Korean J Radiol.
2011 Aug;12(4):403-415. 10.3348/kjr.2011.12.4.403.
Consensus Report of the 4th International Forum for Gadolinium-Ethoxybenzyl-Diethylenetriamine Pentaacetic Acid Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 110-744, Korea. jmsh@snu.ac.kr
- 2Institute of Clinical Radiology, University Hospitals Munich, Munchen 81377, Germany.
- 3Department of Digestive Diseases and Internal Medicine, St. Orsola-Malpighi University Hospital, Bologna 40128, Italy.
- 4Division of Surgery, Karolinska Institute Danderyds Sjukhus, Stockholm 18288, Sweden.
- 5Department of Radiology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul 120-752, Korea.
- 6Department of Radiology, Kanazawa University, Graduate School of Medical Science, Ishikawa 920-8641, Japan.
- 7Department of Radiology and Head of MRI, Duke University, Durham, NC 27710, USA.
- 8Department of Pathology Graduate School of Medicine, Keio University School of Medicine, Tokyo 160-8582, Japan.
- KMID: 1783206
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2011.12.4.403
Abstract
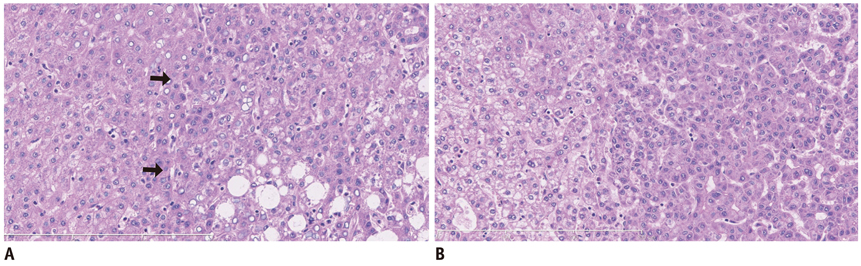
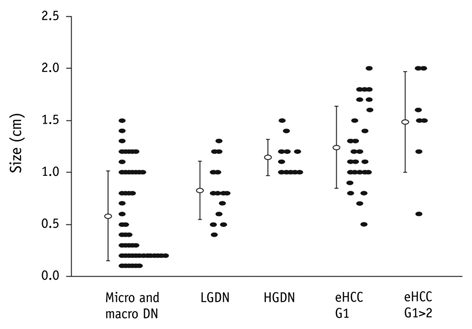
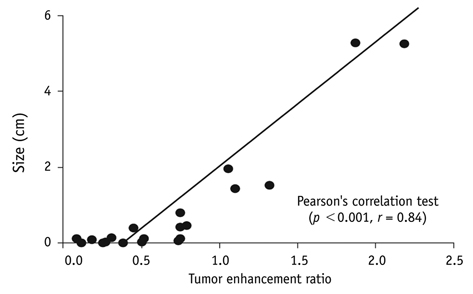
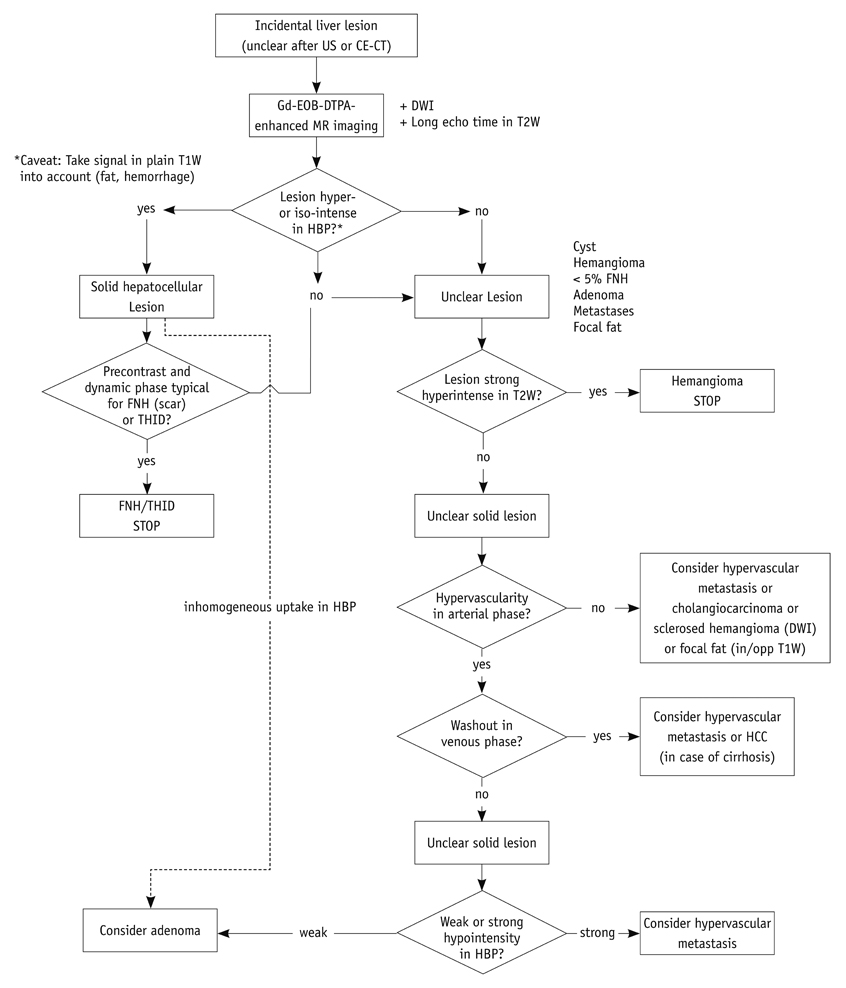
- This paper reports on issues relating to the optimal use of gadolinium-ethoxybenzyl-diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid magnetic resonance imaging (Gd-EOB-DTPA MR imaging) together with the generation of consensus statements from a working group meeting, which was held in Seoul, Korea (2010). Gd-EOB-DTPA has been shown to improve the detection and characterization of liver lesions, and the information provided by the hepatobiliary phase is proving particularly useful in differential diagnoses and in the characterization of small lesions (around 1-1.5 cm). Discussion also focused on advances in the role of organic anion-transporting polypeptide 8 (OATP8) transporters. Gd-EOB-DTPA is also emerging as a promising tool for functional analysis, enabling the calculation of post-surgical liver function in the remaining segments. Updates to current algorithms were also discussed.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Algorithms
Contrast Media/*diagnostic use/metabolism
Diagnosis, Differential
Gadolinium DTPA/*diagnostic use/metabolism
Humans
Liver Diseases/*diagnosis/metabolism/surgery
Liver Function Tests
*Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Organic Anion Transporters, Sodium-Independent/metabolism
Postoperative Complications/diagnosis
Practice Guidelines as Topic
Figure
Reference
-
1. Liver Cancer Incidence and Mortality Worldwide in 2008 Summary. 2010. Last accessed December 13. Available at: http://globocan.iarc.fr/factsheets/cancers/liver.asp.2. Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005. 55:74–108.3. Reimer P, Schneider G, Schima W. Hepatobiliary contrast agents for contrast-enhanced MRI of the liver: properties, clinical development and applications. Eur Radiol. 2004. 14:559–578.4. Rohrer M, Bauer H, Mintorovitch J, Requardt M, Weinmann HJ. Comparison of magnetic properties of MRI contrast media solutions at different magnetic field strengths. Invest Radiol. 