J Korean Med Sci.
2011 Dec;26(12):1556-1562. 10.3346/jkms.2011.26.12.1556.
Prognostic Value of Immunohistochemical Biomarkers at Different Cut-off Values in Patients with Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Treated with CHOP Chemotherapy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Hematology/Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Oncology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jrhuh@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 1786010
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2011.26.12.1556
Abstract
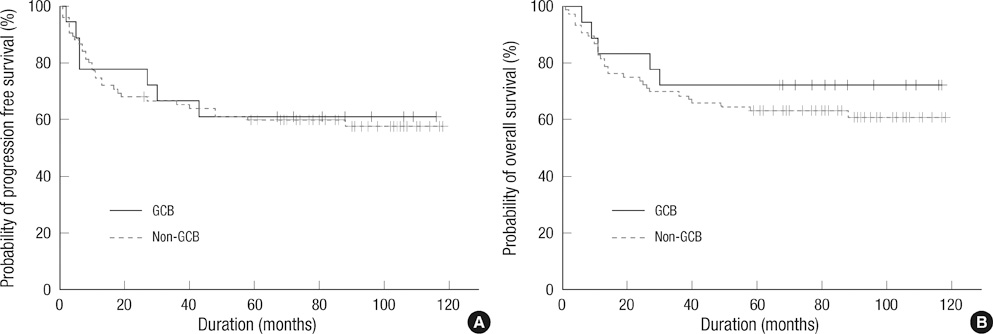
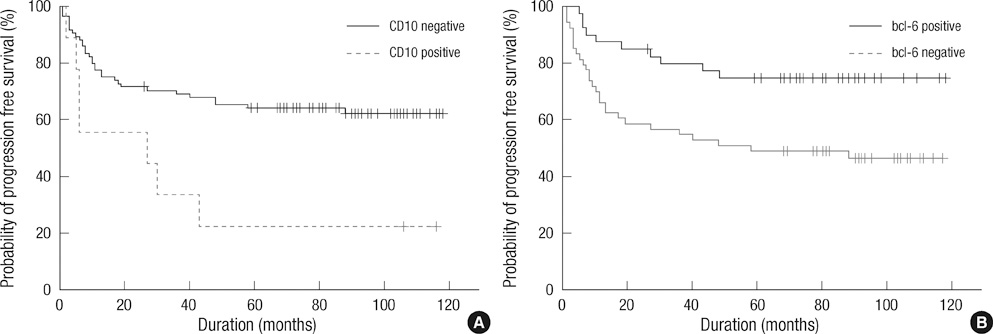
- Many predictive models have been proposed for better stratification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Hans' algorithm has been widely used as standard to sub-classify DLBCL into germinal center B-cell (GCB) and non-GCB origins. However, there have been disagreements in the literature regarding its prognostic significance. Here, we retrospectively analyzed Hans' algorithm and the individual immunohistochemical biomarkers at different cut-off values (5%, 30%, 50% or 75%) in 94 Korean patients with DLBCL treated with combination chemotherapy with cyclophosphamide, daunorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone. No significant differences were observed between the GCB (18 patients, 19.1%) and non-GCB (76, 80.9%) groups. Among individual biomarkers, CD10 negativity (cut point: 30%) and bcl-6 positivity (cut point: 5%) were independent good prognostic markers in progression-free survival (PFS), whereas bcl-6 (cut point: 5%) positivity was an independent good prognostic marker in overall survival irrelevant of international prognostic index. The present study showed the lack of predictability of Hans' algorithm in DLBCL patients, and that CD10, Bcl-6 may have diverse prognostic significance at different cut-off values. Our results suggest that the proposed cut-off value may not be applied universally, and that the optimal cut-off value may need to be optimized for individual laboratory.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Aged
Aged, 80 and over
Algorithms
Antineoplastic Combined Chemotherapy Protocols/*therapeutic use
Cyclophosphamide/therapeutic use
DNA-Binding Proteins/analysis
Doxorubicin/therapeutic use
Female
Humans
Lymphoma, Large B-Cell, Diffuse/classification/*drug therapy
Male
Middle Aged
Neprilysin/analysis
Prednisone/therapeutic use
Prognosis
Republic of Korea
Retrospective Studies
Tumor Markers, Biological/*analysis
Vincristine/therapeutic use
Figure
Reference
-
1. The Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Classification Project. A clinical evaluation of the International Lymphoma Study Group classification of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Blood. 1997. 89:3909–3918.2. Anderson JR, Armitage JO, Weisenburger DD. Epidemiology of the non-Hodgkin's lymphomas: distributions of the major subtypes differ by geographic locations. The Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Classification Project. Ann Oncol. 1998. 9:717–720.3. Colomo L, López-Guillermo A, Perales M, Rives S, Martinez A, Bosch F, Colomer D, Falini B, Montserrat E, Campo E. Clinical impact of the differentiation profile assessed by immunophenotyping in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2003. 101:78–84.4. The International Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Prognostic Factors Poject. A predictive model for aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 1993. 329:987–994.5. Barrans SL, Carter I, Owen RG, Davies FE, Patmore RD, Haynes AP, Morgan GJ, Jack AS. Germinal center phenotype and bcl-2 expression combined with the International Prognostic Index improves patient risk stratification in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2002. 99:1136–1143.6. Alizadeh AA, Eisen MB, Davis RE, Ma C, Lossos IS, Rosenwald A, Boldrick JC, Sabet H, Tran T, Yu X, Powell JI, Yang L, Marti GE, Moore T, Hudson J Jr, Lu L, Lewis DB, Tibshirani R, Sherlock G, Chan WC, Greiner TC, Weisenburger DD, Armitage JO, Warnke R, Levy R, Wilson W, Grever MR, Byrd JC, Botstein D, Brown PO, Staudt LM. