment after hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats. J Korean Med Sci. 2006. 21:490–494.
Article23. Levison SW, Rothstein RP, Romanko MJ, Snyder MJ, Meyers RL, Vannucci SJ. Hypoxia/ischemia depletes the rat perinatal subventricular zone of oligodendrocyte progenitors and neural stem cells. Dev Neurosci. 2001. 23:234–247.
Article24. Vannucci RC, Vannucci SJ. A model of perinatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1997. 835:234–249.
Article25. Grow JL, Liu YQ, Barks JD. Can lateralizing sensorimotor deficits be identified after neonatal cerebral hypoxia-ischemia in rats? Dev Neurosci. 2003. 25:394–402.
Article26. Gustavsson M, Anderson MF, Mallard C, Hagberg H. Hypoxic preconditioning confers long-term reduction of brain injury and improvement of neurological ability in immature rats. Pediatr Res. 2005. 57:305–309.
Article27. Mandarim-de-Lacerda CA. Stereological tools in biomedical research. An Acad Bras Cienc. 2003. 75:469–486.
Article28. Swanson L. Brain maps III: structure of the rat brain: an atlas with printed and electronic templates for data, models, and schematics. 2004. 3 ed. San Diego, CA, USA: Elsivier Academic Press.29. Lois C, Alvarez-Buylla A. Proliferating subventricular zone cells in the adult mammalian forebrain can differentiate into neurons and glia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1993. 90:2074–2077.
Article30. Goldman JE. Lineage, migration, and fate determination of postnatal subventricular zone cells in the mammalian CNS. J Neurooncol. 1995. 24:61–64.
Article31. Luskin MB. Restricted proliferation and migration of postnatally generated neurons derived from the forebrain subventricular zone. Neuron. 1993. 11:173–189.
Article32. Zhang RL, Zhang ZG, Zhang L, Chopp M. Proliferation and differentiation of progenitor cells in the cortex and the subventricular zone in the adult rat after focal cerebral ischemia. Neuroscience. 2001. 105:33–41.
Article33. Skoff RP, Bessert DA, Barks JD, Song D, Cerghet M, Silverstein FS. Hypoxic-ischemic injury results in acute disruption of myelin gene expression and death of oligodendroglial precursors in neonatal mice. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2001. 19:197–208.
Article34. Lie DC, Song H, Colamarino SA, Ming GL, Gage FH. Neurogenesis in the adult brain: new strategies for central nervous system diseases. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2004. 44:399–421.35. Schallert T, Fleming SM, Leasure JL, Tillerson JL, Bland ST. CNS plasticity and assessment of forelimb sensorimotor outcome in unilateral rat models of stroke, cortical ablation, parkinsonism and spinal cord injury. Neuropharmacology. 2000. 39:777–787.
Article36. Cohen AD, Tillerson JL, Smith AD, Schallert T, Zigmond MJ. Neuroprotective effects of prior limb use in 6-hydroxydopamine-treated rats: possible role of GDNF. J Neurochem. 2003. 85:299–305.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury and Erythropoietin
- E-selectin Mrna and Protein Expression Increase Transiently After Unilateral Cerebral hypoxia-ischemia in Neonatal Rats
- The effect of erythropoietin in neonatal rat model of hypoxic-ischemic brain injury
- Expression of ICAM-1 mRNA after Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury in Neonatal Rats
- Neuroprotective Effect of Growth Hormone in Neonatal Rat with Hypoxic Ischemic Brain Injury