J Korean Med Sci.
2008 Aug;23(4):573-578. 10.3346/jkms.2008.23.4.573.
Screening of Subtelomeric Rearrangements in 100 Korean Pediatric Patients with Unexplained Mental Retardation and Anomalies Using Subtelomeric FISH (Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization)
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine & Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sunnyhk@skku.edu
- 2Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, School of Medicine, Konkuk University, Chungju, Korea.
- 3Department of Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics, Seoul Medical Science Institute, Seoul Clinical Laboratories, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Laboratory Mecidine, Masan Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Masan, Korea.
- KMID: 1785812
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2008.23.4.573
Abstract
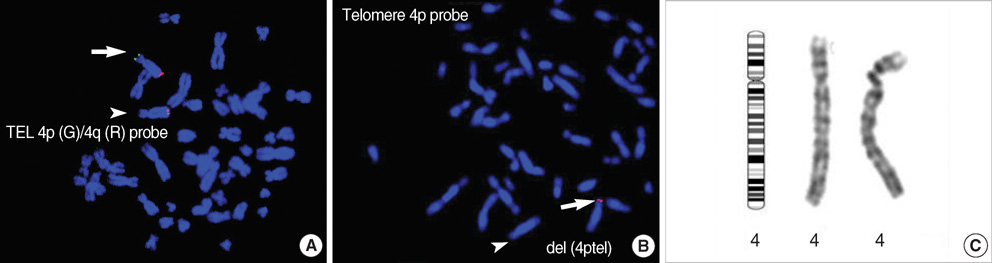
- Rearrangements of the subtelomeric regions of chromosomes account for a significant proportion of the underlying genetic defects in both idiopathic mental retardation (MR) and multiple congenital anomalies. To detect the rearrangements, a set of subtelomeric fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) probes has been developed. The aim of this study was to reveal the frequency of subtelomeric rearrangements in Korean patients with MR or multiple anomalies. We performed a FISH study using a commercially available subtelomeric FISH probes on a series of unrelated Korean pediatric patients with MR or multiple anomalies without identifiable causes. We used a checklist to evaluate the developmental delay and/or MR. Patients who were shown to have chromosome abnormalities, metabolic disorders, or recognizable dysmorphic syndromes by clinical and laboratory findings were excluded. As a result, 100 patients were eligible for the Subtelomeric FISH study, and a total of 29 patients (29%) were suspected to have subtelomeric rearrangements on initial screening by the multiprobe FISH kit. Among theses, confirmatory FISH studies by using single locus-specific FISH probes were performed in 24 patients. One patient (a 10- yr-old girl) was confirmed to have rearrangement, deletion of the telomeric portion of the short arm of chromosome 4 (4p). Her clinical manifestation was compatible with Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome, which is known to be caused by 4p deletion. The frequency of subtelomeric rearrangements in this study was 1.1% (1/95), lower than those previously reported (0.5-16.3%). We suggest that subtelomeric FISH test is a useful screening tool for patients with idiopathic MR and/or dysmorphism regardless of its false positive value.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Flint J, Wilkie AO. The genetics of mental retardation. Br Med Bull. 1996. 52:453–464.
Article2. Shaffer LG, Lupski JR. Molecular mechanisms for constitutional chromosomal rearrangements in humans. Annu Rev Genet. 2000. 34:297–329.
Article3. Colleaux L, Rio M, Heuertz S, Moindrault S, Turleau C, Ozilou C, Gosset P, Raoult O, Lyonnet S, Cormier-Daire V, Amiel J, Le Merrer M, Picq M, de Blois MC, Prieur M, Romana S, Cornelis F, Vekemans M, Munnich A. A novel automated strategy for screening cryptic telomeric rearrangements in children with idiopathic mental retardation. Eur J Hum Genet. 2001. 9:319–327.
Article4. Rio M, Molinari F, Heuertz S, Ozilou C, Gosset P, Raoul O, Cormier-Daire V, Amiel J, Lyonnet S, Le Merrer M, Turleau C, de Blois MC, Prieur M, Romana S, Vekemans M, Munnich A, Colleaux L. Automated fluorescent genotyping detects 10% of cryptic subtelomeric rearrangements in idiopathic syndromic mental retardation. J Med Genet. 2002. 39:266–270.5. van Karnebeek CD, Koevoets C, Sluijter S, Bijlsma EK, Smeets DF, Redeker EJ, Hennekam RC, Hoovers JM. Prospective screening for subtelomeric rearrangements in children with mental retardation of unknown aetiology: the Amsterdam experience. J Med Genet. 2002. 39:546–553.
Article6. Koolen DA, Nillesen WM, Versteeg MH, Merkx GF, Knoers NV, Kets M, Vermeer S, van Ravenswaaij CM, de Kovel CG, Brunner HG, Smeets D, de Vries BB, Sistermans EA. Screening for subtelomeric rearrangements in 210 patients with unexplained mental retardation using multiplex ligation dependent probe amplification (MLPA). J Med Genet. 2004. 41:892–899.
Article7. Armour JA, Sismani C, Patsalis PC, Cross G. Measurement of locus copy number by hybridisation with amplifiable probes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000. 28:605–609.
Article8. Sismani C, Armour JA, Flint J, Girgalli C, Regan R, Patsalis PC. Screening for subtelomeric chromosome abnormalities in children with idiopathic mental retardation using multiprobe telomeric FISH and the new MAPH telomeric assay. Eur J Hum Genet. 2001. 9:527–532.
