J Korean Med Sci.
2010 Sep;25(9):1330-1335. 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.9.1330.
Stress-induced Alterations in Mast Cell Numbers and Proteinase-activated Receptor-2 Expression of the Colon: Role of Corticotrophin-releasing Factor
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Gastroenterology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. kjleemd@hotmail.com
- 2Department of Pathology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- KMID: 1785913
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2010.25.9.1330
Abstract
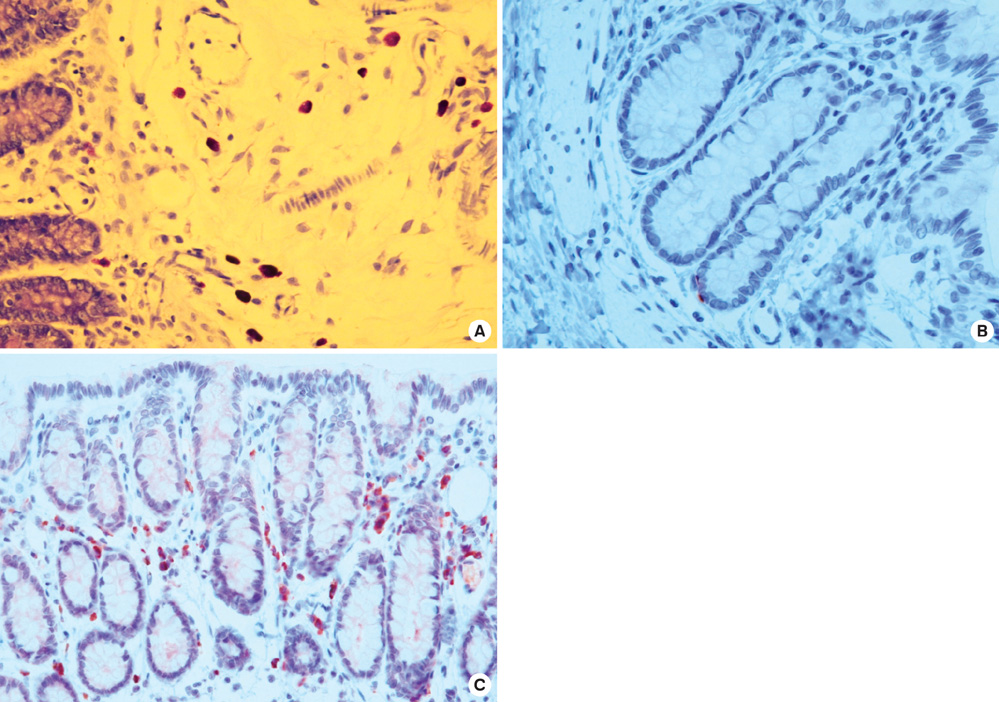
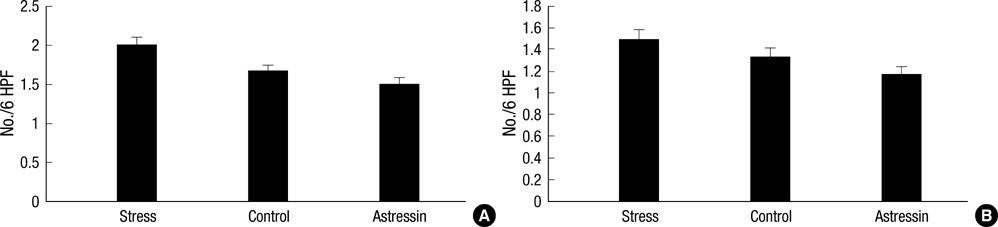
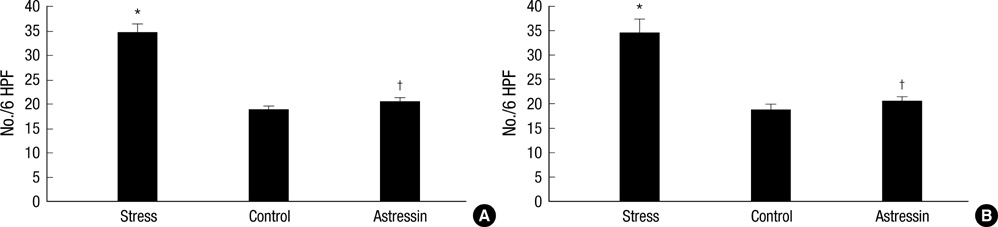
- This study was performed in order to assess whether acute stress can increase mast cell and enterochromaffin (EC) cell numbers, and proteinase-activated receptor-2 (PAR2) expression in the rat colon. In addition, we aimed to investigate the involvement of corticotrophin-releasing factor in these stress-related alterations. Eighteen adult rats were divided into 3 experimental groups: 1) a saline-pretreated non-stressed group, 2) a saline-pretreated stressed group, and 3) an astressin-pretreated stressed group. The numbers of mast cells, EC cells, and PAR2-positive cells were counted in 6 high power fields. In proximal colonic segments, mast cell numbers of stressed rats tended to be higher than those of non-stressed rats, and their PAR2-positive cell numbers were significantly higher than those of non-stressed rats. In distal colonic segments, mast cell numbers and PAR2-positive cell numbers of stressed rats were significantly higher than those of non-stressed rats. Mast cell and PAR2-positive cell numbers of astressin-pretreated stressed rats were significantly lower than those of saline-pretreated stressed rats. EC cell numbers did not differ among the three experimental groups. Acute stress in rats increases mast cell numbers and mucosal PAR2 expression in the colon. These stress-related alterations seem to be mediated by release of corticotrophin-releasing factor.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Colon/*metabolism
Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone/antagonists & inhibitors/metabolism/pharmacology/*physiology
Enterochromaffin Cells/cytology
Male
Mast Cells/*cytology/immunology/metabolism
Peptide Fragments/pharmacology
Rats
Rats, Wistar
Receptor, PAR-2/*metabolism
Restraint, Physical
*Stress, Physiological
Figure
Reference
-
1. Fukudo S. Role of corticotrophin-releasing hormone in irritable bowel syndrome and intestinal inflammation. J Gastroenterol. 2007. 42:Suppl 17. 48–51.2. Gue M, Del Rio-Lacheze C, Eutamene H, Theodorou V, Fioramonti J, Bueno L. Stress-induced visceral hypersensitivity to rectal distension in rats: role of CRF and mast cells. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 1997. 9:271–279.
