Yonsei Med J.
2008 Dec;49(6):942-948. 10.3349/ymj.2008.49.6.942.
Prevalence of Foxp3 Positive T Regulatory Cells is Increased during Progression of Cutaneous Squamous Tumors
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Kyongju, Korea. taejung@mail.dongguk.ac.kr
- KMID: 1782942
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2008.49.6.942
Abstract
- PURPOSE
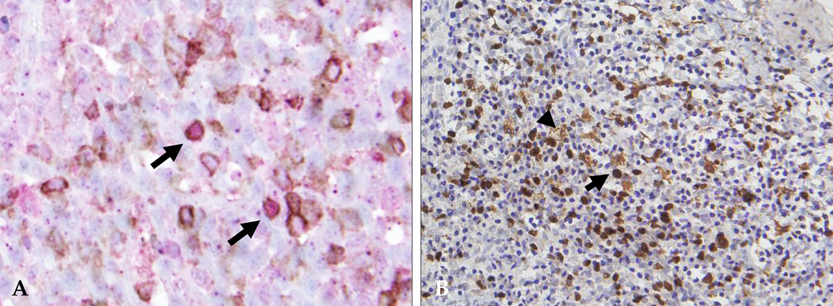
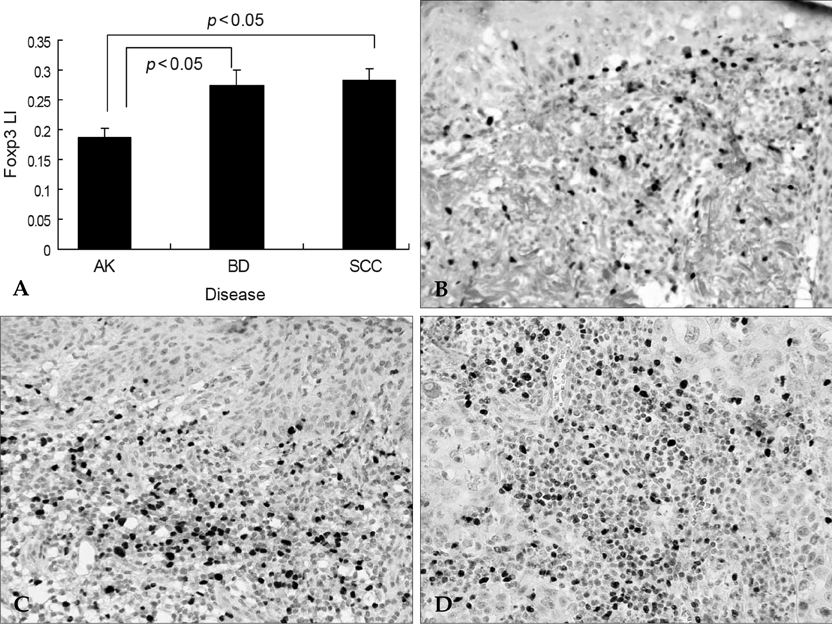
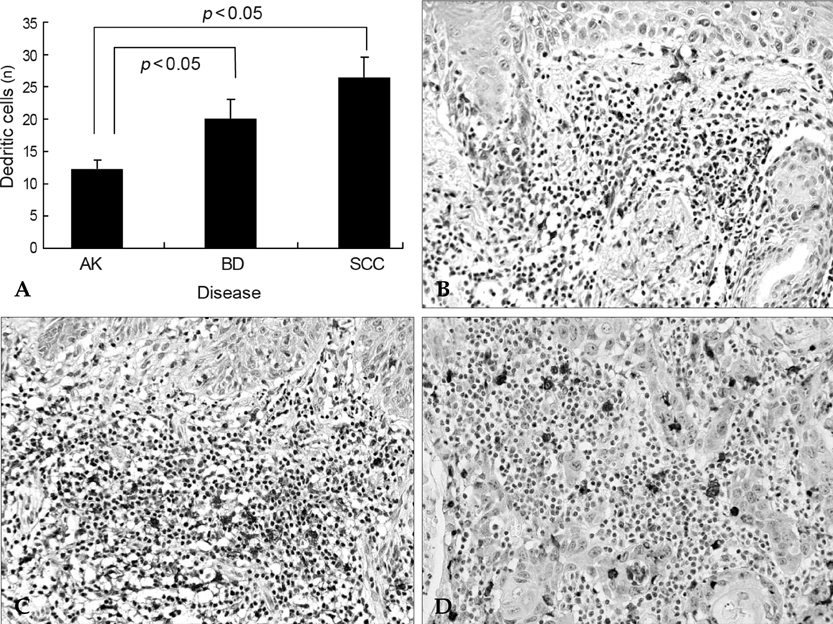
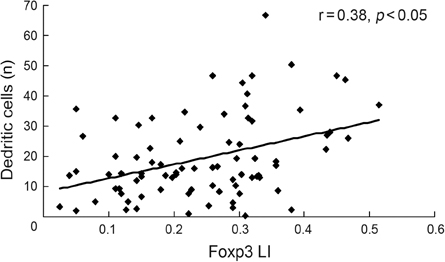
Forkhead box p3 (Foxp3) positive T regulatory cells (Tregs) have a functionally immunosuppressive property that prevents effector cells from acting against self in autoimmune diseases or a tumor. It is known that Tregs may be highly relevant in cancer progression. Dendritic cells (DCs) induce cutaneous immune response, however several studies have suggested that DCs are involved in immunosuppression. The aim of this study is to evaluate the prevalence of Tregs and DCs infiltration in cutaneous premalignant and malignant squamous lesions. MATERIALS AND METHODS: We evaluated Tregs and DCs in skin tissue samples obtained from 83 patients with actinic keratosis, Bowen's disease or squamous cell carcinoma by immunohistochemistry. RESULTS: The prevalence of Tregs and DCs was significantly higher in squamous cell carcinoma and Bowen's disease than in actinic keratosis. In addition, the number of DCs was closely correlated with the prevalence of Tregs, and DCs were also located in direct proximity to Tregs. CONCLUSION: Tregs is related to cutaneous squamous tumor progression.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Bowen's Disease/immunology/metabolism/pathology
Carcinoma, Squamous Cell/immunology/metabolism/pathology
