Korean J Radiol.
2010 Apr;11(2):222-230. 10.3348/kjr.2010.11.2.222.
Multislice CT Virtual Intravascular Endoscopy for Assessing Pulmonary Embolisms: a Pictorial Review
- Affiliations
-
- 1Discipline of Medical Imaging, Department of Imaging and Applied Physics, Curtin University of Technology, Perth, Western Australia, Australia. z.sun@curtin.edu.au
- 2Department of Radiology, Kind Saud Hospital, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
- 3Department of Radiology, Military Hospital, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
- KMID: 1783199
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2010.11.2.222
Abstract
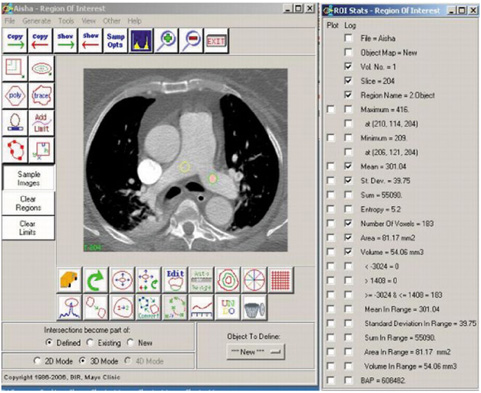
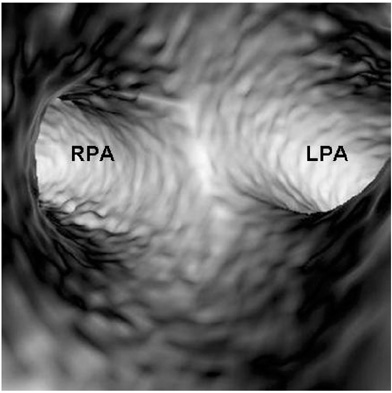
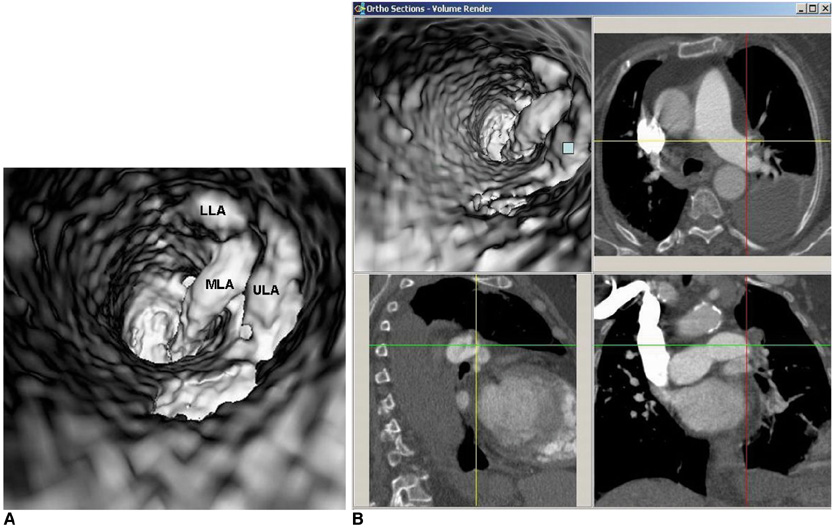
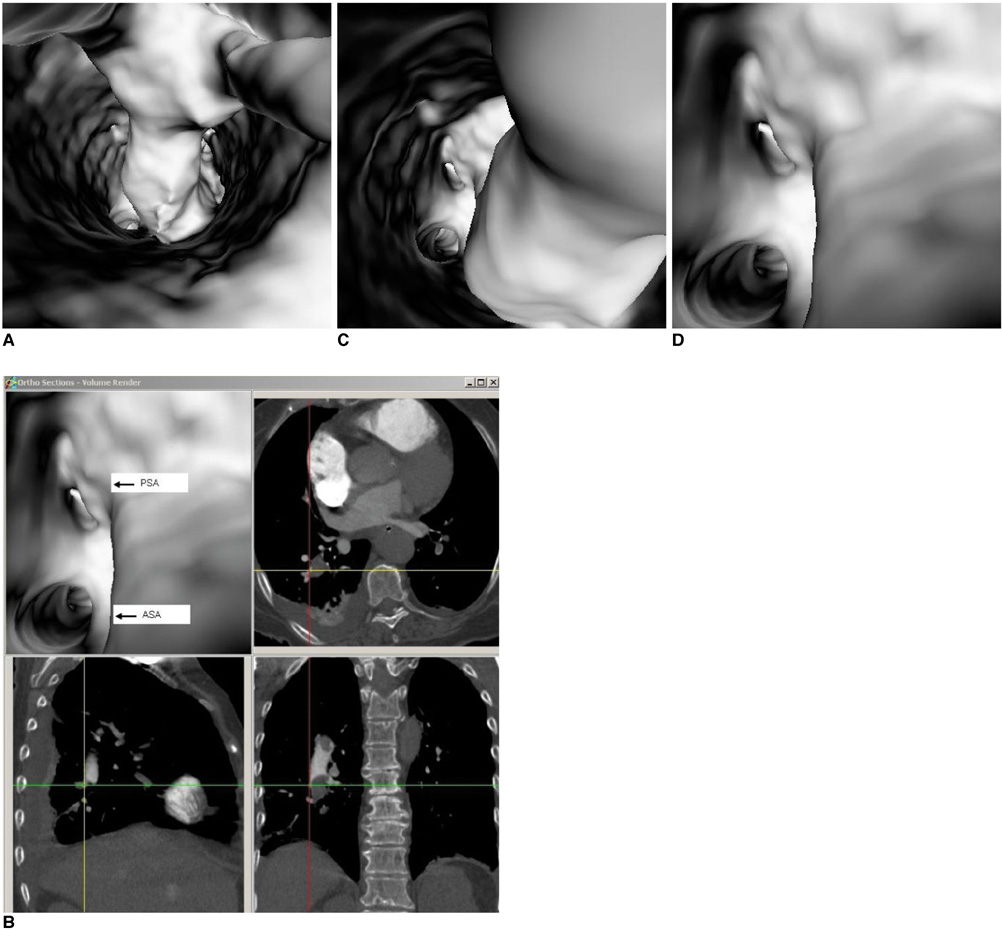
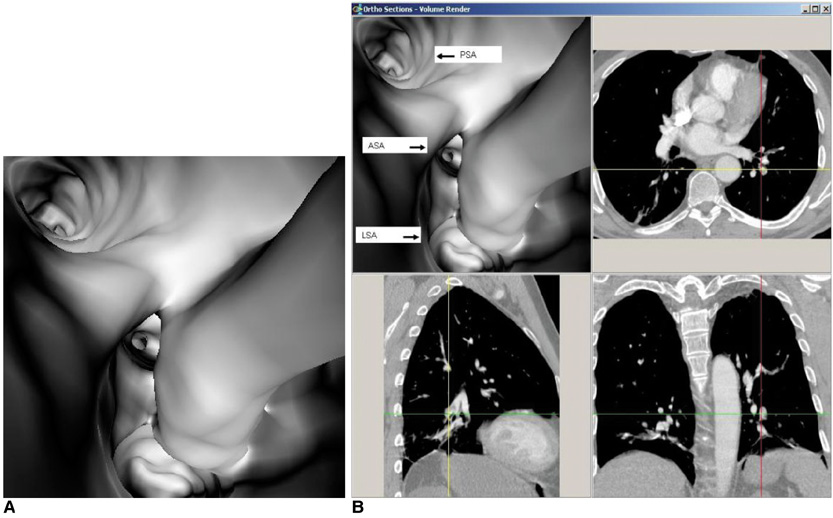
- Multislice CT has been widely used in clinical practice for diagnosing cardiovascular disease due to its reduced invasiveness and its high spatial and temporal resolution. As a reliable alternative to conventional pulmonary angiography, multislice CT angiography has been recognized as the first line technique for detecting and diagnosing pulmonary embolism. A pulmonary embolism located in the main pulmonary artery, as well as being located in the segmental branches, can be accurately detected with multislice CT imaging, and especially with the use of 16- and 64-slice CT scanners. Visualization of pulmonary embolisms has traditionally been limited to 2D, multiplanar reformation and the 3D external surface visualizations. In this pictorial review, we present our experience of using 3D virtual intravascular endoscopy to characterize and evaluate the intraluminal appearance of pulmonary embolisms in a group of patients who were suspected of having pulmonary embolism and who were undergoing multislice CT angiography. We expect that the research findings from this study will provide insight into the extent of disease and the luminal changes to the pulmonary arteries that are due to the presence of thrombus, and so monitoring of the progress of disease and predicting the treatment outcome can well be achieved.
