J Korean Med Sci.
2009 Oct;24(5):941-944. 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.5.941.
Increased Transforming Growth Factor-beta1 in Alcohol Dependence
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Psychiatry, College of Medicine, Korea University, Ansan Hospital, Ansan, Korea.
- 2Department of Neuropsychiatry, Hallym University Hangang Sacred Heart Hospital, Seoul, Korea. ihngeun@hallym.or.kr
- 3Department of Neuropsychiatry, Hanyang University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Anatomy and Neurobiology, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 5Division of Molecular & Life Science, Hanyang University College of Sciences, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1782019
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2009.24.5.941
Abstract
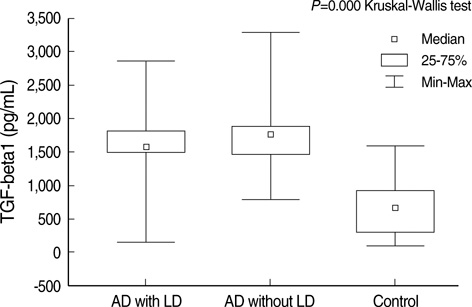
- Ethanol and its metabolite acetaldehyde increase transforming growth factor beta1 (TGF-beta1) expression in animal studies. TGF-beta1 is related with the hepatic stellate cell (the key element of hepatic fibrogenesis) and the radial glia (the key element of neuronal migration). Blood samples were collected from 41 patients with alcohol dependence, TGF-beta1 levels measured by ELISA were compared with 41 normal subjects. Plasma TGF-beta1 levels in the patients with alcohol dependence (1,653.11+/-532.45 pg/mL) were significantly higher than those of healthy subjects (669.87+/-366.53 pg/mL) (P=0.000). Patients with or without liver pathology showed no difference in TGF-beta1 (P=0.36). Increased TGF-beta1 may mediate deleterious effect of alcohol such as hepatic fibrosis and suppressed neuronal developments in alcohol dependence patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Breitkopf K, Haas S, Wiercinska E, Singer MV, Dooley S. Anti-TGF-beta strategies for the treatment of chronic liver disease. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005. 29(11):Suppl. 121S–131S.2. Arteel GE. Oxidants and antioxidants in alcohol-induced liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2003. 124:778–790.
Article3. Lieber CS. Metabolism of alcohol. Clin Liver Dis. 2005. 9:1–35.
Article4. Kwon OS, Song SH, Ju KT, Chung MG, Park DK, Kim SS, Kim YS, Koo YS, Kim YK, Choi DJ, Kim JH, Hwang YJ, Byun KS, Lee CH. Polymorphism in codons 10 and 25 of the transforming growth factor-beta1 gene in Korean population and in patients with liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2003. 42:212–219.5. Blobe GC, Schiemann WP, Lodish HF. Role of transforming growth factor beta in human disease. N Engl J Med. 2000. 342:1350–1358.6. Pepper MS. Transforming growth factor-beta: vasculogenesis, angiogenesis, and vessel wall integrity. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 1997. 8:21–43.
Article7. Ravitz MJ, Wenner CE. Cyclin-dependent kinase regulation during G1 phase and cell cycle regulation by TGF-beta. Adv Cancer Res. 1997. 71:165–207.8. Schuster N, Krieglstein K. Mechanisms of TGF-beta-mediated apoptosis. Cell Tissue Res. 2002. 307:1–14.9. Elliott RL, Blobe GC. Role of transforming growth factor beta in human cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005. 23:2078–2093.
Article10. Chen A. Acetaldehyde stimulates the activation of latent transforming growth factor-beta1 and induces expression of the type II recepor of the cytokine in rat cultured hepatic stellate cells. Biochem J. 2002. 368:683–693.11. Maehara Y, Kakeji Y, Kabashima A, Emi Y, Watanabe A, Akazawa K, Baba H, Kohnoe S, Sugimachi K. Role of transforming growth factor-beta 1 in invasion and metastasis in gastric carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 1999. 17:607–614.12. Luo J, Miller MW. Transforming growth factor beta1-regulated cell proliferation and expression of neural cell adhesion molecule in B104 neuroblastoma cells: differential effects of ethanol. J Neurochem. 1999. 72:2286–2293.13. Miller MW, Luo J. Effects of ethanol and transforming growth factor beta (TGF beta) on neuronal proliferation and nCAM expression. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2002. 26:1281–1285.14. Kuhn P, Sarkar DK. Ethanol induces apoptotic death of beta-endorphin neurons in the rat hypothalamus by a TGF-beta 1-dependent mechanism. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2008. 32:706–714.15. Nanji AA, Tahan SR, Golding M, Khwaja S, Rahemtulla A, Lalani EN. Role of transforming growth factor-[beta]1 in inhibiting endothelial cell proliferation in experimental alcoholic liver disease. Am J Pathol. 1996. 148:739–747.16. Chen WX, Li YM, Yu CH, Cai WM, Zheng M, Chen F. Quantitative analysis of transforming growth factor beta 1 mRNA in patients with alcoholic liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2002. 8:379–381.