Article3. Monnikes H, Schmidt BG, Tache Y. Psychological stress-induced accelerated colonic transit in rats involves hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing factor. Gastroenterology. 1993. 104:716–723.
Article4. Williams CL, Peterson JM, Villar RG, Burks TF. Corticotropin-releasing factor directly mediates colonic responses to stress. Am J Physiol. 1987. 253:G582–G586.
Article5. Williams CL, Villar RG, Peterson JM, Burks TF. Stress-induced changes in intestinal transit in the rat: a model for irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1988. 94:611–621.
Article6. Lenz HJ, Raedler A, Greten H, Vale WW, Rivier JE. Stress-induced gastrointestinal secretory and motor responses in rats are mediated by endogenous corticotrophin-releasing factor. Gastroenterology. 1988. 95:1510–1517.7. Sant GR, Theoharides TC. The role of the mast cell in interstitial cystitis. Urol Clin North Am. 1994. 21:41–53.
Article8. Castagliuolo I, Lamont JT, Qiu B, Fleming SM, Bhaskar KR, Nikulasson ST, Kornetsky C, Pothoulakis C. Acute stress causes mucin release from rat colon: role of corticotrophin releasing factor and mast cells. Am J Physiol. 1996. 271:G884–G892.9. Annese V, Bassotti G, Napolitano G, Usai P, Andriulli A, Vantrappen G. Gastrointestinal motility disorders in patients with inactive Crohn's disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1997. 32:1107–1117.
Article10. Vermillion DL, Huizinga JD, Riddell RH, Collins SM. Altered small intestinal smooth muscle function in Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 1993. 104:1692–1699.
Article11. Dunlop SP, Jenkins D, Neal KR, Spiller RC. Relative importance of enterochromaffin cell hyperplasia, anxiety, and depression in postinfectious IBS. Gastroenterology. 2003. 125:1651–1659.
Article12. Lee KJ, Kim YB, Kim JH, Kwon HC, Kim DK, Cho SW. The alteration of enterochromaffin cell, mast cell, and lamina propria T lymphocyte numbers in irritable bowel syndrome and its relationship with psychological factors. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008. 23:1689–1694.
Article13. Park CH, Joo YE, Choi SK, Rew JS, Kim SJ, Lee MC. Activated mast cells infiltrate in close proximity to enteric nerves in diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. J Korean Med Sci. 2003. 18:204–210.
Article14. Dunlop SP, Jenkins D, Spiller RC. Distinctive clinical, psychological, and histological features of postinfective irritable bowel syndrome. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003. 98:1578–1583.
Article15. Gué M, Del Rio-Lacheze C, Eutamene H, Théodorou V, Fioramonti J, Buéno L. Stress-induced visceral hypersensitivity to rectal distension in rats: role of CRF and mast cells. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 1997. 9:271–279.