MeSH Terms
-
Adolescent
Adult
Aged
Aged, 80 and over
Contrast Media/diagnostic use
Endoscopy/*methods
Female
Humans
Imaging, Three-Dimensional/methods
Iohexol/diagnostic use
Male
Middle Aged
Pulmonary Artery/radiography
Pulmonary Embolism/*radiography
Radiographic Image Enhancement/methods
Radiographic Image Interpretation, Computer-Assisted/*methods
Tomography, X-Ray Computed/*methods
User-Computer Interface
Young Adult
Figure
Reference
-
1. Stein PD, Athanasoulis C, Alavi A, Greenspan RH, Hales CA, Saltzman HA, et al. Complications and validity of pulmonary angiography in acute pulmonary embolism. Circulation. 1992. 85:462–468.2. Mills SR, Jackson DC, Older RA, Heaston DK, Moore AV. The incidence, etiologies, and avoidance of complications of pulmonary angiography in a large series. Radiology. 1980. 136:295–299.3. Diffin DC, Leyendecker JR, Johnson SP, Zucker RJ, Grebe PJ. Effect of anatomic distribution of pulmonary emboli on interobserver agreement in the interpretation of pulmonary angiography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1998. 171:1085–1089.4. Meaney JF, Weg JG, Chenevert TL, Stafford-Johnson D, Hamilton BH, Prince MR. Diagnosis of pulmonary embolism with magnetic resonance angiography. N Engl J Med. 1997. 336:1422–1427.5. Oudkerk M, van Beek EJ, Wielopolski P, van Ooijen PM, Brouwers-Kuyper EM, Bongaerts AH, et al. Comparison of contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography and conventional pulmonary angiography for the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism: a prospective study. Lancet. 2002. 359:1643–1647.6. Keilholz SD, Bozlar U, Fujiwara N, Mata JF, Berr SS, Corot C, et al. MR diagnosis of a pulmonary embolism: comparison of P792 and Gd-DOTA for first pass perfusion MRI and contrast-enhanced 3D MRA in a rabbit model. Korean J Radiol. 2009. 10:447–454.7. British Thoracic Society Standards of Care Committee Pulmonary Embolism Guideline Development Group. British Thoracic Society guidelines for the management of suspected acute pulmonary embolism. Thorax. 2003. 58:470–483.8. Hayashino Y, Goto M, Noguchi Y, Fukui T. Ventilation-perfusion scanning and helical CT in suspected pulmonary embolism: meta-analysis of diagnostic performance. Radiology. 2005. 234:740–748.9. Guilabert JP, Manzur DN, Tarrasa MJ, Llorens ML, Braun P, Arques MP. Can multislice CT alone run out reliably pulmonary embolism? A prospective study. Eur J Radiol. 2007. 62:220–226.10. Schoepf UJ, Goldhaber SZ, Costello P. Spiral computed tomography for acute pulmonary embolism. Circulation. 2004. 109:2160–2167.11. Rathbun SW, Raskob GE, Whitsett TL. Sensitivity and specificity of helical computed tomography in the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism: a systematic review. Ann Intern Med. 2000. 132:227–232.12. Van Strijen MJ, De Monye W, Kieft GJ, Pattynama PM, Prins MH, Huisman MV. Accuracy of single-detector spiral CT in the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism: a prospective multicenter cohort study of consecutive patients with abnormal perfusion scintigraphy. J Thromb Haemost. 2005. 3:17–25.13. Perrier A, Roy PM, Sanchez O, Le Gal G, Meyer G, Gourdier AL, et al. Multidetector-row computed tomography in suspected pulmonary embolism. N Engl J Med. 2005. 352:1760–1768.14. Sun Z, Winder RJ, Kelly BE, Ellis PK, Hirst DG. CT virtual intravascular endoscopy of abdominal aortic aneurysms treated with suprarenal endovascular stent grafting. Abdom Imaging. 2003. 28:580–587.15. Sun Z, Winder RJ, Kelly BE, Ellis PK, Kennedy PT, Hirst DG. Diagnostic value of CT virtual intravascular endoscopy in aortic stent-grafting. J Endovasc Ther. 2004. 11:13–25.16. Sun Z, Allen YB, Nadkarni S, Knight R, Hartley DE, Lawrence-Brown MM. CT virtual intravascular endoscopy in the visualization of fenestrated stent-grafts. J Endovasc Ther. 2008. 15:42–51.17. Sun Z. 3D multislice CT angiography in post-aortic stent grafting: a pictorial essay. Korean J Radiol. 2006. 7:205–211.18. Sun Z, Mwipatayi BP, Allen YB, Hartley DE, Lawrence-Brown MM. Multislice CT angiography of fenestrated endovascular stent grafting for treating abdominal aortic aneurysms: a pictorial review of the 2D/3D visualizations. Korean J Radiol. 2009. 10:285–293.19. Wittram C, Maher MM, Yoo AJ, Kalra MK, Shepard JA, McLoud TC. CT angiography of pulmonary embolism: diagnostic criteria and causes of misdiagnosis. Radiographics. 2004. 24:1219–1238.20. Jones SE, Wittram C. The indeterminate CT pulmonary angiogram: imaging characteristics and patient clinical outcome. Radiology. 2005. 237:329–337.21. Yavas US, Calisir C, Ozkan IR. The interobserver agreement between residents and experienced radiologists for detecting pulmonary embolism and DVT with using CT pulmonary angiography and indirect CT venography. Korean J Radiol. 2008. 9:498–502.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- 3D Multislice CT Angiography in Post-Aortic Stent Grafting: A Pictorial Essay
- Pulmonary and Renal Cement Embolisms During Balloon Kyphoplasty: A Case Report
- Virtual Endoscopy of Impacted Foreign Bodies in Tracheal and Esophageal Model
- Virtual CT Colonoscopy and Virtual CT Barium Enema using Multidetector-row CT
- Virtual Endoscopy Using Spiral CT in Head and Neck Lesions