2005. 40:715–724.5. Shuter B, Tofts PS, Wang SC, Pope JM. The relaxivity of Gd-EOB-DTPA and Gd-DTPA in liver and kidney of the Wistar rat. Magn Reson Imaging. 1996. 14:243–253.6. Vander Elst L, Maton F, Laurent S, Seghi F, Chapelle F, Muller RN. A multinuclear MR study of Gd-EOB-DTPA: comprehensive preclinical characterization of an organ specific MRI contrast agent. Magn Reson Med. 1997. 38:604–614.7. Kitao A, Zen Y, Matsui O, Gabata T, Kobayashi S, Koda W, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma: signal intensity at gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR Imaging--correlation with molecular transporters and histopathologic features. Radiology. 2010. 256:817–826.8. Narita M, Hatano E, Arizono S, Miyagawa-Hayashino A, Isoda H, Kitamura K, et al. Expression of OATP1B3 determines uptake of Gd-EOB-DTPA in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol. 2009. 44:793–798.9. Bartolozzi C, Crocetti L, Lencioni R, Cioni D, Della Pina C, Campani D. Biliary and reticuloendothelial impairment in hepatocarcinogenesis: the diagnostic role of tissue-specific MR contrast media. Eur Radiol. 2007. 17:2519–2530.10. International Consensus Group for Hepatocellular Neoplasia. Pathologic diagnosis of early hepatocellular carcinoma: a report of the international consensus group for hepatocellular neoplasia. Hepatology. 2009. 49:658–664.11. Kojiro M, Nakashima O. Histopathologic evaluation of hepatocellular carcinoma with special reference to small early stage tumors. Semin Liver Dis. 1999. 19:287–296.12. Takayama T, Makuuchi M, Hirohashi S, Sakamoto M, Yamamoto J, Shimada K, et al. Early hepatocellular carcinoma as an entity with a high rate of surgical cure. Hepatology. 1998. 28:1241–1246.13. Sakamoto M, Effendi K, Masugi Y. Molecular diagnosis of multistage hepatocarcinogenesis. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2010. 40:891–896.14. Oikawa T, Ojima H, Yamasaki S, Takayama T, Hirohashi S, Sakamoto M. Multistep and multicentric development of hepatocellular carcinoma: histological analysis of 980 resected nodules. J Hepatol. 2005. 42:225–229.15. Sakamoto M, Hirohashi S, Shimosato Y. Early stages of multistep hepatocarcinogenesis: adenomatous hyperplasia and early hepatocellular carcinoma. Hum Pathol. 1991. 22:172–178.16. Sakamoto M, Hirohashi S. Natural history and prognosis of adenomatous hyperplasia and early hepatocellular carcinoma: multi-institutional analysis of 53 nodules followed up for more than 6 months and 141 patients with single early hepatocellular carcinoma treated by surgical resection or percutaneous ethanol injection. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 1998. 28:604–608.17. Kudo M. The 2008 Okuda lecture: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: from surveillance to molecular targeted therapy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010. 25:439–452.18. Kim RB. Organic anion-transporting polypeptide (OATP) transporter family and drug disposition. Eur J Clin Invest. 2003. 33:Suppl 2. 1–5.19. Konig J, Cui Y, Nies AT, Keppler D. Localization and genomic organization of a new hepatocellular organic anion transporting polypeptide. J Biol Chem. 2000. 