Dendritic Cells/immunology/metabolism/pathology
Forkhead Transcription Factors/immunology/*metabolism
Humans
Immune Tolerance
Keratosis, Actinic/immunology/metabolism/pathology
Skin Neoplasms/*immunology/metabolism/pathology
T-Lymphocytes, Regulatory/*immunology/metabolism/pathology
Figure
Reference
-
1. Urbach F. Ultraviolet radiation and skin cancer of humans. J Photochem Photobiol B. 1997. 40:3–7.
Article2. Beissert S, Loser K. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of photocarcinogenesis. Photochem Photobiol. 2008. 84:29–34.
Article3. Simon JC, Hara H, Denfeld RW, Martin S. UVB-irradiated dendritic cells induce nonproliferating, regulatory type T cells. Skin Pharmacol Appl Skin Physiol. 2002. 15:330–334.4. Lutz MB, Schuler G. Immature, semi-mature and fully mature dendritic cells: which signals induce tolerance or immunity? Trends Immunol. 2002. 23:445–449.
Article5. Enk AH. Dendritic cells in tolerance induction. Immunol Lett. 2005. 99:8–11.
Article6. Loser K, Mehling A, Loeser S, Apelt J, Kuhn A, Grabbe S, et al. Epidermal RANKL controls regulatory T-cell numbers via activation of dendritic cells. Nat Med. 2006. 12:1372–1379.
Article7. Mahnke K, Qian Y, Knop J, Enk AH. Induction of CD4+/CD25+ regulatory T cells by targeting of antigens to immature dendritic cells. Blood. 2003. 101:4862–4869.
Article8. Jonuleit H, Schmitt E, Stassen M, Tuettenberg A, Knop J, Enk AH. Identification and functional characterization of human CD4(+)CD25(+) T cells with regulatory properties isolated from peripheral blood. J Exp Med. 2001. 193:1285–1294.
Article9. Ng WF, Duggan PJ, Ponchel F, Matarese G, Lombardi G, Edwards AD, et al. Human CD4(+)CD25(+) cells: a naturally occurring population of regulatory T cells. Blood. 2001. 98:2736–2744.