Article17. Nieto N, Friedman SL, Cederbaum AI. Stimulation and proliferation of primary rat hepatic stellate cells by cytochrome P450 2E1-derived reactive oxygen species. Hepatology. 2002. 35:62–73.
Article18. Su GL. Lipopolysaccharides in liver injury: molecular mechanisms of Kupffer cell activation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2002. 283:G256–G265.
Article19. Dooley S, Delvoux B, Lahme B, Mangasser-Stephan K, Gressner AM. Modulation of transforming growth factor beta response and signaling during transdifferentiation of rat hepatic stellate cells to myofibroblasts. Hepatology. 2000. 31:1094–1106.20. Dooley S, Delvoux B, Streckert M, Bonzel L, Stopa M, ten Dijke P, Gressner AM. Transforming growth factor beta signal transduction in hepatic stellate cells via Smad2/3 phosphorylation, a pathway that is abrogated during in vitro progression to myofibroblasts. TGFbeta signal transduction during transdifferentiation of hepatic stellate cells. FEBS Lett. 2001. 502:4–10.21. Stopa M, Anhuf D, Terstegen L, Gatsios P, Gressner AM, Dooley S. Participation of Smad2, Smad3, and Smad4 in transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta)-induced activation of Smad7. THE TGF-beta response element of the promoter requires functional Smad binding element and E-box sequences for transcriptional regulation. J Biol Chem. 2000. 275:29308–29317.22. Fang C, Lindros KO, Badger TM, Ronis MJ, Ingelman-Sundberg M. Zonated expression of cytokines in rat liver: effect of chronic ethanol and the cytochrome P450 2E1 inhibitor, chlormethiazole. Hepatology. 1998. 27:1304–1310.
Article23. Tsutsumi M, Lasker JM, Shimizu M, Rosman AS, Lieber CS. The intralobular distribution of ethanol-inducible P450IIE1 in rat and human liver. Hepatology. 1989. 10:437–446.
Article24. Siegenthaler JA, Miller MW. Transforming growth factor beta1 modulates cell migration in rat cortex: effects of ethanol. Cereb Cortex. 2004. 14:791–802.25. Flanders KC, Ludecke G, Engels S, Cissel DS, Roberts AB, Kondaiah P, Lafyatis R, Sporn MB, Unsicker K. Localization and actions of transforming growth factor-beta s in the embryonic nervous system. Development. 1991. 113:183–191.
Article26. Krieglstein K, Strelau J, Schober A, Sullivan A, Unsicker K. TGF-beta and the regulation of neuron survival and death. J Physiol Paris. 2002. 96:25–30.27. Pelton RW, Saxena B, Jones M, Moses HL, Gold LI. Immunohistochemical localization of TGF beta 1, TGF beta 2, and TGF beta 3 in the mouse embryo: expression patterns suggest multiple roles during embryonic development. J Cell Biol. 1991. 115:1091–1105.
Article28. Gressens P. Mechanisms and disturbances of neuronal migration. Pediatr Res. 2000. 48:725–730.
Article29. Kastin AJ, Akerstrom V, Pan W. Circulating TGF-beta1 does not cross the intact blood-brain barrier. J Mol Neurosci. 2003. 21:43–48.30. Unsicker K, Strelau J. Functions of transforming growth factor-beta isoforms in the nervous system. Cues based on localization and experimental in vitro and in vivo evidence. Eur J Biochem. 2000. 24:6972–6975.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Transforming Growth Factor-beta1 Expression in Normal Laryngeal Mucosa, Laryngeal Dysplasia and Laryngeal Carcinoma
- Differential Expression of TGF-beta Isoforms in Human Kerationocytes by Narrow Band UVB
- Inhibition of Cell Growth and Suppression of c-myc Gene Expression by Transforming Growth Factor-beta1 in Cervical Carcinoma Cell Lines
- Expression of Transforming Growth Factor-beta1 and Its Effects on the Extracellular Matrix Formation and Angiogenesis in Gastric Carcinoma
- Regulation of the Levels of Trabecular Matrix Metalloproteinase and Inhibitor by Transforming Growth Factor-beta1