J Korean Med Sci.
2010 Sep;25(9):1379-1383. 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.9.1379.
Genetic Analyses of the Chimeric CYP11B1/CYP11B2 Gene in a Korean Family with Glucocorticoid-Remediable Aldosteronism
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Endocrinology, Department of Internal Medicine, Incheon Medical Center, Incheon, Korea.
- 2Division of Endocrinology, Department of Internal Medicine, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. ysmrj@cnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1785922
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2010.25.9.1379
Abstract
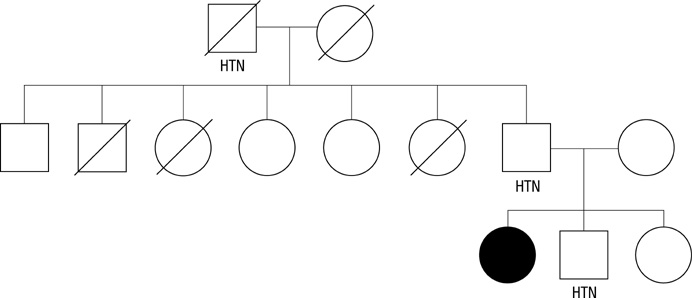
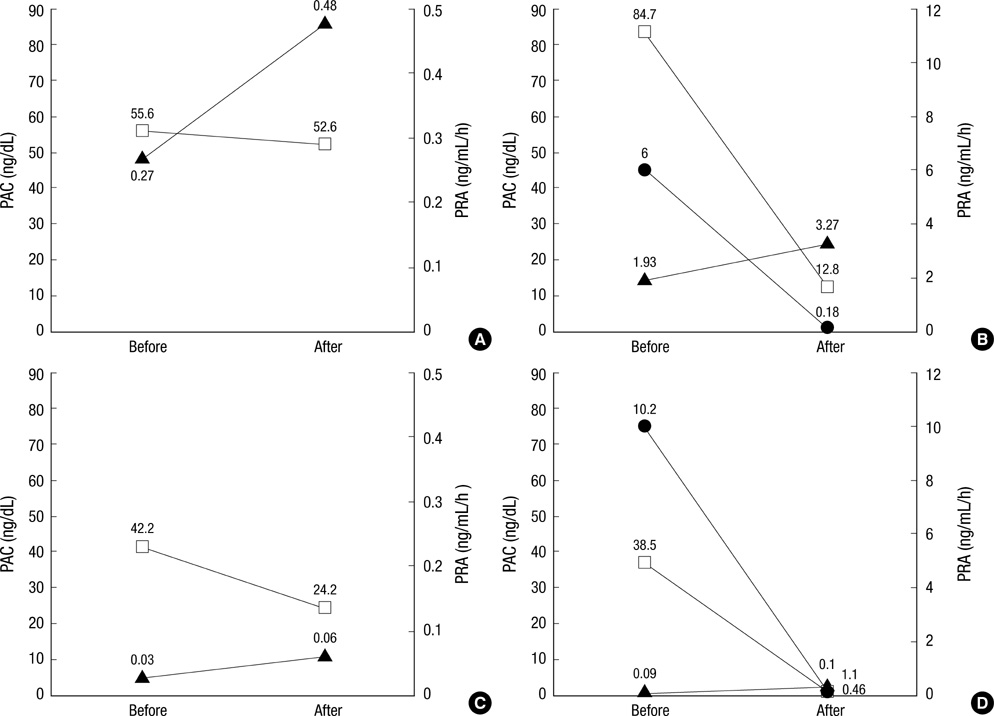
- Glucocorticoid-remediable aldosteronism (GRA) is an autosomal-dominant inheritable form of hyperaldosteronism with early onset hypertension. GRA is caused by unequal crossing-over of the steroid 11beta-hydroxylase (CYP11B1) and aldosterone synthase (CYP11B2) genes. As a result of chimeric gene duplication, aldosterone is ectopically synthesized in the adrenal zona fasciculata under the control of adrenocorticotropin. Here, we describe three cases of GRA in a Korean family. The proband-a 21-yr-old female-was incidentally found to have high blood pressure (170/108 mmHg). Her 46-yr-old father had been treated twice for cerebral hemorrhage at the ages of 29 and 39 yr. Her 15-yr-old brother had a 2-yr history of hypertension; however, he was never treated. Their laboratory test results showed normokalemia, hyporeninemia, hyperaldosteronism, and a high plasma aldosterone concentration-to-plasma renin activity ratio. Normal saline loading failed to suppress aldosterone secretion. However, dexamethasone administration effectively suppressed their plasma aldosterone concentrations. Following genetic analyses with PCR and direct sequencing to document the chimeric gene and crossover site, respectively, we identified CYP11B1/CYP11B2 and determined the breakpoint of unequal crossover to be located between intron 2 of CYP11B1 and exon 3 of CYP11B2.