Article10. Sakaguchi S, Sakaguchi N, Asano M, Itoh M, Toda M. Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by activated T cells expressing IL-2 receptor alpha-chains (CD25). Breakdown of a single mechanism of self-tolerance causes various autoimmune diseases. J Immunol. 1995. 155:1151–1164.11. Fontenot JD, Gavin MA, Rudensky AY. Foxp3 programs the development and function of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Nat Immunol. 2003. 4:330–336.12. Hori S, Nomura T, Sakaguchi S. Control of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor Foxp3. Science. 2003. 299:1057–1061.13. Brunkow ME, Jeffery EW, Hjerrild KA, Paeper B, Clark LB, Yasayko SA, et al. Disruption of a new forkhead/winged-helix protein, scurfin, results in the fatal lymphoproliferative disorder of the scurfy mouse. Nat Genet. 2001. 27:68–73.
Article14. Chatila TA, Blaeser F, Ho N, Lederman HM, Voulgaropoulos C, Helms C, et al. JM2, encoding a fork head-related protein, is mutated in X-linked autoimmunity-allergic disregulation syndrome. J Clin Invest. 2000. 106.
Article15. Shimizu J, Yamazaki S, Sakaguchi S. Induction of tumor immunity by removing CD25+CD4+ T cells: a common basis between tumor immunity and autoimmunity. J Immunol. 1999. 163:5211–5218.16. Woo EY, Chu CS, Goletz TJ, Schlienger K, Yeh H, Coukos G, et al. Regulatory CD4(+)CD25(+) T cells in tumors from patients with early-stage non-small cell lung cancer and late-stage ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 2001. 61:4766–4772.17. Liyanage UK, Moore TT, Joo HG, Tanaka Y, Herrmann V, Doherty G, et al. Prevalence of regulatory T cells is increased in peripheral blood and tumor microenvironment of patients with pancreas or breast adenocarcinoma. J Immunol. 2002. 169:2756–2761.
Article18. Ormandy LA, Hillemann T, Wedemeyer H, Manns MP, Greten TF, Korangy F. Increased populations of regulatory T cells in peripheral blood of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2005. 65:2457–2464.
Article19. Mizukami Y, Kono K, Kawaguchi Y, Akaike H, Kamimura K, Sugai H, et al. Localisation pattern of Foxp3+ regulatory T cells is associated with clinical behaviour in gastric cancer. Br J Cancer. 2008. 98:148–153.20. Hiraoka N, Onozato K, Kosuge T, Hirohashi S. Prevalence of Foxp3+ regulatory T cells increases during the progression of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and its premalignant lesions. Clin Cancer Res. 2006. 12:5423–5434.
Article21. Sakaguchi S. Naturally arising Foxp3-expressing CD25+CD4+ regulatory T cells in immunological tolerance to self and non-self. Nat Immunol. 2005. 6:345–352.
Article22. von Boehmer H. Mechanisms of suppression by suppressor T cells. Nat Immunol. 2005. 6:338–344.
Article23. Fontenot JD, Rudensky AY. A well adapted regulatory contrivance: regulatory T cell development and the forkhead family transcription factor Foxp3. Nat Immunol. 2005. 6:331–337.
Article24. Fontenot JD, Rasmussen JP, Williams LM, Dooley JL, Farr AG, Rudensky AY. Regulatory T cell lineage specification by the forkhead transcription factor Foxp3. Immunity. 2005. 22:329–341.25. Chen ML, Pittet MJ, Gorelik L, Flavell RA, Weissleder R, von Boehmer H, et al. Regulatory T cells suppress tumor-specific CD8 T cell cytotoxicity through TGF-bata signals in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. 102:419–424.
Article26. Shimizu J, Yamazaki S, Sakaguchi S. Induction of tumor immunity by removing CD25+CD4+ T cells: a common basis between tumor immunity and autoimmunity. J Immunol. 1999. 163:5211–5218.27. Onizuka S, Tawara I, Shimizu J, Sakaguchi S, Fujita T, Nakayama E. Tumor rejection by in vivo administration of anti-CD25 (interleukin-2 receptor α) monoclonal antibody. Cancer Res. 1999. 59:3128–3133.28. Nishikawa H, Kato T, Tawara I, Takemitsu T, Saito K, Wang L, et al. Accelerated chemically induced tumor development mediated by CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in wild-type hosts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. 102:9253–9257.