Article9. White SJ, Breuning MH, den Dunnen JT. Detecting copy number changes in genomic DNA: MAPH and MLPA. Methods Cell Biol. 2004. 75:751–768.
Article10. Boehm D, Herold S, Kuechler A, Liehr T, Laccone F. Rapid detection of subtelomeric deletion/duplication by novel real-time quantitative PCR using SYBR-green dye. Hum Mutat. 2004. 23:368–378.
Article11. Le Caignec C, Boceno M, Saugier-Veber P, Jacquemont S, Joubert M, David A, Frebourg T, Rival JM. Detection of genomic imbalances by array based comparative genomic hybridisation in fetuses with multiple malformations. J Med Genet. 2005. 42:121–128.
Article12. Rooms L, Reyniers E, Kooy RF. Subtelomeric rearrangements in the mentally retarded: a comparison of detection methods. Hum Mutat. 2005. 25:513–524.
Article13. Riegel M, Baumer A, Jamar M, Delbecque K, Herens C, Verloes A, Schinzel A. Submicroscopic terminal deletions and duplications in retarded patients with unclassified malformation syndromes. Hum Genet. 2001. 109:286–294.
Article14. Baralle D. Chromosomal aberrations, subtelomeric defects, and mental retardation. Lancet. 2001. 358:7–8.
Article15. de Vries BB, White SM, Knight SJ, Regan R, Homfray T, Young ID, Super M, McKeown C, Splitt M, Quarrell OW, Trainer AH, Niermeijer MF, Malcolm S, Flint J, Hurst JA, Winter RM. Clinical studies on submicroscopic subtelomeric rearrangements: a checklist. J Med Genet. 2001. 38:145–150.
Article16. Walter S, Sandig K, Hinkel GK, Mitulla B, Ounap K, Sims G, Sitska M, Utermann B, Viertel P, Kalscheuer V, Bartsch O. Subtelomere FISH in 50 children with mental retardation and minor anomalies, identified by a checklist, detects 10 rearrangements including a de novo balanced translocation of chromosomes 17p13.3 and 20q13.33. Am J Med Genet A. 2004. 128:364–373.
Article17. Biesecker LG. The end of the beginning of chromosome ends. Am J Med Genet. 2002. 107:263–266.
Article18. Joyce CA, Dennis NR, Cooper S, Browne CE. Subtelomeric rearrangements: results from a study of selected and unselected probands with idiopathic mental retardation and control individuals by using high-resolution G-banding and FISH. Hum Genet. 2001. 109:440–451.
Article19. Kirchhoff M, Rose H, Lundsteen C. High resolution comparative genomic hybridisation in clinical cytogenetics. J Med Genet. 2001. 38:740–744.
Article20. Anderlid BM, Schoumans J, Anneren G, Sahlen S, Kyllerman M, Vujic M, Hagberg B, Blennow E, Nordenskjold M. Subtelomeric rearrangements detected in patients with idiopathic mental retardation. Am J Med Genet. 2002. 107:275–284.
Article21. Baker E, Hinton L, Callen DF, Altree M, Dobbie A, Eyre HJ, Sutherland GR, Thompson E, Thompson P, Woollatt E, Haan E. Study of 250 children with idiopathic mental retardation reveals nine cryptic and diverse subtelomeric chromosome anomalies. Am J Med Genet. 2002. 107:285–293.
Article22. Clarkson B, Pavenski K, Dupuis L, Kennedy S, Meyn S, Nezarati MM, Nie G, Weksberg R, Withers S, Quercia N, Teebi AS, Teshima I. Detecting rearrangements in children using subtelomeric FISH and SKY. Am J Med Genet. 2002. 107:267–274.
Article23. Hogervorst FB, Nederlof PM, Gille JJ, McElgunn CJ, Grippeling M, Pruntel R, Regnerus R, van Welsem T, van Spaendonk R, Menko FH, Kluijt I, Dommering C, Verhoef S, Schouten JP, van't Veer LJ, Pals G. Large genomic deletions and duplications in the BRCA1 gene identified by a novel quantitative method. Cancer Res. 2003. 63:1449–1453.24. Janssen B, Hartmann C, Scholz V, Jauch A, Zschocke J. MLPA analysis for the detection of deletions, duplications and complex rearrangements in the dystrophin gene: potential and pitfalls. Neurogenetics. 2005. 6:29–35.
Article25. Schwartz M, Duno M. Multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification is superior for detecting deletions/duplications in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Clin Genet. 2005. 67:189–191.
Article26. Shao H, Lip V, Wu BL. Effectiveness of multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification assay used for detecting deletion of Prader-Willi syndrome. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao. 2005. 37:64–67.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Unbalanced translocation der(8)t(8:13)(p23.3;q32.1)dn identified by array CGH and subtelomeric FISH in a patient with mental retardation
- Cytogenetic evaluation of a patient with ring chromosome 9 presenting failure to thrive and developmental delay
- A Case of Identification of Marker Chromosome by comparative genomic hybridization and fluorescence in situ hybridization
- Rapid prenatal diagnosis of chromosome aneuploidies in 943 uncultured amniotic fluid samples by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH)
- A Case of Mosaic Ring Chromosome 4 with Subtelomeric 4p Deletion