275:23161–23168.20. Vavricka SR, Jung D, Fried M, Grutzner U, Meier PJ, Kullak-Ublick GA. The human organic anion transporting polypeptide 8 (SLCO1B3) gene is transcriptionally repressed by hepatocyte nuclear factor 3beta in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2004. 40:212–218.21. Tsuda N, Matsui O. Cirrhotic rat liver: reference to transporter activity and morphologic changes in bile canaliculi--gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology. 2010. 256:767–773.22. Sangiovanni A, Manini MA, Iavarone M, Romeo R, Forzenigo LV, Fraquelli M, et al. The diagnostic and economic impact of contrast imaging techniques in the diagnosis of small hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis. Gut. 2010. 59:638–644.23. Bruix J, Sherman M. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2005. 42:1208–1236.24. Bruix J, Sherman M. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: an update. Hepatology. 2011. 53:1020–1022.25. Clinical Practice Guidelines for Hepatocellular Carcinoma - The Japan Society of Hepatology 2009 update. Hepatol Res. 2010. 40:Suppl 1. 2–144.26. El-Serag HB, Marrero JA, Rudolph L, Reddy KR. Diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2008. 134:1752–1763.27. Lee JM, Kim SJ, Kim SH, Kim KW, Lee JY, Han JK, et al. Enhancement patterns of hepatocellular carcinoma on gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR imaging in the cirrhotic liver: comparison with multiphasic liver CT. In : RSNA 2009; Abstract no. SSA07-07.28. Ahn SS, Kim MJ, Lim JS, Hong HS, Chung YE, Choi JY. Added value of gadoxetic acid-enhanced hepatobiliary phase MR imaging in the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiology. 2010. 255:459–466.29. Di Martino M, Marin D, Guerrisi A, Baski M, Galati F, Rossi M, et al. Intraindividual comparison of gadoxetate disodium-enhanced MR imaging and 64-section multidetector CT in the Detection of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis. Radiology. 2010. 256:806–816.30. Ichikawa T, Saito K, Yoshioka N, Tanimoto A, Gokan T, Takehara Y, et al. Detection and characterization of focal liver lesions: a Japanese phase III, multicenter comparison between gadoxetic acid disodium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging and contrast-enhanced computed tomography predominantly in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and chronic liver disease. Invest Radiol. 2010. 45:133–141.31. Marin D, Di Martino M, Guerrisi A, De Filippis G, Rossi M, Ginanni Corradini S, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis: qualitative comparison of gadobenate dimeglumine-enhanced MR imaging and multiphasic 64-section CT. Radiology. 2009. 251:85–95.32. Sun HY, Lee JM, Shin CI, Lee DH, Moon SK, Kim KW, et al. Gadoxetic acid-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for differentiating small hepatocellular carcinomas (< or = 2 cm in diameter) from arterial enhancing pseudolesions: special emphasis on hepatobiliary phase imaging. Invest Radiol. 2010. 45:96–103.33. Motosugi U, Ichikawa T, Sou H, Sano K, Tominaga L, Muhi A, et al. Distinguishing hypervascular pseudolesions of the liver from hypervascular hepatocellular carcinomas with gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology. 