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature. 2000. 403:503–511.7. Rosenwald A, Wright G, Chan WC, Connors JM, Campo E, Fisher RI, Gascoyne RD, Muller-Hermelink HK, Smeland EB, Giltnane JM, Hurt EM, Zhao H, Averett L, Yang L, Wilson WH, Jaffe ES, Simon R, Klausner RD, Powell J, Duffey PL, Longo DL, Greiner TC, Weisenburger DD, Sanger WG, Dave BJ, Lynch JC, Vose J, Armitage JO, Montserrat E, Lopez-Guillermo A, Grogan TM, Miller TP, LeBlanc M, Ott G, Kvaloy S, Delabie J, Holte H, Krajci P, Stokke T, Staudt LM. Lymphoma/Leukemia Molecular Profiling Project. The use of molecular profiling to predict survival after chemotherapy for diffuse large-B cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2002. 346:1937–1947.8. Hans CP, Weisenburger DD, Greiner TC, Gascoyne RD, Delabie J, Ott G, Müller-Hermelink HK, Campo E, Braziel RM, Jaffe ES, Pan Z, Farinha P, Smith LM, Falini B, Banham AH, Rosenwald A, Staudt LM, Connors JM, Armitage JO, Chan WC. Confirmation of the molecular classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by immunohistochemistry using a tissue microarray. Blood. 2004. 103:275–282.9. Oh YH, Park CK. Prognostic evaluation of nodal diffuse large B cell lymphoma by immunohistochemical profiles with emphasis on CD138 expression as a poor prognostic factor. J Korean Med Sci. 2006. 21:397–405.10. Chang CC, McClintock S, Cleveland RP, Trzpuc T, Vesole DH, Logan B, Kajdacsy-Balla A, Perkins SL. Immunohistochemical expression patterns of germinal center and activation B-cell markers correlate with prognosis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2004. 28:464–470.11. Hill ME, MacLennan KA, Cunningham DC, Vaughan Hudson B, Burke M, Clarke P, Di Stefano F, Anderson L, Vaughan Hudson G, Mason D, Selby P, Linch DC. Prognostic significance of BCL-2 expression and bcl-2 major breakpoint region rearrangement in diffuse large cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: a British National Lymphoma Investigation Study. Blood. 1996. 88:1046–1051.12. Gascoyne RD, Adomat SA, Krajewski S, Krajewska M, Horsman DE, Tolcher AW, O'Reilly SE, Hoskins P, Coldman AJ, Reed JC, Connors JM. Prognostic significance of Bcl-2 protein expression and Bcl-2 gene rearrangement in diffuse aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Blood. 1997. 90:244–251.13. Yamaguchi M, Seto M, Okamoto M, Ichinohasama R, Nakamura N, Yoshino T, Suzumiya J, Murase T, Miura I, Akasaka T, Tamaru J, Suzuki R, Kagami Y, Hirano M, Morishima Y, Ueda R, Shiku H, Nakamura S. De novo CD5+ diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a clinicopathologic study of 109 patients. Blood. 2002. 99:815–821.14. van Imhoff GW, Boerma EJ, van der Holt B, Schuuring E, Verdonck LF, Kluin-Nelemans HC, Kluin PM. Prognostic impact of germinal center-associated proteins and chromosomal breakpoints in poor-risk diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2006. 24:4135–4142.15. Nyman H, Adde M, Karjalainen-Lindsberg ML, Taskinen M, Berglund M, Amini RM, Blomqvist C, Enblad G, Leppä S. Prognostic impact of immunohistochemically defined germinal center phenotype in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients treated with immunochemotherapy. Blood. 2007. 109:4930–4935.16. Wilson WH, Dunleavy K, Pittaluga S, Hegde U, Grant N, Steinberg SM, Raffeld M, Gutierrez M, Chabner BA, Staudt L, Jaffe ES, Janik JE. Phase II study of dose-adjusted EPOCH and rituximab in untreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with analysis of germinal center and post-germinal center biomarkers. J Clin Oncol. 2008. 26:2717–2724.17. Fu K, Weisenburger DD, Choi WW, Perry KD, Smith LM, Shi X, Hans CP, Greiner TC, Bierman PJ, Bociek RG, Armitage JO, Chan WC, Vose JM. Addition of rituximab to standard chemotherapy improves the survival of both the germinal center B-cell-like and non-germinal center B-cell-like subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2008. 26:4587–4594.18. Veelken H, Vik Dannheim S, Schulte Moenting J, Martens UM, Finke J, Schmitt-Graeff A. Immunophenotype as prognostic factor for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in patients undergoing clinical risk-adapted therapy. Ann Oncol. 