Korean J Radiol.
2011 Aug;12(4):463-472. 10.3348/kjr.2011.12.4.463.
Assessment of Cortical Visual Impairment in Infants with Periventricular Leukomalacia: a Pilot Event-Related fMRI Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang 110004, China. guoqy@sj-hospital.org
- 2Department of Radiology, The First Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang 110001, China.
- 3Training Department of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Greater China Region of Philips, Shanghai 200233, China.
- KMID: 1783213
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2011.12.4.463
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
We wanted to investigate the usefulness of event-related (ER) functional MRI (fMRI) for the assessment of cortical visual impairment in infants with periventricular leukomalacia (PVL).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
FMRI data were collected from 24 infants who suffered from PVL and from 12 age-matched normal controls. Slow ER fMRI was performed using a 3.0T MR scanner while visual stimuli were being presented. Data analysis was performed using Statistical Parametric Mapping software (SPM2), the SPM toolbox MarsBar was used to analyze the region of interest data, and the time to peak (TTP) of hemodynamic response functions (HRFs) was estimated for the surviving voxels. The number of activated voxels and the TTP values of HRFs were compared. Pearson correlation analysis was performed to compare visual impairment evaluated by using Teller Acuity Cards (TAC) with the number of activated voxels in the occipital lobes in all patients.
RESULTS
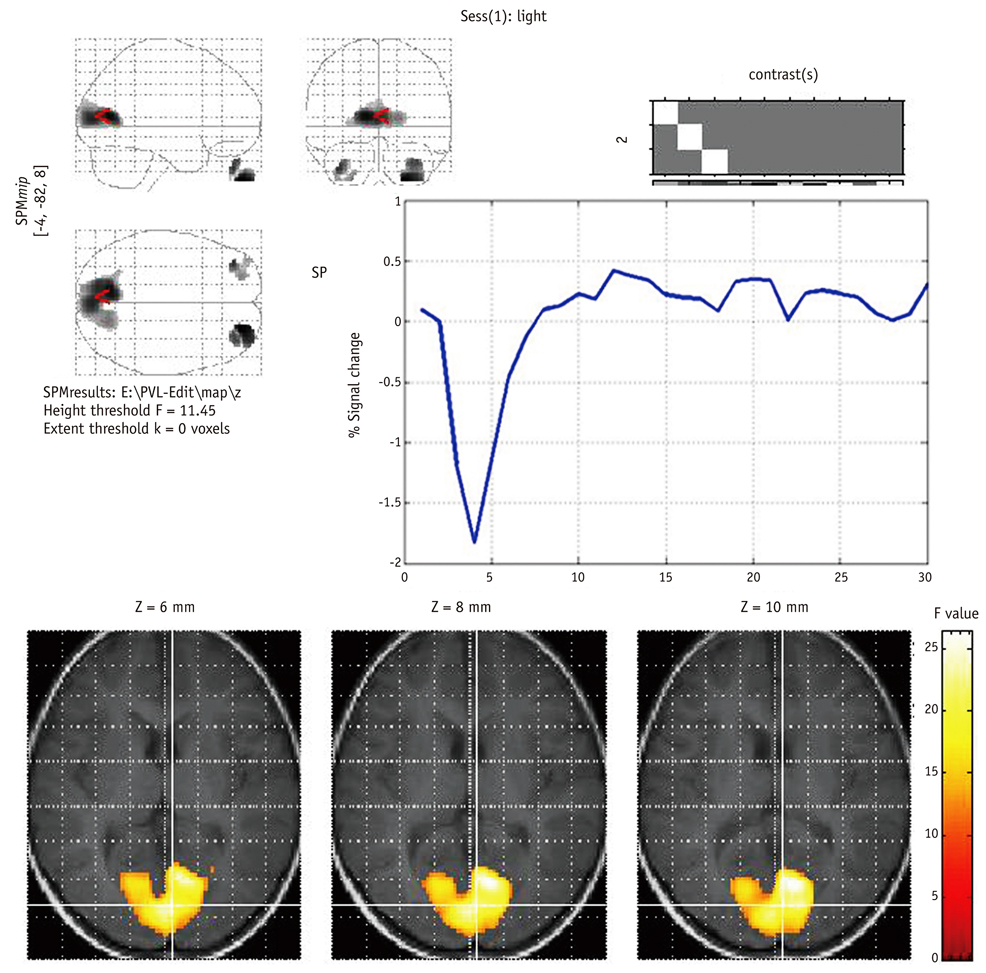