2010. 256:151–158.34. Tajima T, Honda H, Taguchi K, Asayama Y, Kuroiwa T, Yoshimitsu K, et al. Sequential hemodynamic change in hepatocellular carcinoma and dysplastic nodules: CT angiography and pathologic correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002. 178:885–897.35. Kogita S, Imai Y, Okada M, Kim T, Onishi H, Takamura M, et al. Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced magnetic resonance images of hepatocellular carcinoma: correlation with histological grading and portal blood flow. Eur Radiol. 2010. 20:2405–2413.36. Boutros C, Katz SC, Espat NJ. Management of an incidental liver mass. Surg Clin North Am. 2010. 90:699–718.37. Marin D, Furlan A, Federle MP, Midiri M, Brancatelli G. Imaging approach for evaluation of focal liver lesions. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009. 7:624–634.38. Chamberlain RS, Jarnagin WR, DeCorato D. Steele GD, Phillips TL, Chabner BA, editors. Incidentally discovered hepatic lesions. Hepatobiliary Cancer. 2001. Hamilton, London: American Cancer Society Atlas of Clinical Oncology;31–42.39. Zech CJ, Grazioli L, Jonas E, Ekman M, Niebecker R, Gschwend S, et al. Health-economic evaluation of three imaging strategies in patients with suspected colorectal liver metastases: Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI vs. extracellular contrast media-enhanced MRI and 3-phase MDCT in Germany, Italy and Sweden. Eur Radiol. 2009. 19:Suppl 3. S753–S763.40. Assy N, Nasser G, Djibre A, Beniashvili Z, Elias S, Zidan J. Characteristics of common solid liver lesions and recommendations for diagnostic workup. World J Gastroenterol. 2009. 15:3217–3227.41. Soussan M, Aube C, Bahrami S, Boursier J, Valla DC, Vilgrain V. Incidental focal solid liver lesions: diagnostic performance of contrast-enhanced ultrasound and MR imaging. Eur Radiol. 2010. 20:1715–1725.42. Little JM, Richardson A, Tait N. Hepatic dystychoma: a five year experience. HPB Surg. 1991. 4:291–297.43. Zech CJ, Grazioli L, Breuer J, Reiser MF, Schoenberg SO. Diagnostic performance and description of morphological features of focal nodular hyperplasia in Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced liver magnetic resonance imaging: results of a multicenter trial. Invest Radiol. 2008. 43:504–511.44. Kamaya A, Maturen KE, Tye GA, Liu YI, Parti NN, Desser TS. Hypervascular liver lesions. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 2009. 30:387–407.45. Allaire GS, Rabin L, Ishak KG, Sesterhenn IA. Bile duct adenoma. A study of 152 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1988. 12:708–715.46. Bhathal PS, Hughes NR, Goodman ZD. The so-called bile duct adenoma is a peribiliary gland hamartoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 1996. 20:858–864.47. Tajima T, Honda H, Kuroiwa T, Yoshimitsu K, Irie H, Aibe H, et al. Radiologic features of intrahepatic bile duct adenoma: a look at the surface of the liver. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1999. 