J Korean Med Sci.
2008 Aug;23(4):714-717. 10.3346/jkms.2008.23.4.714.
Development of Tibiofemoral Angle in Korean Children
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Seoul National University Children's Hospital, Seoul, Korea. inhoc@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Soonchunhyang University Hospital, Bucheon, Korea.
- KMID: 1785835
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2008.23.4.714
Abstract
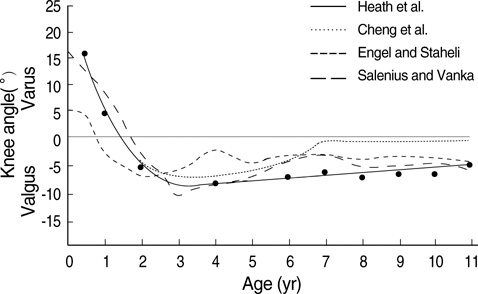
- This study was performed to identify the chronological changes of the knee angle or the tibiofemoral angles in normal healthy Korean children. Full-length anteroposterior view standing radiographs of 818 limbs of 452 Korean children were analyzed. The overall patterns of the chronological changes in the knee angle were similar to those described previously in western or Asian children, but the knee angle development was delayed, i.e., genu varum before 1 yr, neutral at 1.5 yr, increasing genu valgum with maximum a value of 7.8 degrees at 4 yr, followed by a gradual decrease to approximately 5-6 degrees of genu valgum of the adult level at 7 to 8 yr of age. These normative data on chronological changes of knee angles should be taken into consideration when evaluating lower limb alignment in children.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. McDade W. Bow legs and knock knees. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1977. 24:825–839.
Article2. Morley AJ. Knock-knee in children. Br Med J. 1957. 2:976–979.
Article3. Sherman M. Physiologic bowing of the legs. South Med J. 1960. 53:830–836.
Article4. Engel GM, Staheli LT. The natural history of torsion and other factors influencing gait in childhood. A study of the angle of gait, tibial torsion, knee angle, hip rotation, and development of the arch in normal children. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1974. 99:12–17.5. Hachiya M. A roentgenographical study on chronological changes in genu varum and valgum in children (author's transl). Nippon Seikeigeka Gakkai Zasshi. 1981. 55:31–43.6. Levine AM, Drennan JC. Physiological bowing and tibia vara. The metaphyseal-diaphyseal angle in the measurement of bowleg deformities. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1982. 64:1158–1163.
Article7. Heath CH, Staheli LT. Normal limits of knee angle in white children--genu varum and genu valgum. J Pediatr Orthop. 1993. 13:259–262.8. Cheng JC, Chan PS, Chiang SC, Hui PW. Angular and rotational profile of the lower limb in 2,630 Chinese children. J Pediatr Orthop. 1991. 11:154–161.
Article9. Moreland JR, Bassett LW, Hanker GJ. Radiographic analysis of the axial alignment of the lower extremity. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1987. 69:745–749.
Article10. Salenius P, Vankka E. The development of the tibiofemoral angle in children. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1975. 57:259–261.
Article11. Shrout PE, Fleiss JL. Intraclass correlations: Uses in assessing rater reliability. Psychol Bull. 1979. 86:420–428.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A New Method in the Measurement of Tibiofemoral Angle
- The Influence of Postoperative Tibiofemoral Alignment on the Clinical Results of Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty
- Factors Affecting the Tibiofemoral Alignment in Minimally Invasive Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty
- The Effect of Tibiofemoral Alignment on the Results of Total Knee Arthroplasty
- The Relation Between Clinical Results and Correction Angle in Proximal Tibial Osteotomy