J Korean Acad Nurs.
2012 Jun;42(3):311-321. 10.4040/jkan.2012.42.3.311.
Structural Equation Modeling on Successful Aging in Elders: Focused on Selection, Optimization, Compensation Strategy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nursing, The Research Institute for Basic Science, Hoseo University, Asan, Korea. doonoh@hoseo.edu
- KMID: 1785215
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.3.311
Abstract
- PURPOSE
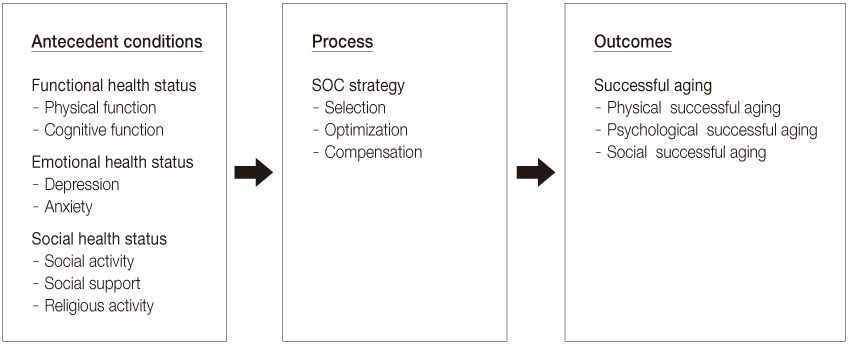
This study was designed to construct and test a structural equation modeling on specific domain health status and the Selection, Optimization, Compensation (SOC) strategy affecting successful aging in elderly people.
METHODS
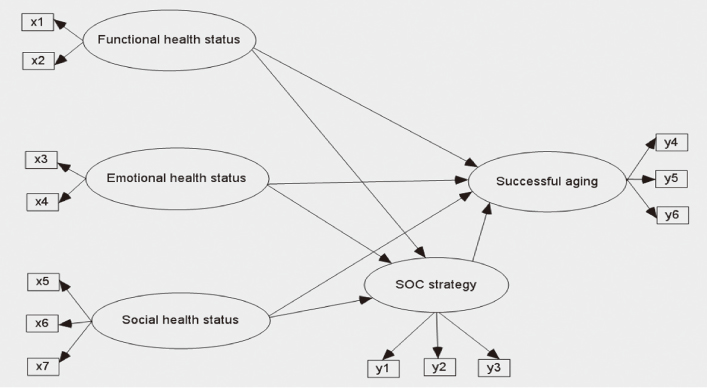
The model construction was based on the SOC model by Baltes and Baltes. Interviews were done with 201 elderly people aged 65 or older. Interview contents included demographics, functional health status, emotional health status, social health status, SOC strategies, and successful aging. Data were analyzed using SPSS 15.0 and AMOS 7.0.
RESULTS
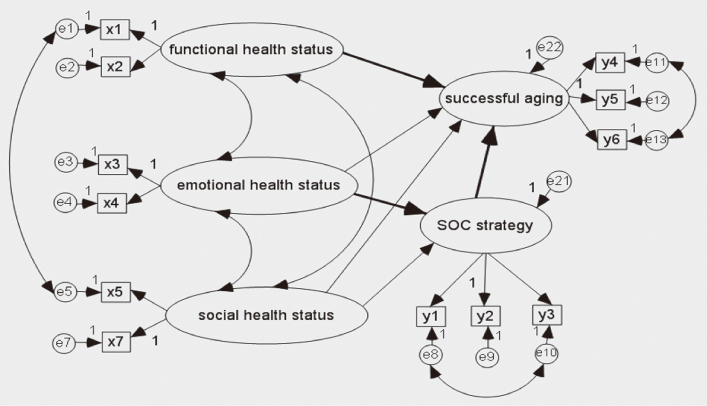
Model fit indices for the modified model were GFI=.93, CFI=.94, and RMSEA=.07. Three out of 7 paths were found to have a significant effect on successful aging in this final model. Functional health status had a direct and positive effect on successful aging. Emotional health status influenced successful aging through SOC strategies.
CONCLUSION
This study suggests that interventions for improving functional health status and for strengthening SOC strategies are critical for successful aging. Continuous development of a variety of successful aging programs using SOC strategy is suggested.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Development of a scale to measure selection, optimization, compensation (SOC) strategy in late middle-aged women: a methodological study
Do-Young Lee, Gie Ok Noh
Womens Health Nurs. 2024;30(3):216-225. doi: 10.4069/whn.2024.08.10.