2007. 18:931–939.19. Dupuis J, Gaulard P, Hemery F, Itti E, Gisselbrecht C, Rahmouni A, Copie-Bergman C, Brière J, El Gnaoui T, Gaillard I, Meignan M, Haioun C. Respective prognostic values of germinal center phenotype and early (18) fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography scanning in previously untreated patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Haematologica. 2007. 92:778–783.20. Ott G, Ziepert M, Klapper W, Horn H, Szczepanowski M, Bernd HW, Thorns C, Feller AC, Lenze D, Hummel M, Stein H, Müller-Hermelink HK, Frank M, Hansmann ML, Barth TF, Moller P, Cogliatti S, Pfreundschuh M, Schmitz N, Trümper L, Loeffler M, Rosenwald A. Immunoblastic morphology but not the immunohistochemical GCB/nonGCB classifier predicts outcome in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in the RICOVER-60 trial of the DSHNHL. Blood. 2010. 116:4916–4925.21. Choi WW, Weisenburger DD, Greiner TC, Piris MA, Banham AH, Delabie J, Braziel RM, Geng H, Iqbal J, Lenz G, Vose JM, Hans CP, Fu K, Smith LM, Li M, Liu Z, Gascoyne RD, Rosenwald A, Ott G, Rimsza LM, Campo E, Jaffe ES, Jaye DL, Staudt LM, Chan WC. A new immunostain algorithm classifies diffuse large B-cell lymphoma into molecular subtypes with high accuracy. Clin Cancer Res. 2009. 15:5494–5502.22. Shiozawa E, Yamochi-Onizuka T, Takimoto M, Ota H. The GCB subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma is less frequent in Asian countries. Leuk Res. 2007. 31:1579–1583.23. Chen Y, Han T, Iqbal J, Irons R, Chan WC, Zhu X, Fu K. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in Chinese patients: immunophenotypic and cytogenetic analyses of 124 cases. Am J Clin Pathol. 2010. 133:305–313.24. Kerckaert JP, Deweindt C, Tilly H, Quief S, Lecocq G, Bastard C. LAZ3, a novel zinc-finger encoding gene, is disrupted by recurring chromosome 3q27 translocations in human lymphomas. Nat Genet. 1993. 5:66–70.25. Ye BH, Cattoretti G, Shen Q, Zhang J, Hawe N, de Waard R, Leung C, Nouri-Shirazi M, Orazi A, Chaganti RS, Rothman P, Stall AM, Pandolfi PP, Dalla-Favera R. The BCL-6 proto-oncogene controls germinal-centre formation and Th2-type inflammation. Nat Genet. 1997. 16:161–170.26. Winter JN, Weller EA, Horning SJ, Krajewska M, Variakojis D, Habermann TM, Fisher RI, Kurtin PJ, Macon WR, Chhanabhai M, Felgar RE, Hsi ED, Medeiros LJ, Weick JK, Reed JC, Gascoyne RD. Prognostic significance of Bcl-6 protein expression in DLBCL treated with CHOP or RCHOP: a prospective correlative study. Blood. 2006. 107:4207–4213.27. Gaidano G, Carbone A. MUM1: a step ahead toward the understanding of lymphoma histogenesis. Leukemia. 2000. 14:563–566.28. Burns BF, Warnke RA, Doggett RS, Rouse RV. Expression of a T-cell antigen (Leu-1) by B-cell lymphomas. Am J Pathol. 1983. 113:165–171.29. Lossos IS, Morgensztern D. Prognostic biomarkers in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2006. 24:995–1007.30. de Jong D, Rosenwald A, Chhanabhai M, Gaulard P, Klapper W, Lee A, Sander B, Thorns C, Campo E, Molina T, Norton A, Hagenbeek A, Horning S, Lister A, Raemaekers J, Gascoyne RD, Salles G, Weller E. Lunenburg Lymphoma Biomarker Consortium. Immunohistochemical prognostic markers in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: validation of tissue microarray as a prerequisite for broad clinical applications--a study from the Lunenburg Lymphoma Biomarker Consortium. J Clin Oncol. 2007. 25:805–812.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Successfully Treated in a Pregnant Patient
- A Case of Primary Adrenal Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Achieving Complete Remission with Rituximab-CHOP Chemotherapy
- Rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP) chemotherapy for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in pregnancy may be associated with preterm birth
- Treatment results of radiotherapy following CHOP or R-CHOP in limited-stage head-and-neck diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a single institutional experience
- The Modified Glasgow Prognostic Scores as a Predictor in Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma Treated with R-CHOP Regimen