J Korean Soc Magn Reson Med.
2010 Jun;14(1):64-68. 10.13104/jksmrm.2010.14.1.64.
Isolated Aspergillosis of the Brain in an Immunocompetent Patient: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University, Korea. suhsh11@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Diagnostic Pathology, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurosurgery, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University, Korea.
- KMID: 1782995
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13104/jksmrm.2010.14.1.64
Abstract
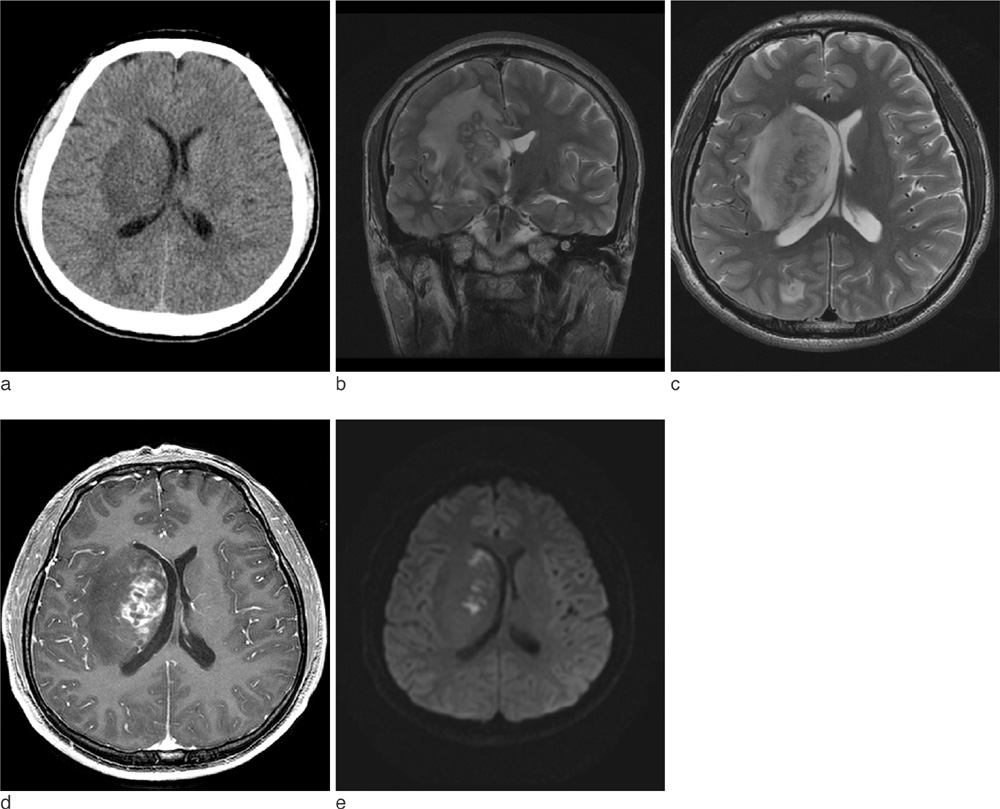
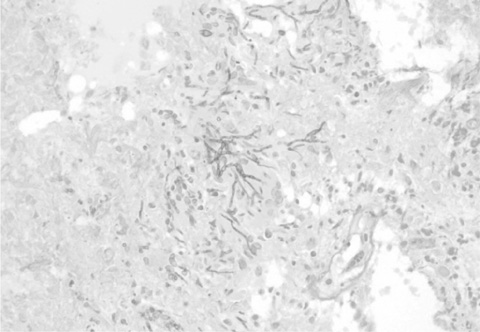
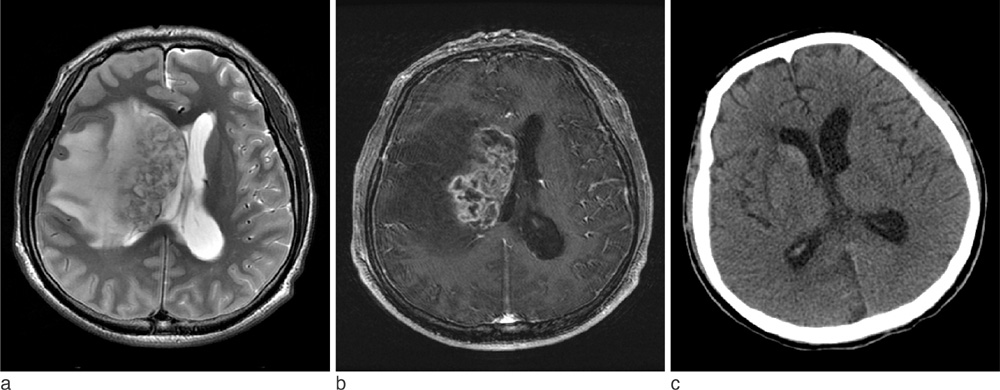
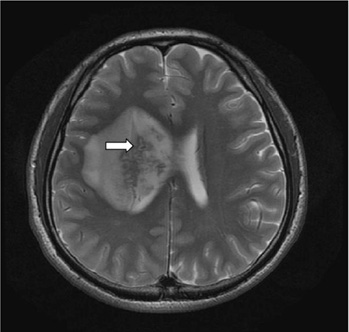
- Brain aspergillosis has been increasing remarkably. They are known to occur commonly in immunocompromised individuals by hematogenous spread from other primary sites or by direct extension from adjacent structures to central nervous system. We report a rare case of a 29-year-old male without any known medical history, who had isolated brain lesion and the pathology from stereotactic biopsy confirmed cerebral aspergillosis.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Beal MF, O'Carroll CP, Kleinman GM, Grossman RI. Aspergillosis of the nervous system. Neurology. 1982. 32:473–447.2. Yuh WT, Nguyen HD, Gao F, Tali ET, Fisher DJ, Mayr NA, et al. Brain parenchymal infection in bone marrow transplantation patients: CT and MR findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1994. 162:425–430.3. Ashdown BC, Tien RD, Felsberg GJ. Aspergillosis of the brain and paranasal sinuses in immunocompromised patients: CT and MR imaging findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1994. 162:155–159.4. DeLone DR, Goldstein RA, Petermann G, Salamat MS, Miles JM, Knechtle SJ, et al. Disseminated aspergillosis involving the brain: distribution and imaging characteristics. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1999. 20:1597–1604.5. Kim DG, Hong SC, Kim HJ, Chi JG, Han MH, Choi KS, et al. Cerebral aspergillosis in immunologically competent patients. Surgical neurology. 1993. 40:326–331.6. Narayan SK, Kumar K, Swaminathan RP, Roopeshkumar VR, Bhavna B. Isolated cerebral aspergilloma in a young immunocompetent patient. Practical neurology. 2009. 9:166–168.7. Phuttharak W, Hesselink JR, Wixom C. MR features of cerebral aspergillosis in an immunocompetent patient: Correlation with histology and elemental analysis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005. 26:835–838.8. Siddiqui AA, Shah AA, Bashir SH. Craniocerebral aspergillosis of sinonasal origin in immunocompetent patients: clinical spectrum and outcome in 25 cases. Neurosurgery. 2004. 55:602–611. discussion 611-603.9. Khachane SO, kumar V, Sanghvi DA. Central nervous system aspergillosis in immunocompetent patient. Eur J Radiol Extra. 2007. 63:53–56.10. Yamada K, Zoarski GH, Rothman MI, Zagardo MT, Nishimura T, Sun CC. An intracranial aspergilloma with low signal on t2-weighted images corresponding to iron accumulation. Neuroradiology. 2001. 43:559–561.11. Keyik B, Edguer T, Hekimoglu B. Conventional and diffusionweighted MR imaging of cerebral aspergillosis. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2005. 11:199–201.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Concurrent Nocardia Related Brain Abscess and Semi-Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in an Immunocompetent Patient
- A Case of Primary Cutaneous Aspergillosis
- A Case of Aspergillosis of the Central Nervous System in an Immunocompetent Patient
- Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis Invaded to Thoracic Vertebra in a Immunocompetent Host: A case report
- Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in a Immunocompetent Patient after Congenital Heart Disease Surgery: A Case Report