MeSH Terms
-
Adolescent
Aldosterone/blood
Aldosterone Synthase/*genetics
Asian Continental Ancestry Group/*genetics
Dexamethasone/therapeutic use
Family
Female
Glucocorticoids/*therapeutic use
Humans
Hyperaldosteronism/diagnosis/drug therapy/*genetics
Hypertension/etiology
Magnetic Resonance Angiography
Male
Middle Aged
Renin/blood/metabolism
Republic of Korea
Sequence Analysis, DNA
Steroid 11-beta-Hydroxylase/*genetics
Young Adult
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sutherland DJ, Ruse JL, Laidlaw JC. Hypertension, increased aldosterone secretion and low plasma renin activity relieved by dexamethasone. Can Med Assoc J. 1966. 95:1109–1119.2. Lifton RP, Dluhy RG, Powers M, Rich GM, Cook S, Ulick S, Lalouel JM. A chimaeric 11 beta-hydroxylase/aldosterone synthase gene causes glucocorticoid-remediable aldosteronism and human hypertension. Nature. 1992. 355:262–265.3. Mosso L, Gomez-Sanchez CE, Foecking MF, Fardella C. Serum 18-hydroxycortisol in primary aldosteronism, hypertension, and normotensives. Hypertension. 2001. 38:688–691.
Article4. Fardella CE, Mosso L, Gómez-Sánchez C, Cortés P, Soto J, Gómez L, Pinto M, Huete A, Oestreicher E, Foradori A, Montero J. Primary hyperaldosteronism in essential hypertensives: prevalence, biochemical profile, and molecular biology. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000. 85:1863–1867.
Article5. Jonsson JR, Klemm SA, Tunny TJ, Stowasser M, Gordon RD. A new genetic test for familial hyperaldosteronism type I aids in the detection of curable hypertension. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995. 207:565–571.
Article6. Loh KC, Koay ES, Khaw MC, Emmanuel SC, Young WF Jr. Prevalence of primary aldosteronism among Asian hypertensive patients in Singapore. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000. 85:2854–2859.
Article7. Pizzolo F, Trabetti E, Guarini P, Mulatero P, Ciacciarelli A, Blengio GS, Corrocher R, Olivieri O. Glucocorticoid remediable aldosteronism (GRA) screening in hypertensive patients from a primary care setting. J Hum Hypertens. 2005. 19:325–327.
Article8. McMahon GT, Dluhy RG. Glucocorticoid-remediable aldosteronism. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol. 2004. 48:682–686.
Article9. Gates LJ, Benjamin N, Haites NE, MacConnachie AA, McLay JS. Is random screening of value in detecting glucocorticoid-remediable aldosteronism within a hypertensive population? J Hum Hypertens. 2001. 15:173–176.
Article10. Litchfield WR, New MI, Coolidge C, Lifton RP, Dluhy RG. Evaluation of The dexamethasone suppression test for the diagnosis of glucocorticoid-remediable aldosteronism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997. 82:3570–3573.
Article11. Stowasser M, Gordon RD. Familial hyperaldosteronism. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2001. 78:215–229.
Article12. Stowasser M, Gunasekera TG, Gordon RD. Familial varieties of primary aldosteronism. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2001. 28:1087–1090.
Article13. Stowasser M, Bachmann AW, Huggard PR, Rossetti TR, Gordon RD. Severity of hypertension in familial hyperaldosteronism type I: relationship to gender and degree of biochemical disturbance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000. 85:2160–2166.
Article14. Dluhy RG, Lifton RP. Glucocorticoid-remediable aldosteronism (GRA): diagnosis, variability of phenotype and regulation of potassium homeostasis. Steroids. 1995. 60:48–51.
Article15. Stowasser M, Bachmann AW, Huggard PR, Rossetti TR, Gordon RD. Treatment of familial hyperaldosteronism type I: only partial suppression of adrenocorticotropin required to correct hypertension. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000. 85:3313–3318.
Article16. Dluhy RG, Lifton RP. Glucocorticoid-remediable aldosteronism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1999. 84:4341–4344.
Article17. Dluhy RG, Anderson B, Harlin B, Ingelfinger J, Lifton R. Glucocorticoid-remediable aldosteronism is associated with severe hypertension in early childhood. J Pediatr. 2001. 138:715–720.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Moleculan Genetics of Glucocorticoid Remediable Aldosteronism
- Aldosterone Synthase Gene (CYP11B2) Polymorphism in Korean End-Stage Renal Disease Patients on Hemodialysis
- Two Case of Primary Aldosteronism Induced by Aldosterone Producing Adrenal Adenoma in a Family
- ChimerDB - Database of Chimeric Sequences in the GenBank
- The Effects of an Aldosterone Synthase (CYP11B2) Gene Polymorphism on the Risk of Myocardial Infarction