J Korean Med Sci.
2007 Dec;22(6):1060-1064. 10.3346/jkms.2007.22.6.1060.
Long-term Experience with the Bjork-Shiley Monostrut Tilting Disc Valve
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kkh726@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1785770
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2007.22.6.1060
Abstract
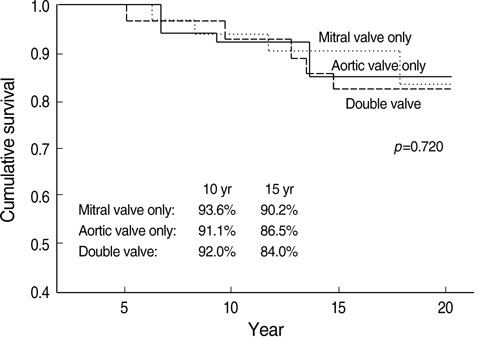
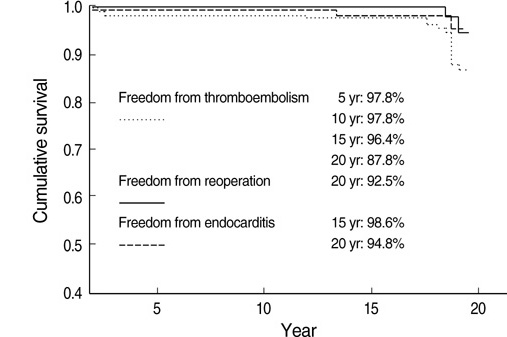
- The Bjork-Shiley Monostrut valve is tilting disc mechanical valve prosthesis. This study was designed to present the long-term outcome of our experience. One hundred and thirty-seven Bjork-Shiley Monostrut valves were implanted in 101 consecutive patients from November 1983 to February 1990. There were 60 male and 41 female with mean age of 34.5 yr at the time of operation. Fifty-nine patients underwent single valve replacement, 38 had double valve, and 4 had triple valve replacement. There were six in-hospital deaths (5.9%): three from cardiopulmonary bypass weaning failure and one each from septic shock, sudden cardiac arrest, and uncontrollable bleeding. Mean duration of follow-up was 181.2+/-76.2 months. Overall survival was 86.2% at 15 yr and 83.1% at 20 yr. Patients with mitral valve replacement had 93.5% and 90.2% cumulative survival at 10 and 15 yr, respectively, while patients with aortic valve replacement had 91.1% and 86.5% cumulative survival at 10 and 15 yr. Two groups had no significant difference in survival. Double valve replacement patients had 92.2% and 84.0% survival at 10 and 15 yr, respectively. There were no significant differences in survival between the single and double valve replacement groups. Freedom from thromboembolism was noted in: 97.8%, 97.8%, 96.4% and 87.8% at 5, 10, 15 and 20 yr, respectively. Absence of endocarditis was noted in 98.6% and 94.8% at 15 and 20 yr. Absence of reoperation was 92.5% at 20 yr. In conclusion, the Bjork-Shiley Monostrut valve is reliable, with a similar incidence of valve-related morbidity as in other mechanical valves.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Crawford FA Jr. Current heart valve prostheses. Cardiac Surgery. 1987. 1:183–202.2. Björk VO. A new tilting disc valve prosthesis. Scand J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1969. 3:1–10.3. Lindblom D, Björk VO, Semb BK. Mechanical failure of the Björk-Shiley valve. Incidence, clinical presentation and management. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1986. 92:894–907.4. Edmunds LH Jr, Clark RE, Cohn LH, Grunkemeier GL, Miller DC, Weisel RD. Guidelines for reporting morbidity and mortality after cardiac valvular operations. Ad Hoc Liaison Committee for Standardizing Definitions of Prosthetic Heart Valve Morbidity of The American Association for Thoracic Surgery and The Society of Thoracic Surgeons. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1996. 112:708–711.5. Björk VO. The pyrolytic carbon occluder for the Björk-Shiley tilting disc valve prosthesis. Scand J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1972. 6:109–113.
Article6. Björk VO, Henze A, Hindmarsh T. Radiopaque marker in the tilting disc of the Björk-Shiley heart valve. Evaluation of in vivo prosthetic valve function by cineradiography. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1977. 73:563–569.7. Orszulak TA, Schaff HV, DeSmet JM, Danielson GK, Pluth JR, Puga FJ. Late results of valve replacement with the Björk-Shiley valve (1973 to 1982). J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1993. 105:302–312.8. Nakano SN, Kawashima Y, Matsuda H, Kawamoto T, Shintani H, Mitsuno M, Ueda T. A five-year appraisal and hemodynamic evaluation of the Björk-Shiley Monostrut valve. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1991. 101:881–887.
Article9. Lindblom D, Lindblom U, Henze A, Björk VO, Semb BK. Three-year clinical results with the Monostrut Björk-Shiley prosthesis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1987. 94:34–43.
Article10. Nashef MD. An evaluation of the Björk-Shiley Monostrut valve: Abst. of monostrut valve symposium. Dallas Tx. 1987. 30.11. Daenen W, Van Kerrebroeck C, Stalpaert G, Mertens B, Lesaffre E. The Björk-Shiley Monostrut valve. Clinical experience in 647 patients. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1993. 106:918–927.12. Aris A, Padro JM, Camara ML, Crexells C, Augé JM, Caralps JM. Clinical and hemodynamic results of cardiac valve replacement with the Monostrut Björk-Shiley prosthesis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1988. 95:423–431.
Article13. Thulin LI, Bain WH, Huysmans HH, van Ingen G, Prieto I, Basile F, Lindblom DA, Olin CL. Heart valve replacement with the Björk-Shiley Monostrut valve: early results of a multicenter clinical investigation. Ann Thorac Surg. 1988. 45:164–170.
Article14. Canivet P, Vitoux B, Vahanian A, Michel PL, Cormier B, Enriquez Sarano L, Richaud C, Acar J. Björk-Shiley-Monostrut prosthesis of the aortic valve. Mid-term development. Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss. 1991. 84:57–62.15. Dietrich MS, Nashef SA, Bain WH. Heart valve replacement with the Björk-Shiley Monostrut valve in patients over 60 years of age. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1998. 37:131–134.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Long-term experience with the Bjork-Shiley monostrut valve
- Changes of Doppler Echocardiographic Findings After Mitral Valve Operation
- In vitro pressure drop comparison between two mechanical valve prostheses
- Unusual Disc Dislodgement of a Björk-Shiley Valve after Long-term Implantation
- Long-Term Results of the Cardiac Valve Replacement-Experiences in Seoul National University Hospital(1968-1994)