J Korean Med Sci.
2008 Jun;23(3):470-476. 10.3346/jkms.2008.23.3.470.
Fragile X Syndrome in Korea: A Case Series and a Review of the Literature
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- 2Department of Medical Genetics, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. genetics@kornet.net
- KMID: 1786887
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2008.23.3.470
Abstract
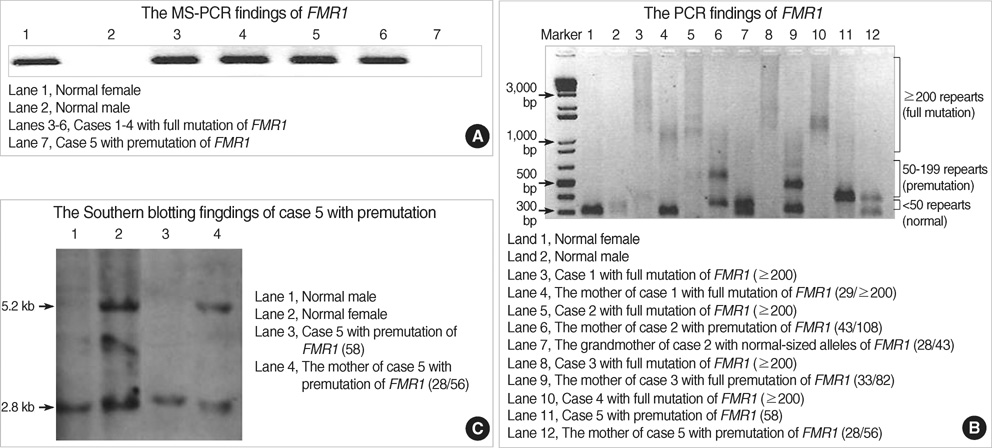
- The purposes of this study were to present DNA analysis findings of our case series of fragile X syndrome (FXS) based on methylation-specific polymerase chain reaction (MS-PCR), PCR, and Southern blotting alongside developmental characteristics including psychological profiles and to review the literature on FXS in Korea. The reports of 65 children (male:female, 52:13; age, 6.12+/-4.00 yrs) referred for the diagnosis of FXS over a 26-months period were retrospectively reviewed for the identification of full mutation or premutation of fragile X mental retardation 1 (FMR1). Among the 65 children, there were 4 boys with full mutation, and one boy showed premutation of FMR1, yielding a 6.15% positive rate of FXS. All 4 children with full mutation showed significant developmental delay, cognitive dysfunction, and varying degrees of autistic behaviors. The boys with premutation showed also moderate mental retardation, severe drooling, and behavioral problems as severe as the boys with full mutation. Thirteen articles on FXS in Korea have been published since 1993, and they were reviewed. The positive rate of FXS was in the range of 0.77-8.51%, depending on the study groups and the method of diagnosis. Finally, the population-based prevalence study on FXS in Korea is required in the near future.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Phalen JA. Fragile X syndrome. Pediatr Rev. 2005. 26:181–182.
Article2. O'Connell CD, Atha DH, Jakupciak JP, Amos JA, Richie K. Standardization of PCR amplification for fragile X trinucleotide repeat measurements. Clin Genet. 2002. 61:13–20.3. Panagopoulos I, Lassen C, Kristoffersson U, Aman P. A methylation PCR approach for detection of fragile X syndrome. Hum Mutat. 1999. 14:71–79.
Article4. Gold B, Radu D, Balanko A, Chiang CS. Diagnosis of Fragile X syndrome by Southern blot hybridization using a chemiluminescent probe: a laboratory protocol. Mol Diagn. 2000. 5:169–178.
Article5. Maddalena A, Richards CS, McGinniss MJ, Brothman A, Desnick RJ, Grier RE, Hirsch B, Jacky P, McDowell GA, Popovich B, Watson M, Wolff DJ. Technical standards and guidelines for fragile X: the first of a series of disease-specific supplements to the Standards and Guidelines for Clinical Genetics Laboratories of the American College of Medical Genetics. Quality Assurance Subcommittee of the Laboratory Practice Committee. Genet Med. 2001. 3:200–205.6. Choi YM, Hwang DY, Jun JK, Choe J, Park SH, Noh MK, Oh SK, Ku SY, Suh CS, Kim SH, Yang SW, Cho SC, Moon SY, Lee JY. Incidence of Fragile X Syndrome in Korean Patients with Mental Retardation. Korean J Obstet Gynecol. 1999. 42:2458–2464.7. Chung HJ, Cha KE, Lee SH. Fragile X Syndrome : Clinical Characteristics and EEG Findings. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1997. 40:1110–1119.8. Hong KM, Kim JH, Moon SY, Oh SK. Chromosomal abnormalities in child psychiatric patients. J Korean Med Sci. 1999. 14:377–385.
Article9. Hong SD, Lee S, Oh MR, Jin DK. DNA Testing for Fragile X Syndrome in School for Emotionally Severely Handicapped Children in Korea. J Genet Med. 1998. 2:83–86.10. Hur CY, Choi YM, Park SH, Yoon BK, Lee KS, Na YJ, Lee BS, Rheu CH, Lee HJ, Seol HW, Oh SK, Ku SY, Suh CS, Kim SH, Kim JG, Moon SY. Fragile X Premutation in Patients with Idiopathic Premature Ovarian Failure. Korean J Obstet Gynecol. 2003. 46:978–983.11. Kang KM, Kwak DI, Lee MS. Molecular Genetic Study for FMR-1 Gene in Autistic Children. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 1999. 38:1479–1487.12. Kim GJ, Kim SY, Hwang BC, Park CY, Choi YD, Whang YJ. Prenatal Diagnosis of Fragile X Syndrome using Amniotic Fluid DNA. Korean J Obstet Gynecol. 2001. 44:558–565.13. Kwon SH, Lee KS, Hyun MC, Song KE, Kim JK. Molecular screening for fragile x syndrome in mentally handicapped children in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2001. 16:271–275.
