J Korean Med Sci.
2010 Sep;25(9):1272-1276. 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.9.1272.
Seroprevalence of Tissue Invading Parasitic Infections Diagnosed by ELISA in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hyekim@cau.ac.kr
- 2Department of Medical Environmental Biology, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1785904
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2010.25.9.1272
Abstract
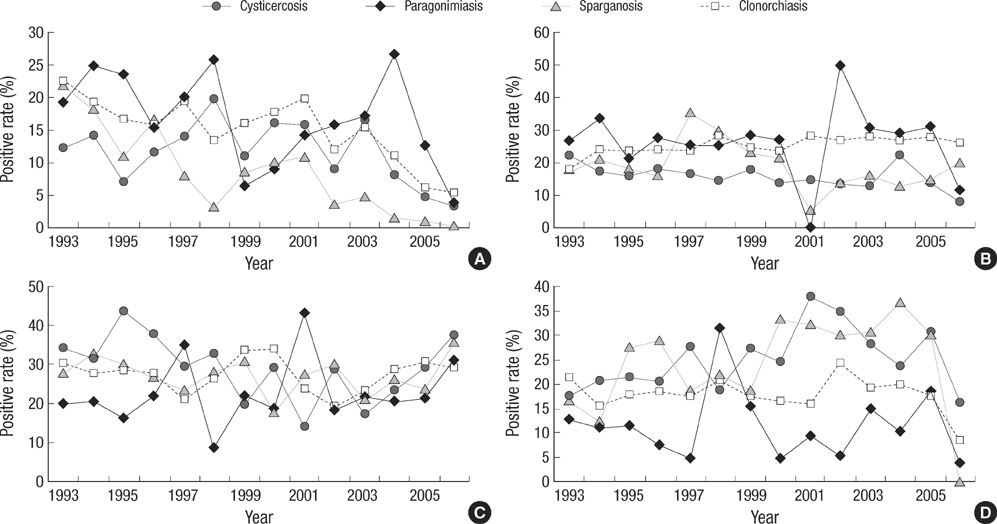
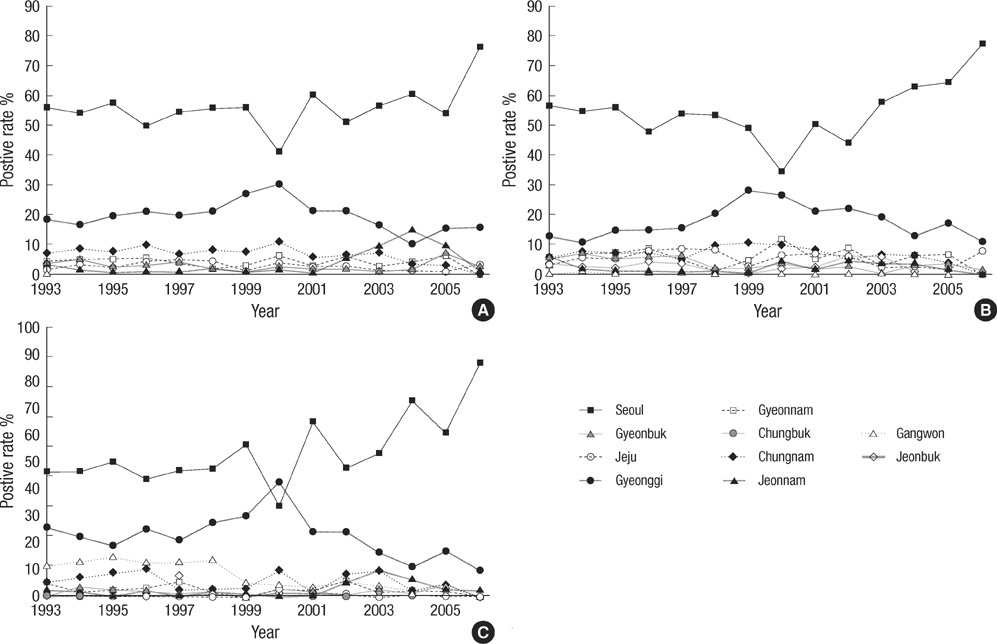
- Seroprevalence of the IgG antibodies for Clonorchis sinensis, Paragonimus westermani, Taenia solium metacestode (cysticercus), and Spirometra erinacei plerocercoid (sparganum) was measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) in sera of patients in Korea from 1993 to 2006. A total of 74,448 specimens referred nationwide from 121 hospitals revealed an IgG positive rate of 7.6% for the 4 parasites. The IgG positive rate (18.7%) for the 4 parasites in 1993 decreased gradually to 6.6% in 2006. Individual positive rate decreased from 5.2% (1993) to 1.6% (2006) for C. sinensis, from 2.8% (1993) to 1.1% (2006) for P. westermani, from 8.3% (1993) to 2.2% (2006) for cysticercus, and from 2.6% (1993) to 1.6% (2006) for sparganum. The positive rate was highest (21.2%) in the group of patients who ranged in age from 50-59 yr old, and in the group that was referred from the Seoul area (55.9%). In conclusion, our results suggest that tissue invading parasitic infections should always be included in differential diagnosis for patients with eosinophilia associated lesions of the central nervous system, liver, and lungs in Korea.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adolescent
Adult
Age Factors
Aged
Aged, 80 and over
Animals
Antibodies, Helminth/*blood
Child
Child, Preschool
Clonorchiasis/diagnosis/*epidemiology
Clonorchis sinensis/immunology/isolation & purification
Cysticercosis/diagnosis/*epidemiology
Cysticercus/immunology/isolation & purification
Diagnosis, Differential
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Eosinophilia/immunology
Female
Humans
Immunoglobulin G/blood
Infant
Male
Middle Aged
Paragonimiasis/diagnosis/*epidemiology
Paragonimus westermani/immunology/isolation & purification
Republic of Korea/epidemiology
Seroepidemiologic Studies
Sparganosis/diagnosis/*epidemiology
Sparganum/immunology/isolation & purification
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
A Case of Severe Anemia by Necator americanus Infection in Korea
Hee Jae Hyun, Eun-Min Kim, So Yeon Park, Jun-Oh Jung, Jong-Yil Chai, Sung-Tae Hong
J Korean Med Sci. 2010;25(12):1802-1804. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.12.1802.Chemotherapeutic drugs for common parasitic diseases in Korea
Sun Huh
J Korean Med Assoc. 2013;56(6):513-522. doi: 10.5124/jkma.2013.56.6.513.Status of common parasitic diseases in Korea in 2019
Sun Huh
J Korean Med Assoc. 2019;62(8):437-456. doi: 10.5124/jkma.2019.62.8.437.A Case of Pulmonary Paragonimiasis with Chronic Abdominal Pain and Erythematous Rash in a 6-year-old Girl
Ju Young Kim, Min Kyu Park, Yong Ju Lee, Sun Huh, Ky Young Cho