Reference
-
1. Ainlay SC, Smith DR. Aging and religious participation. Journal of Gerontology. 1984. 39(3):357–363.2. Baltes PB, Baltes MM, editors. Successful aging: Perspectives from the behavioral sciences. 1990. New York: Cambridge University Press.3. Baltes PB, Baltes MM, Freund AM, Lang FR. Measurement of selective optimization with compensation by questionnaire. 1995. Berlin: Max Planck Institute for Human Development and Education.4. Cho SB. Structural equation model. 1996. Seoul: Youngji Munwhasa.5. Crosnoe R, Elder GH. Successful adaptation in the later years: A life course approach to aging. Social Psychology Quarterly. 2002. 65(4):309–328. http://dx.doi.org/10.2307/3090105.6. Goldberg D, Bridges K, Ducan-Jones P, Grayson D. Detecting anxiety and depression in general medical settings. British Medical Journal. 1988. 297:897–899. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.297.6653.897.7. Ha JY, Oh YJ. Variables that affect Selective Optimization with Compensation (SOC) for successful aging among middle-class elderly. Journal of Korean Home Management Association. 2003. 21(2):131–144.8. Holstein MB, Minkler M. Self, society and the new gerontology. The Gerontologist. 2003. 43(6):787–796. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/geront/43.6.787.9. Kee BS, Lee CW. A preliminary study for the standardization of geriatric depression scale in Korea. Journal of Korean Neuropsychiatric Association. 1995. 129(6):1875–1885.10. Kim IJ, Suh MJ, Kim KS, Cho NO. The relationship between the characteristics of social support and post-stroke depression. Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing. 1999. 2(2):206–214.11. Kim MH, Shin KR, Kang I, Kang MS. A study of successful aging experience of Korean elderly. Journal of the Korea Gerontological Society. 2004. 24(2):79–95.12. Kline RB. Principles and practice of structural equation modeling. 2005. 2nd ed. New York: The Guilford Press.13. Korea Institute for Health & Social Affairs. 2004 National survey of the elderly life and welfare. 2005. Seoul: Author.14. Lee JM, Lym YL, Oh SW, Oh DN. Developing a comprehensive interdisciplinary healthcare program for the elderly in senior residence. The Middle European Journal of Medicine. 2009. 121:Suppl 1. 75–77. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00508-009-1195-6.15. Lee KO. A structural analysis of successful aging factors of rural elders. 2007. Seoul: Seoul National University;Unpublished doctoral dissertation.16. Lim JY, Lee SH, Cha YS, Sun WS. Reliability and validity of anxiety screening scale. Journal of the Korean Academy of Family Medicine. 2001. 22(8):1224–1232.17. Rowe JW, Kahn RL. Successful aging. 1998. New York: Pantheon Books.18. Russell RD. Social health: An attempt to clarify this dimension of well-being. International Journal of Health Education. 1973. 16(2):74–84.19. Seeman TE, Bruce ML, McAvay GJ. Social network characteristics and onset of ADL disability: MacArthur studies of successful aging. The Journals of Gerontology. Series B, Psychological Sciences and Social Sciences. 1996. 51(4):S191–S200. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/geronb/51B.4.S191.20. Seo EJ. Constructing the successful aging model of the older adults. 2009. Seoul: Kyung Hee University;Unpublished doctoral dissertation.21. Sheikh JI, Yesavage JA. Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS). Recent evidence and development of a shorter version. Clinical Gerontologist. 1986. 5(1-2):165–173. http://dx.doi.org/10.1300/J018v05n01_09.22. Shin HC, Kim CH, Cho BL, Won JW, Song SW, Park YK, et al. The development of a Korean health status measure for the elderly. Journal of the Korean Academy of Family Medicine. 2002. 23(4):440–457.23. Song HJ. The effects of the elderly's role performance on successful aging: Focused on SOC coping strategies as mediators. 2009. Cheongju: Cheongju University;Unpublished doctoral dissertation.24. Statistics Korea. Estimated population. 2008. Seoul: Author.25. Strawbridge WJ, Wallhagen MI, Cohen RD. Successful aging and well-being: Self-rated compared with Rowe and Kahn. The Gerontologist. 2002. 42(6):727–733. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/geront/42.6.727.26. Tabbarah M, Crimmins EM, Seeman TE. The relationship between cognitive and physical performance: MacArthur studies of successful aging. The Journals of Gerontology. Series A, Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences. 2002. 57(4):M228–M235. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/gerona/57.4.M228.27. Vaillant GE, Mukamal K. Successful aging. American Journal of Psychiatry. 2001. 158(6):839–847. http://dx.doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.158.6.839.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Structural Equation Modeling on Successful Aging in Elders with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Based on Selection-Optimization-Compensation Strategy
- Academic burnout and selection-optimization-compensation strategy in medical students
- The effects of individual, occupational, and supportive factors on successful return to work using a structural equation model
- The Effect of Job Stress on Health Promoting Behaviors among Nurses: Mediating Selection, Optimization and Compensation Strategy
- The Effects of a Self-Management Program on Successful Aging