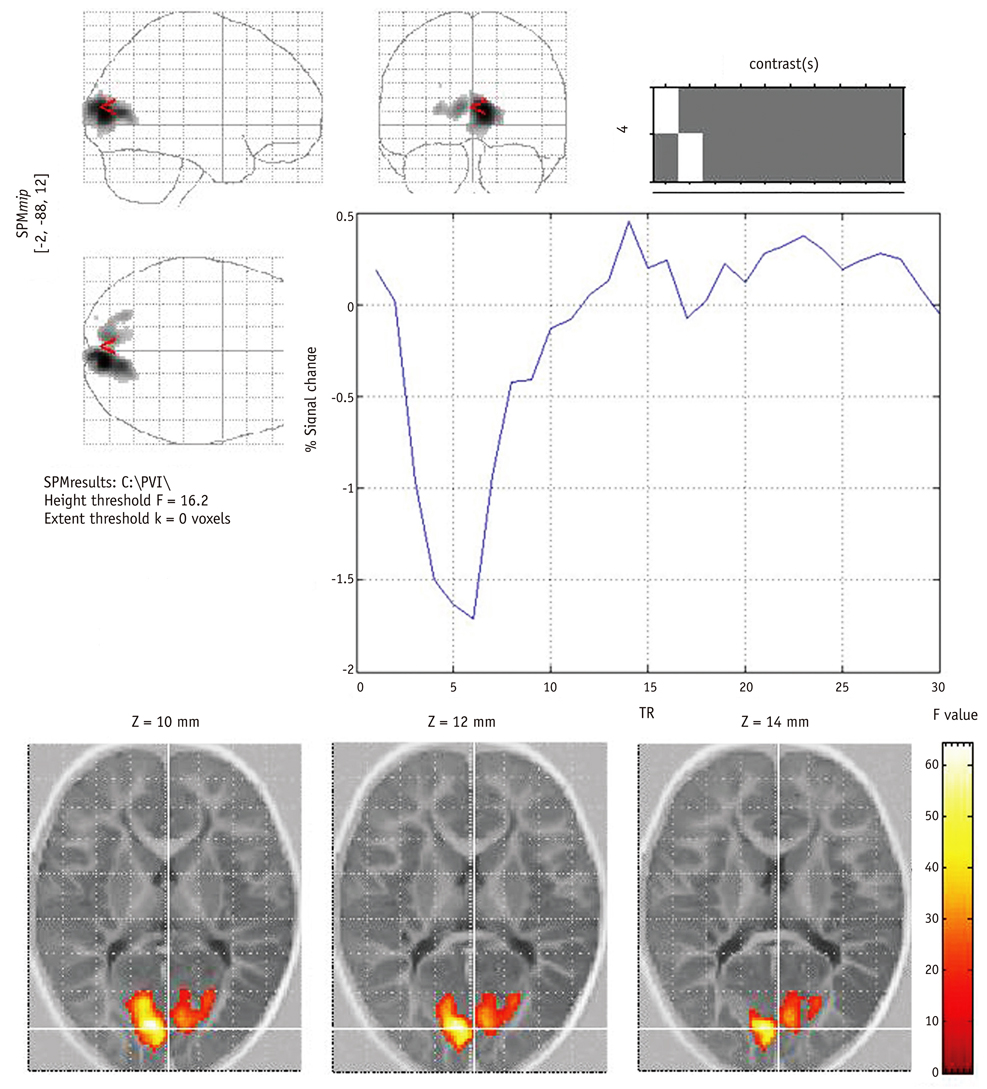
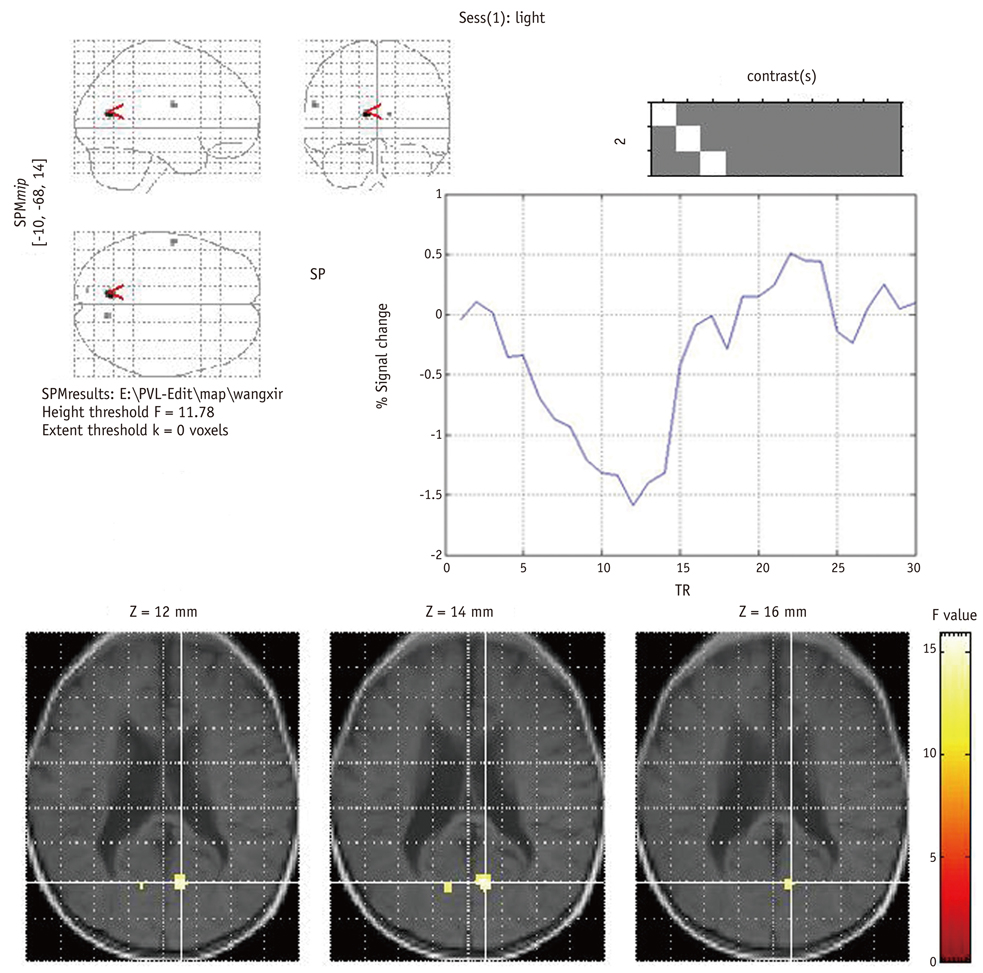
In all 12 control infants, the blood oxygenation level-dependent (BOLD) signal was negative and the maximum response was located in the anterior and superior part of the calcarine fissure, and this might correspond to the anterior region of the primary visual cortex (PVC). In contrast, for the 24 cases of PVL, there were no activated pixels in the PVC in four subjects, small and weak activations in six subjects, deviated activations in seven subjects and both small and deviated activations in three subjects. The number of active voxels in the occipital lobe was significantly correlated with the TAC-evaluated visual impairment (p < 0.001). The mean TTP of the HRFs was significantly delayed in the cases of PVL as compared with that of the normal controls.
