J Vet Sci.
2014 Jun;15(2):327-334. 10.4142/jvs.2014.15.2.327.
Distribution, quantitative load and characterization of Salmonella associated with swine farms in upper-northern Thailand
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Food Animal Clinic, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai 50200, Thailand. patprapas@gmail.com
- 2National Center for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, National Science and Technology Development Agency, Pathum Thani 12120, Thailand.
- 3Department of Veterinary Public Health, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok 10330, Thailand.
- 4Department of Veterinary Preventive Medicine, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Ohio State University, Columbus, OH 43210, USA.
- KMID: 1784655
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2014.15.2.327
Abstract
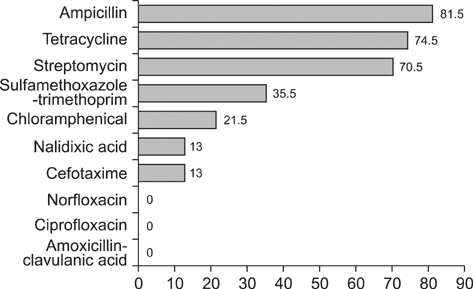
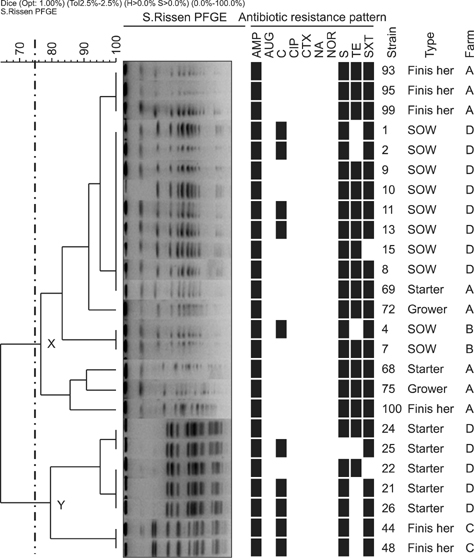
- This study was conducted to analyze the prevalence and quantitative loads of Salmonella spp. on pig farms in Chiang Mai, Lamphun, Thailand to assess loading levels before slaughtering. The serotype diversity, antimicrobial-resistance pattern and pulse-field type of Salmonella spp. were also characterized to assess the dynamic propagation of the pathogen. The Salmonella-positive prevalence was 246/805 (30.56%), and the quantitative loads varied from 1.48~4.04 Log10MPN/g, with a mean +/- standard deviation of 2.11 +/- 0.57. AMP/S/TE (ampicillin/streptomycin/tetracycline) was the highest frequency antimicrobial resistance pattern found in this study. In addition, Salmonella Rissen was the primary serotype in this region. PFGE results indicated the occurrence of infection by cross contamination among pig farms. Our study showed that pork is easily contaminated with this pathogen. Farm control programs must be based on strict biosecurity and hygienic measures, which could further reduce the contamination pressure at slaughterhouses or retail shops.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Abattoirs
Animals
Anti-Bacterial Agents/*pharmacology
Bacterial Load/veterinary
Colony Count, Microbial/veterinary
Drug Resistance, Multiple, Bacterial/*drug effects
Electrophoresis, Gel, Pulsed-Field/veterinary
Feces/microbiology
Female
Male
Prevalence
Salmonella/classification/*drug effects/*genetics/isolation & purification
Salmonella Infections, Animal/*epidemiology/microbiology/transmission
Serotyping/veterinary
Swine
Swine Diseases/*epidemiology/microbiology/transmission
Thailand/epidemiology
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Figure
Reference
-
1. Berends BR, Van Knapen F, Mossel DA, Burt SA, Snijders JM. Impact on human health of Salmonella spp. on pork in The Netherlands and the anticipated effects of some currently proposed control strategies. Int J Food Microbiol. 1998; 44:219–229.
Article2. Berends BR, Van Knapen F, Mossel DAA, Burt SA, Snijders JMA. Salmonella spp. on pork at cutting plants and at the retail level and the influence of particular risk factors. Int J Food Microbiol. 1998; 44:207–217.
Article3. Berends BR, Van Knapen F, Snijders JM, Mossel DA. Identification and quantification of risk factors regarding Salmonella spp. on pork carcasses. Int J Food Microbiol. 1997; 36:199–206.
Article4. CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disc Susceptibility Test; Approved standard-Ninth Edition. CLSI document M2-A9. Wayne: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2006.5. Delhalle L, Saegerman C, Farnir F, Korsak N, Maes D, Messens W, De Sadeleer L, De Zutter L, Daube G. Salmonella surveillance and control at post-harvest in the Belgian pork meat chain. Food Microbiol. 2009; 26:265–271.
Article6. Dorn-in S, Fries R, Padungtod P, Kyule MN, Baumann MP, Srikitjakarn L, Chantong W, Sanguangiat A, Zessin KH. A cross-sectional study of Salmonella in pre-slaughter pigs in a production compartment of northern Thailand. Prev Vet Med. 2009; 88:15–23.
Article7. Escartín EF, Lozano JS, Rodríguez O, Gonzáles NM, Torres JA. Incidence and level of Salmonella serovars in raw pork obtained from mexican butcher shops. Food Microbiol. 1995; 12:435–439.