Article14. Lee SH, Kim UK, Kwak IP, Kim JW, Lee WS, Kim SB, Cha KY. Molecular Genetics in Fragile X syndrome (1). Korean J Obstet Gynecol. 1995. 38:2293–2302.15. Moon HR, Moon SY. Fragile site X chromosomes in mentally retarded boys. J Korean Med Sci. 1993. 8:192–196.
Article16. Park W, Lee KJ, Choi EY. A Study on Prevalence of Premutation Sized FMR1 Gene Using Polymerase Chain Reaction. J Korean Child Neurol Soc. 1999. 7:42–47.17. Shin SK, Yoo HW. Etiological Classification of Mentally Retarded Children Enrolled in a Special Educational Institution. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1994. 37:1437–1448.18. Song KC, Kim GJ, Whang YJ, Choi SR, Lee SP, Whang BC, Lee ED. Allele distribution of FMR1 gene in Korean women. Korean J Obstet Gynecol. 2002. 45:990–993.19. Pembrey ME, Barnicoat AJ, Carmichael B, Bobrow M, Turner G. An assessment of screening strategies for fragile X syndrome in the UK. Health Technol Assess. 2001. 5:1–95.
Article20. Han XD, Powell BR, Phalin JL, Chehab FF. Mosaicism for a full mutation, premutation, and deletion of the CGG repeats results in 22% FMRP and elevated FMR1 mRNA levels in a high-functioning fragile X male. Am J Med Genet A. 2006. 140:1463–1471.21. Sabaratnam M, Laver S, Butler L, Pembrey M. Fragile-X syndrome in North East Essex: towards systematic screening: clinical selection. J Intellect Disabil Res. 1994. 38(Pt 1):27–35.
Article22. Turner G, Webb T, Wake S, Robinson H. Prevalence of fragile X syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1996. 64:196–197.
Article23. Crawford DC, Meadows KL, Newman JL, Taft LF, Scott E, Leslie M, Shubek L, Holmgreen P, Yeargin-Allsopp M, Boyle C, Sherman SL. Prevalence of the fragile X syndrome in African-Americans. Am J Med Genet. 2002. 110:226–233.
Article24. Goldman A, Jenkins T, Krause A. Molecular evidence that fragile X syndrome occurs in the South African black population. J Med Genet. 1998. 35:878.
Article25. Arinami T, Kondo I, Nakajima S. Frequency of the fragile X syndrome in Japanese mentally retarded males. Hum Genet. 1986. 73:309–312.
Article26. Rousseau F, Rouillard P, Morel ML, Khandjian EW, Morgan K. Prevalence of carriers of premutation-size alleles of the FMRI gene--and implications for the population genetics of the fragile X syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1995. 57:1006–1018.27. Nolin SL, Brown WT, Glicksman A, Houck GE Jr, Gargano AD, Sullivan A, Biancalana V, Brondum-Nielsen K, Hjalgrim H, Holinski-Feder E, Kooy F, Longshore J, Macpherson J, Mandel JL, Matthijs G, Rousseau F, Steinbach P, Vaisanen ML, von Koskull H, Sherman SL. Expansion of the fragile X CGG repeat in females with premutation or intermediate alleles. Am J Hum Genet. 2003. 72:454–464.
Article28. Moore CJ, Daly EM, Schmitz N, Tassone F, Tysoe C, Hagerman RJ, Hagerman PJ, Morris RG, Murphy KC, Murphy DG. A neuropsychological investigation of male premutation carriers of fragile X syndrome. Neuropsychologia. 2004. 42:1934–1947.
Article29. Van Esch H. The Fragile X premutation: new insights and clinical consequences. Eur J Med Genet. 2006. 49:1–8.30. Tassone F, Hagerman RJ, Taylor AK, Mills JB, Harris SW, Gane LW, Hagerman PJ. Clinical involvement and protein expression in individuals with the FMR1 premutation. Am J Med Genet. 2000. 91:144–152.31. Aziz M, Stathopulu E, Callias M, Taylor C, Turk J, Oostra B, Willemsen R, Patton M. Clinical features of boys with fragile X premutations and intermediate alleles. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2003. 121:119–127.
Article32. Koukoui SD, Chaudhuri A. Neuroanatomical, molecular genetic, and behavioral correlates of fragile X syndrome. Brain Res Rev. 2007. 53:27–38.
Article33. Lombroso PJ. Genetics of childhood disorders: XLVIII. Learning and memory, Part 1: Fragile X syndrome update. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2003. 42:372–375.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Fragile site X chromosomes in mentally retarded boys
- Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection in a female patient with fragile X syndrome
- Fragile X-Associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome: An Illustrative Case
- Incidence of Fragile X Syndrome in Korean Patients with Mental Retardation
- DNA Testing for Fragile X Syndrome in School for Emotionally Severely Handicapped Children in Korea