Article16. Williams CL, Villar RG, Peterson JM, Burks TF. Stress-induced changes in intestinal transit in the rat: a model for irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1988. 94:611–621.
Article17. Strausbaugh HJ, Dallman MF, Levine JD. Repeated, but not acute, stress suppresses inflammatory plasma extravasation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999. 96:14629–14634.
Article18. Barone FC, Deegan JF, Price WJ, Fowler PJ, Fondacaro JD, Ormsbee HS 3rd. Cold-restraint stress increases rat fecal pellet output and colonic transit. Am J Physiol. 1990. 258:G329–G337.
Article19. Singh VK. Stimulatory effect of corticotrophin-releasing neurohormone on human lymphocyte proliferation and interleukin-2 receptor expression. J Neuroimmunol. 1989. 23:257–262.20. Webster EL, Tracey DE, Jutila MA, Wolfe SA Jr, De Souza EB. Corticotropin-releasing factor receptors in mouse spleen: identification of receptor-bearing cells as resident macrophages. Endocrinology. 1990. 127:440–452.
Article21. Eutamene H, Theodorou V, Fioramonti J, Bueno L. Acute stress modulates the histamine content of mast cells in the gastrointestinal tract through interleukin-1 and corticotrophin-releasing factor release in rats. J Physiol. 2003. 553:959–966.22. Park JH, Rhee PL, Kim HS, Lee JH, Kim YH, Kim JJ, Rhee JC. Mucosal mast cell counts correlate with visceral hypersensitivity in patients with diarrhea predominant irritable bowel syndrome. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006. 21:71–78.
Article23. Barbara G, Stanghellini V, De Giorgio R, Cremon C, Cottrell GS, Santini D, Pasquinelli G, Morselli-Labate AM, Grady EF, Bunnett NW, Collins SM, Corinaldesi R. Activated mast cells in proximity to colonic nerves correlate with abdominal pain in irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. 2004. 126:693–702.
Article24. Bueno L, Fioramonti J, Delvaux M, Frexinos J. Mediators and pharmacology of visceral sensitivity: from basic to clinical investigations. Gastroenterology. 1997. 112:1714–1743.
Article25. Nystedt S, Emilsson K, Larsson AK, Strombeck B, Sundelin J. Molecular cloning and functional expression of the gene encoding the human proteinase-activated receptor 2. Eur J Biochem. 1995. 232:84–89.
Article26. Vergnolle N, Bunnett NW, Sharkey KA, Brussee V, Compton SJ, Grady EF, Cirino G, Gerard N, Basbaum AI, Andrade-Gordon P, Hollenberg MD, Wallace JL. Proteinase-activated receptor-2 and hyperalgesia: a novel pain pathway. Nat Med. 2001. 7:821–826.
Article27. Vergnolle N. Clinical relevance of proteinase activated receptors (PARS) in the gut. Gut. 2005. 54:867–874.
Article28. Coelho AM, Vergnolle N, Guiard B, Fioramonti J, Bueno L. Proteinases and proteinase-activated receptor 2: a possible role to promote visceral hyperalgesia in rats. Gastroenterology. 2002. 122:1035–1047.
Article29. Marshall JK, Thabane M, Garg AX, Clark W, Meddings J, Collins SM. WEL Investigators. Intestinal permeability in patients with irritable bowel syndrome after a waterborne outbreak of acute gastroenteritis in Walkerton, Ontario. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2004. 20:1317–1322.
Article30. Gecse K, Roka R, Ferrier L, Leveque M, Eutamene H, Cartier C, Ait-Belgnaoui A, Rosztoczy A, Izbeki F, Fioramonti J, Wittmann T, Bueno L. Increased faecal serine protease activity in diarrhoeic IBS patients: a colonic luminal factor impairing colonic permeability and sensitivity. Gut. 2008. 57:591–599.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Regional Differences in Chronic Stress-induced Alterations in Mast Cell and Protease-activated Receptor-2-positive Cell Numbers in the Colon of Ws/Ws Rats
- Role of Corticotropin-releasing Factor Signaling in Stress-related Alterations of Colonic Motility and Hyperalgesia
- Experimental Study on The Role of Various Antihistaminics to Tissue Mast Cell Changes Elicited by Ultraviolet Ray Inflammation
- Acute Stress-Induced Changes in Follicular Dermal Papilla Cells and Mobilization of Mast Cells: Implications for Hair Growth
- Role of Corticotrophin-releasing Factor in the Stress-induced Dilation of Esophageal Intercellular Spaces