Article8. Foxman B. Molecular Tools and Infectious Disease Epidemiology. 1st ed. Burlington: Academic Press;2012. p. 23–40.9. García-Feliz C, Collazos JA, Carvajal A, Vidal AB, Aladueña A, Ramiro R, De La Fuente M, Echeita MA, Rubio P. Salmonella enterica infections in Spanish swine fattening units. Zoonoses Public Health. 2007; 54:294–300.
Article10. Giovannini A, Prencipe V, Conte A, Marino L, Petrini A, Pomilio F, Rizzi V, Migliorati G. Quantitative risk assessment of Salmonella spp. infection for the consumer of pork products in an Italian region. Food Control. 2004; 15:139–144.
Article11. Gonzales-Barron UA, Redmond G, Butler F. A risk characterization model of Salmonella Typhimurium in Irish fresh pork sausages. Food Res Int. 2012; 45:1184–1193.
Article12. Hauser E, Hebner F, Tietze E, Helmuth R, Junker E, Prager R, Schroeter A, Rabsch W, Fruth A, Malorny B. Diversity of Salmonella enterica serovar Derby isolated from pig, pork and humans in Germany. Int J Food Microbiol. 2011; 151:141–149.
Article13. International Standard Organization. ISO 6579:2002(E). Microbiology of food and animal feeding stuffs - Horizontal method for the detection of Salmonella spp. 4th ed. Geneva: ISO;2002.14. Jawetz E, Melnick JL, Adelberg EA. Review of Medical Microbiology. 16th ed. Los Altos: Lange Medical Publication;1984. p. 244–248.15. Lo Fo Wong DMA, Hald T, van der Wolf PJ, Swanenburg M. Epidemiology and control measures for Salmonella in pigs and pork. Livest Prod Sci. 2002; 76:215–222.16. Mürmann L, dos Santos MC, Cardoso M. Prevalence, genetic characterization and antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella isolated from fresh pork sausages in Porto Alegre, Brazil. Food Control. 2009; 20:191–195.
Article17. Oblinger JL, Koburger JA. Understanding and teaching the most probable number technique. J Milk Food Technol. 1975; 38:540–545.18. Padungtod P, Kaneene JB. Salmonella in food animals and humans in northern Thailand. Int J Food Microbiol. 2006; 108:346–354.19. Patchanee P, Molla B, White N, Line DE, Gebreyes WA. Tracking Salmonella contamination in various watersheds and phenotypic and genotypic diversity. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2010; 7:1113–1120.
Article20. Patchanee P, Zessin KH, Staak C, Srikijkarn L, Taravijitkul P, Tesaprateep T. Pre-slaughther infection of Salmonella spp. and consideration of using the DANISH MIX-ELISA for monitoring Salmonella in pigs. Chiang Mai Vet J. 2003; 1:33–38.21. Prendergast DM, Duggan SJ, Gonzales-Barron U, Fanning S, Butler F, Cormican M, Duffy G. Prevalence, numbers and characteristics of Salmonella spp. on Irish retail pork. Int J Food Microbiol. 2009; 131:233–239.
Article22. Pulsrikarn C, Chaichana P, Pornruangwong S, Morita Y, Yamamoto S, Boonmar S. Serotype, antimicrobial susceptibility, and genotype of Salmonella isolates from swine and pork in Sa Kaew province, Thailand. Wetchasan Sattawaphaet. 2012; 42:21–27.23. Rostagno MH, Callaway TR. Pre-harvest risk factors for Salmonella enterica in pork production. Food Res Int. 2012; 45:634–640.24. Schwaiger K, Huther S, Hölzel C, Kämpf P, Bauer J. Prevalence of antibiotic-resistant enterobacteriaceae isolated from chicken and pork meat purchased at the slaughterhouse and at retail in Bavaria, Germany. Int J Food Microbiol. 2012; 154:206–211.
Article25. Stephens PJ, Joynson JA, Davies KW, Holbrook R, Lappin-Scott HM, Humphrey TJ. The use of an automated growth analyser to measure recovery times of single heat-injured Salmonella cells. J Appl Microbiol. 1997; 83:445–455.
Article26. Swanenburg M, van der Wolf PJ, Urlings HAP, Snijders JMA, van Knapen F. Salmonella in slaughter pigs: the effect of logistic slaughter procedures of pigs on the prevalence of Salmonella in pork. Int J Food Microbiol. 2001; 70:231–242.
Article27. Van Boxstael S, Dierick K, Van Huffel X, Uyttendaele M, Berkvens D, Herman L, Bertrand S, Wildemauwe C, Catry B, Butaye P, Imberechts H. Comparison of antimicrobial resistance patterns and phage types of Salmonella Typhimurium isolated from pigs, pork and humans in Belgium between 2001 and 2006. Food Res Int. 2012; 45:913–918.
Article28. Visscher CF, Klein G, Verspohl J, Beyerbach M, Stratmann-Selke J, Kamphues J. Serodiversity and serological as well as cultural distribution of Salmonella on farms and in abattoirs in Lower Saxony, Germany. Int J Food Microbiol. 2011; 146:44–51.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Serovars distribution and antimicrobial resistance patterns of Salmonella spp. isolated from the swine farms and slaughter houses
- Emergence of virulent pseudorabies virus infection in Northern China
- Prevalence of Specific Clone of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Clones in the Swine Population of Kyungpook Province During 1998 to 2000
- Occurrence and characterization of livestock-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in pig industries of northern Thailand
- Prevalence of Lawsonia intracellularis, Brachyspira hyodysenteriae and Salmonella in swine herds