23:690–695.48. Lordan JT, Karanjia ND, Quiney N, Fawcett WJ, Worthington TR. A 10-year study of outcome following hepatic resection for colorectal liver metastases - The effect of evaluation in a multidisciplinary team setting. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2009. 35:302–306.49. Pawlik TM, Choti MA. Surgical therapy for colorectal metastases to the liver. J Gastrointest Surg. 2007. 11:1057–1077.50. Nordlinger B, Van Cutsem E, Rougier P, Kohne CH, Ychou M, Sobrero A, et al. Does chemotherapy prior to liver resection increase the potential for cure in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer? A report from the European Colorectal Metastases Treatment Group. Eur J Cancer. 2007. 43:2037–2045.51. Ahmad A, Chen SL, Bilchik AJ. Role of repeated hepatectomy in the multimodal treatment of hepatic colorectal metastases. Arch Surg. 2007. 142:526–531. discussion 531-522.52. Kornprat P, Jarnagin WR, Gonen M, DeMatteo RP, Fong Y, Blumgart LH, et al. Outcome after hepatectomy for multiple (four or more) colorectal metastases in the era of effective chemotherapy. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007. 14:1151–1160.53. Kinkel K, Lu Y, Both M, Warren RS, Thoeni RF. Detection of hepatic metastases from cancers of the gastrointestinal tract by using noninvasive imaging methods (US, CT, MR imaging, PET): a meta-analysis. Radiology. 2002. 224:748–756.54. Bipat S, van Leeuwen MS, Comans EF, Pijl ME, Bossuyt PM, Zwinderman AH, et al. Colorectal liver metastases: CT, MR imaging, and PET for diagnosis--meta-analysis. Radiology. 2005. 237:123–131.55. Marcos A, Ham JM, Fisher RA, Olzinski AT, Posner MP. Surgical management of anatomical variations of the right lobe in living donor liver transplantation. Ann Surg. 2000. 231:824–831.56. Catalano OA, Singh AH, Uppot RN, Hahn PF, Ferrone CR, Sahani DV. Vascular and biliary variants in the liver: implications for liver surgery. Radiographics. 2008. 28:359–378.57. Kawarada Y, Das BC, Taoka H. Anatomy of the hepatic hilar area: the plate system. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2000. 7:580–586.58. Uchida K, Taniguchi M, Shimamura T, Suzuki T, Yamashita K, Ota M, et al. Three-dimensional computed tomography scan analysis of hepatic vasculatures in the donor liver for living donor liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2010. 16:1062–1068.59. Scatton O, Plasse M, Dondero F, Vilgrain V, Sauvanet A, Belghiti J. Impact of localized congestion related to venous deprivation after hepatectomy. Surgery. 2008. 143:483–489.60. Radtke A, Sotiropoulos GC, Sgourakis G, Molmenti EP, Schroeder T, Saner FH, et al. Hepatic venous drainage: how much can we learn from imaging studies? Anatomic-functional classification derived from three-dimensional computed tomography reconstructions. Transplantation. 2010. 89:1518–1525.61. Belghiti J, Hiramatsu K, Benoist S, Massault P, Sauvanet A, Farges O. Seven hundred forty-seven hepatectomies in the 1990s: an update to evaluate the actual risk of liver resection. J Am Coll Surg. 2000. 191:38–46.62. Jarnagin WR, Gonen M, Fong Y, DeMatteo RP, Ben-Porat L, Little S, et al. Improvement in perioperative outcome after hepatic resection: analysis of 1,803 consecutive cases over the past decade. Ann Surg. 2002. 