Neurointervention.
2012 Feb;7(1):27-33. 10.5469/neuroint.2012.7.1.27.
Usefulness of Stent Implantation for Treatment of Intracranial Atherosclerotic Stenoses
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Hallym University Hangang Sacred Heart Hospital, Seoul, Korea. mddhhwang@naver.com
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Myungji St. Mary's Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Emergency, Shanghai Saint Luke's Hospital, Shanghai, China.
- 4Department of Radiology, Jiangsu province Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China.
- KMID: 1783996
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5469/neuroint.2012.7.1.27
Abstract
- PURPOSE
We evaluated the usefulness of intracranial stent implantation for treating patients with atherosclerotic stenosis and with recurrent, ischemic, neurological symptoms despite having undergone medical therapy.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Between March 2004 and April 2010, we attempted intracranial, stent-assisted angioplasty in 77 patients with 85 lesions (anterior circulation 73 cases, posterior circulation 12 cases) and who had ischemic neurological symptoms with more than 50% major cerebral artery stenosis. We analyzed the results regarding the technical success rate, complication rate, and restenosis rate during the mean 29.4 month follow-up period.
RESULTS
Intracranial stent implantation was successfully performed in 74 cases (87.1%). In nine cases among the 11, failed cases, stent implantation failure was due to the tortuosity of the target vessel. One patient experienced middle cerebral artery rupture during the procedure, and we embolized the vessel using a microcoil. Five patients developed cerebral infarction in three weeks after the procedure, three of whom improved using conservative management, although the other, two patients expired. The mean number of residual stenoses decreased from 72.3% to 14.7%. Three patients demonstrated significant in-stent restenosis, i.e. more than 50%, during the follow-up period.
CONCLUSION
As stent-assisted angioplasty in intracranial, atherosclerotic stenosis is effective and relatively safe, it can be considered as an alternative treatment for patients with recurrent, ischemic, neurologic symptoms despite having undergone medical therapy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
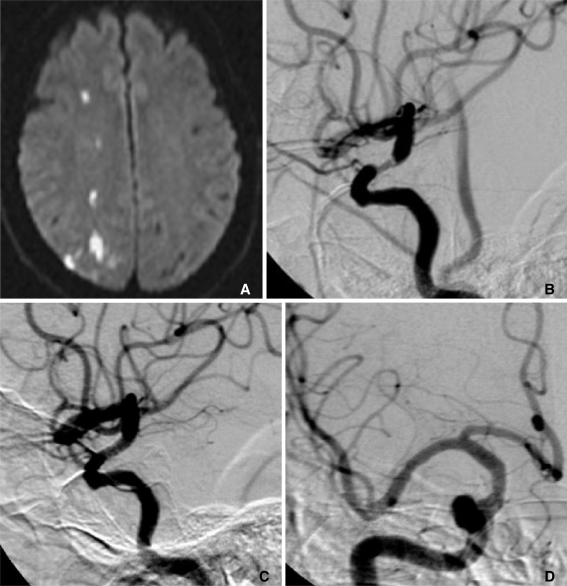
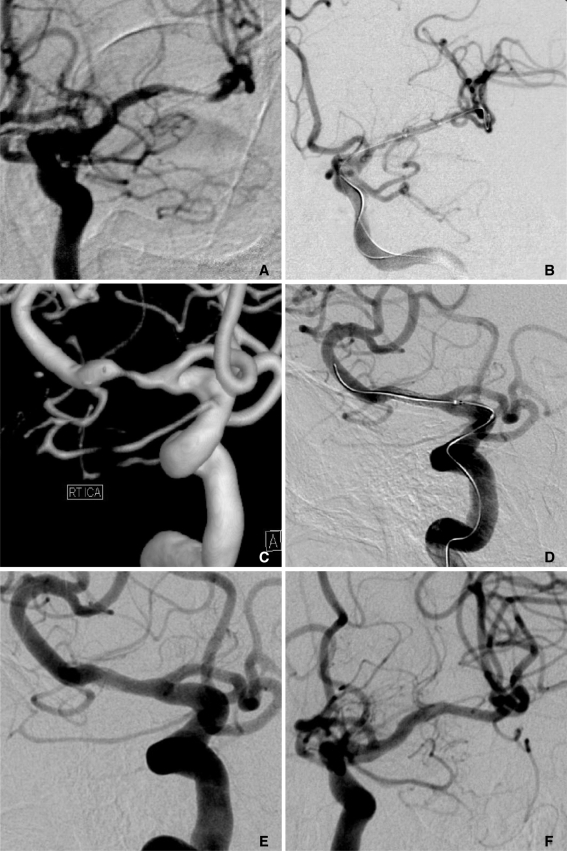
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Efficiency of Air Bubble Removal in Preparation of Low-Profile Angioplasty Balloon Catheter: Bench-Top Comparison of Six Methods
Joon-Ho Choi, Seon Moon Hwang, Deok Hee Lee
Neurointervention. 2019;14(1):27-34. doi: 10.5469/neuroint.2018.01074.