CONCLUSION
Determining the characteristics of both the BOLD response and the ER fMRI activation may play an important role in the cortical visual assessment of infants with PVL.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. van den Hout BM, de Vries LS, Meiners LC, Stiers P, van der Schouw YT, Jennekens-Schinkel A, et al. Visual perceptual impairment in children at 5 years of age with perinatal haemorrhagic or ischaemic brain damage in relation to cerebral magnetic resonance imaging. Brain Dev. 2004. 26:251–261.2. Fan GG, Yu B, Quan SM, Sun BH, Guo QY. Potential of diffusion tensor MRI in the assessment of periventricular leukomalacia. Clin Radiol. 2006. 61:358–364.3. Mercuri E, Atkinson J, Braddick O, Anker S, Cowan F, Rutherford M, et al. Basal ganglia damage and impaired visual function in the newborn infant. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 1997. 77:F111–F114.4. Curnyn KM, Kaufman LM. The eye examination in the pediatrician's office. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2003. 50:25–40.5. Braddick O, Atkinson J, Hood B, Harkness W, Jackson G, Vargha-Khadem F. Possible blindsight in infants lacking one cerebral hemisphere. Nature. 1992. 360:461–463.6. Kim GW, Jeong GW, Kim TH, Baek HS, Oh SK, Kang HK, et al. Functional neuroanatomy associated with natural and urban scenic views in the human brain: 3.0T functional MR imaging. Korean J Radiol. 2010. 11:507–513.7. Sie LTL, Rombouts SA, Valk IJ, Hart AA, Scheltens P, van der Knaap MS. Functional MRI of visual cortex in sedated 18 month-old infants with or without periventricular leukomalacia. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2001. 43:486–490.8. Dale AM, Buckner RL. Selective averaging of rapidly presented individual trials using fMRI. Hum Brain Mapp. 1997. 5:329–340.9. Bandettini PA, Cox RW. Event-related fMRI contrast when using constant interstimulus interval: theory and experiment. Magn Reson Med. 2000. 43:540–548.10. Flodmark O, Lupton B, Li D, Stimac GK, Roland EH, Hill A, et al. MR imaging of periventricular leukomalacia in childhood. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1989. 152:583–590.11. Altman NR, Bernal B. Brain activation in sedated children: auditory and visual functional MR imaging. Radiology. 2001. 221:56–63.12. Pike AA, Marlow N, Reber C. Maturation of the flash visual evoked potential in preterm infants. Early Hum Dev. 1999. 54:215–222.13. Morita T, Kochiyama T, Yamada H, Konishi Y, Yonekura Y, Matsumura M, et al. Difference in the metabolic response to photic stimulation of the lateral geniculate nucleus and the primary visual cortex of infants: a fMRI study. Neurosci Res. 2000. 38:63–70.14. Martin E, Joeri P, Loenneker T, Ekatodramis D, Vitacco D, Hennig J, et al. Visual processing in infants and children studied using functional MRI. Pediatr Res. 1999. 46:135–140.15. Anderson AW, Marois R, Colson ER, Peterson BS, Duncan CC, Ehrenkranz RA, et al. Neonatal auditory activation detected by functional magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Imaging. 2001. 19:1–5.16. Porro G, Wittebol-Post D, Van Nieuwenhuizen O, Schenk Rootlieb AJ, Treffers WF. Longitudinal follow-up of grating acuity in children affected by cerebral palsy: results of a 5 year study. Eye (Lond). 1998. 12(Pt 5):858–862.17. Rombouts SA, Goekoop R, Stam CJ, Barkhof F, Scheltens P. Delayed rather than decreased BOLD response as a marker for early Alzheimer's disease. Neuroimage. 2005. 26:1078–1085.18. Handwerker DA, Ollinger JM, D'Esposito M. Variation of BOLD hemodynamic responses across subjects and brain regions and their effects on statistical analyses. Neuroimage. 2004. 21:1639–1651.19. Sydekum E, Baltes C, Ghosh A, Mueggler T, Schwab ME, Rudin M. Functional reorganization in rat somatosensory cortex assessed by fMRI: elastic image registration based on structural landmarks in fMRI images and application to spinal cord injured rats. Neuroimage. 2009. 44:1345–1354.20. Seghier ML, Lazeyras F, Zimine S, Maier SE, Hanquinet S, Delavelle J, et al. Combination of event-related fMRI and diffusion tensor imaging in an infant with perinatal stroke. Neuroimage. 2004. 21:463–472.21. Kim EY, Park HJ, Kim DH, Lee SK, Kim J. Measuring fractional anisotropy of the corpus callosum using diffusion tensor imaging: mid-sagittal versus axial imaging planes. Korean J Radiol. 2008. 9:391–395.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case Of Periventricular Leukomalacia Related To Chorioamnionitis
- A Case of Schizophrenia with Periventricular Leukomalacia on Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy in Premature Infants: Update on Periventricular Leukomalacia
- Ocular Findings in Children with Cortical Visual Impairment
- Prenatal diagnosis of cystic periventricular leukomalacia in a full term fetus