Pediatr Infect Vaccine. 2018;25(1):54-59. doi: 10.14776/piv.2018.25.1.54.
Reference
-
1. Seo BS, Rim HJ, Loh SH, Cho SY, Park SC, Bae JW, Kim JH, Lee JS, Koo BY, Kim KS. Study on the status of helminthic infections in Koreans. Korean J Parasitol. 1969. 7:53–70.
Article2. Kim CH, Park CH, Kim HJ, Chun HB, Min HK, Koh TY, Soh CT. Prevalence of intestinal parasites in Korea. Korean J Parasitol. 1971. 9:25–38.
Article3. Hong ST, Chai JY, Choi MH, Huh S, Rim HJ, Lee SH. A successful experience of soil-transmitted helminth control in the Republic of Korea. Korean J Parasitol. 2006. 44:177–185.
Article4. Cho SH, Lee KY, Lee BC, Cho PY, Cheun HI, Hong ST, Sohn WM, Kim TS. Prevalence of clonorchiasis in southern endemic areas of Korea in 2006. Korean J Parasitol. 2008. 46:133–137.
Article5. Shim YS, Cho SY, Han YC. Pulmonary paragonimiasis: a Korean perspectives. Sem Resp Med. 1991. 12:35–45.6. Cho SY, Kong Y, Kang SY. Epidemiology of paragonimiasis in Korea. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 1997. 28:Suppl 1. 32–36.7. Kong Y, Cho SY, Cho MS, Kwon OS, Kang WS. Seroepidemiological observation of Taenia solium cysticercosis in epileptic patients in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 1993. 8:145–152.
Article8. Cho SY, Kim SI, Kang SY, Choi DY, Suk JS, Choi KS, Ha YS, Chung CS, Myung HJ. Evaluation of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in serological diagnosis of human neurocysticercosis using paired samples of serum and cerebrospinal fluid. Korean J Parasitol. 1986. 24:25–41.
Article9. Cho SY, Hong ST, Rho YH, Choi SY, Han YC. Application of micro-ELISA in serodiagnosis of human paragonimiasis. Korean J Parasitol. 1981. 19:151–156.
Article10. Kim H, Kim SI, Cho SY. Serological diagnosis of human sparganosis by means of micro-ELISA. Korean J Parasitol. 1984. 22:222–228.
Article11. Kim TS, Cho SH, Huh S, Kong Y, Sohn WM, Hwang SS, Chai JY, Lee SH, Park YK, Oh DK, Lee JK. Working Groups in National Institute of Health and Korea Association of Health Promotion. A nationwide survey on the prevalence of intestinal parasitic infections in the Republic of Korea, 2004. Korean J Parasitol. 2009. 47:37–47.
Article12. Rim HJ. Clonorchiasis: an update. J Helminthol. 2005. 79:269–281.
Article13. Lee SH, Kim MN, Back BY, Chai JY, Kim TH, Hwang YS. Analysis of parasite-specific antibody positive patients for Clonorchis sinensis, Paragonimus westermani, cysticercus and sparganum using ELISA. Korean J Lab Med. 2003. 23:126–131.14. Lee KJ, Bae YT, Kim DH, Deung YJ, Ryang YS. A seroepidemiologic survey for human sparganosis in Gangweon-do. Korean J Parasitol. 2002. 40:177–180.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Serological diagnosis of tissue-invading parasites in Korea
- Seroprevalence of Sarcocystis falcatula in Two Islands of Malaysia using Recombinant Surface Antigen 4
- Seroprevalence of Tissue and Luminal Helminths among Patients in Hanoi Medical University Hospital, Vietnam, 2018
- Tissue Invading Helminthic Diseases
- Familial Infestation of Paragonimus Westermani Diagnosed by ELISA -Report of two families-