236:397–406. discussion 406-407.63. Clavien PA, Oberkofler CE, Raptis DA, Lehmann K, Rickenbacher A, El-Badry AM. What is critical for liver surgery and partial liver transplantation: size or quality? Hepatology. 2010. 52:715–729.64. Fotbolcu H, Yakar T, Duman D, Karaahmet T, Tigen K, Cevik C, et al. Impairment of the left ventricular systolic and diastolic function in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Cardiol J. 2010. 17:457–463.65. Gazzaniga GM, Cappato S, Belli FE, Bagarolo C, Filauro M. Assessment of hepatic reserve for the indication of hepatic resection: how I do it. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2005. 12:27–30.66. Morris-Stiff G, Gomez D, Prasad R. Quantitative assessment of hepatic function and its relevance to the liver surgeon. J Gastrointest Surg. 2009. 13:374–385.67. Jonas E, Hultcrantz R, Slezak P, Blomqvist L, Schnell PO, Jacobsson H. Dynamic 99Tcm-HIDA SPET: non-invasive measuring of intrahepatic bile flow. Description of the method and a study in primary sclerosing cholangitis. Nucl Med Commun. 2001. 22:127–134.68. Harbin WP, Robert NJ, Ferrucci JT Jr. Diagnosis of cirrhosis based on regional changes in hepatic morphology: a radiological and pathological analysis. Radiology. 1980. 135:273–283.69. Garcia JE, Atkins F. A low right-to-left hepatic lobe ratio. Is streamlining of ethanol to the right lobe of the liver the cause? Clin Nucl Med. 1985. 10:807–809.70. Merriman RB, Ferrell LD, Patti MG, Weston SR, Pabst MS, Aouizerat BE, et al. Correlation of paired liver biopsies in morbidly obese patients with suspected nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2006. 44:874–880.71. Nilsson H, Nordell A, Vargas R, Douglas L, Jonas E, Blomqvist L. Assessment of hepatic extraction fraction and input relative blood flow using dynamic hepatocyte-specific contrast-enhanced MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2009. 29:1323–1331.72. Jacobsson H, Jonas E, Hellstrom PM, Larsson SA. Different concentrations of various radiopharmaceuticals in the two main liver lobes: a preliminary study in clinical patients. J Gastroenterol. 2005. 40:733–738.73. Nilsson H, Blomqvist L, Douglas L, Nordell A, Jonas E. Assessment of liver function in primary biliary cirrhosis using Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced liver MRI. HPB (Oxford). 2010. 12:567–576.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case Report of Localized Hepatic Sinusoidal Dilatation: The Diagnostic Usefulness of the Hepatobiliary Phase of Gd-EOB-DTPA-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- Enhancement Pattern of Liver Parenchyma during Late Dynamic Phase Imaging: Comparison between Gd-EOB-DTPA and Gd-DTPA-BMA
- Chronic Progressive Radiation Myelopathy Associated with Radiation Therapy: A case report
- The Proper Scan Delay of the Hepatobiliary Phase of Gadoxetic Acid-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Evaluate Small-Sized (< or = 3 cm) Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Cirrhotic Liver
- Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Gadoxetic Acid-Enhanced MRI: 2016 Consensus Recommendations of the Korean Society of Abdominal Radiology