Article29. Curiel TJ, Coukos G, Zou L, Alvarez X, Cheng P, Mottram P, et al. Specific recruitment of regulatory T cells in ovarian carcinoma fosters immune privilege and predicts reduced survival. Nat Med. 2004. 10:942–949.30. Alvaro T, Lejeune M, Salvado MT, Bosch R, García JF, Jaén J, et al. Outcome in Hodgkin's lymphoma can be predicted from the presence of accompanying cytotoxic and regulatory T cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2005. 11:1467–1473.
Article31. Wolf D, Hochegger K, Wolf AM, Rumpold HF, Gastl G, Tilg H, et al. The expression of the regulatory T cell-specific forkhead box transcription factor FoxP3 is associated with poor prognosis in ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2005. 11:8326–8331.
Article32. Siddiqui SA, Frigola X, Bonne-Annee S, Mercader M, Kuntz SM, Krambeck AE, et al. Tumor infiltrating Foxp3-CD4+CD25+ T cells predict poor survival in renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2007. 13:2075–2081.
Article33. Loddenkemper C, Schernus M, Noutsias M, Stein H, Thiel E, Nagorsen D. In situ anlaysis of FOXP3+ egulatory T cells in human colorectal cancer. J Transl Med. 2006. 4:52.34. Carreras J, Lopez-Guillermo A, Fox BC, Colomo L, Martinez A, Roncador G, et al. High numbers of tumor-infiltrating FOXP3-positive regulatory T cells are associated with improved overall survival in follicular lymphoma. Blood. 2006. 108:2957–2964.35. Nagorsen D, Voigt S, Berg E, Stein H, Thiel E, Loddenkemper C. Tumor-infiltrating macrophages and dendritic cells in human colorectal cancer: relation to local regulatory T cells, systemic T-cell response against tumor-associated antigens and survival. J Transl Med. 2007. 5:62.
Article36. Rutella S, Lemoli RM. Regulatory T cells and tolerogenic dendritic cells: from basic biology to clinical applications. Immunol Lett. 2004. 94:11–26.
Article37. Misra N, Bayry J, Lacroix-Desmazes S, Kazatchkine MD, Kaveri SV. Cutting edge human CD4+CD25+ T cells restrain the maturation and antigen-presenting function of dendritic cells. J Immunol. 2004. 172:4676–4680.
Article38. Cederbom L, Hall H, Ivars F. CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells down-regulate co-stimulatory molecules on antigen-presenting cells. Eur J Immunol. 2000. 30:1538–1543.
Article39. Tadokoro CE, Shakhar G, Shen S, Ding Y, Lino AC, Maraver A, et al. Regulatory T cells inhibit stable contacts between CD4+ T cells and dendritic cells in vivo. J Exp Med. 2006. 203:505–511.
Article40. Tang Q, Adams JY, Tooley AJ, Bi M, Fife BT, Serra P, et al. Visualizing regulatory T cell control of autoimmune responses in nonobese diabetic mice. Nat Immunol. 2006. 7:83–92.
Article41. Mahnke K, Ring S, Johnson TS, Schallenberg S, Schönfeld K, Storn V, et al. Induction of immunosuppressive functions of dendritic cells in vivo by CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells: role of B7-H3 expression and antigen presentation. Eur J Immunol. 2007. 37:2117–2126.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Peripheral Generation of CD4+ CD25+ Foxp3+ Regulatory T Cells
- Presence of Foxp3-expressing CD19(+)CD5(+) B Cells in Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells: Human CD19(+)CD5(+)Foxp3(+) Regulatory B Cell (Breg)
- A Study on the Number of Circulating CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Regulatory T Cells and CD4+CD25-Foxp3+ T Cells in Psoriasis
- Number of FoxP3+ regulatory T-cells are associated with recurrence in vulvar squamous cell carcinoma
- Expansion and characterization of regulatory T cell populations from acute kidney injury patients