Reference
-
1. Kim JS. Stroke in Korea. International Congress Series, Proceedings of the 13th International Atherosclerosis Symphosium. 2004. 1262:p. 348–351.
Article2. Suh DC, Lee SH, Kim KR, Park ST, Lim SM, Kim SJ, et al. Pattern of atherosclerotic carotid stenosis in Korean patients with stroke: different involvement of intracranial versus extracranial vessels. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003; 24:239–244. PMID: 12591640.3. Lylyk P, Cohen JE, Ceratto R, Ferrario A, Miranda C. Angioplasty and stent placement in intracranial atherosclerotic stenoses and dissections. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2002; 23:430–436. PMID: 11901013.4. Chimowitz MI, Kokkinos J, Strong J, Brown MB, Levine SR, Silliman S, et al. The Warfarin-aspirin symptomatic intracranial disease study. Neurology. 1995; 45:1488–1493. PMID: 7644046.
Article5. Kim DJ, Lee BH, Kim DI, Shim WH, Jeon P, Lee TH. Stent assisted angioplasty of symptomatic intracranial vertebrobasilar artery stenosis: feasibility and follow up results. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005; 26:1381–1388. PMID: 15956503.6. Suh DC, Kim JK, Choi JW, Choi BS, Pyun HW, Choi YJ, et al. Intracranial stenting of severe symptomatic intracranial stenosis: results of 100 consecutive patients. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008; 29:781–785. PMID: 18310234.
Article7. Hähnel S, Ringleb P, Hartmann M. Treatment of intracranial stenoses using the Neuroform stent system: initial experience in five cases. Neuroradiology. 2006; 48:479–485. PMID: 16721557.
Article8. The EC/IC Bypass Study Group. Failure of extracranial-intracranial arterial bypass to reduce the risk of ischemic stroke. Results of an international randomized trial. N Engl J Med. 1985; 313:1191–1200. PMID: 2865674.9. Mazighi M, Tanasescu R, Ducrocq X, Vicaut E, Bracard S, Houdart E, et al. Prospective study of symptomatic atherothrombotic intracranial stenoses: the GESICA study. Neurology. 2006; 66:1187–1191. PMID: 16636236.
Article10. SSYLVIA Study Investigators. Stenting of symptomatic atherosclerotic lesions in the vertebral or intracranial arteries (SSYLVIA): study results. Stroke. 2004; 35(6):1388–1392. PMID: 15105508.11. Groschel K, Schnaudigel S, Pilgram SM, Wasser K, Kastrup A. A systematic review on outcome after stenting for intracranial atherosclerosis. Stroke. 2009; 40:e340–e347. PMID: 19182081.
Article12. Qureshi AI, Saad M, Zaidat OO, Suarez JI, Alexander MJ, Suri FK, et al. Intracerebral hemorrhages associated with neurointerventional procedures using a combination of antithrombotic agents including abciximab. Stroke. 2002; 33:1916–1919. PMID: 12105375.
Article13. Choi HW, Koo YB, Lee TH, Kim HJ, Lee JW, Kim CW, et al. New techniques for intracranial stent navigation in patients with tortuous arteries. J Korean Radiol Soc. 2005; 52:101–106.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intracranial Stent Implantation for Drug Resistant Atherosclerotic Stenosis: Results of 52 Cases
- Long-term outcomes of drug-eluting stent implantation in patients with symptomatic extra- and intracranial atherosclerotic stenoses
- The WingSpan Stent System for the Treatment of Intracranial Atherosclerotic Stenoses: A Single Center Experience
- Bench-Top Comparison of Three Different Types of Stents Used for Treatment of Intracranial Atherosclerotic Stenosis
- Angiographic Distribution of the Seve re Stenosis in Korean Patients with Atherosclerotic Cerebral Vascular Disease