J Korean Med Sci.
2009 Oct;24(5):904-909. 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.5.904.
Unrelated Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for Children with Acute Leukemia: Experience at a Single Institution
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Chung-Ang University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Kyung Hee University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Cheju Halla General Hospital, Jeju, Korea.
- 4Department of Pediatrics, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. hojim@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 1782014
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2009.24.5.904
Abstract
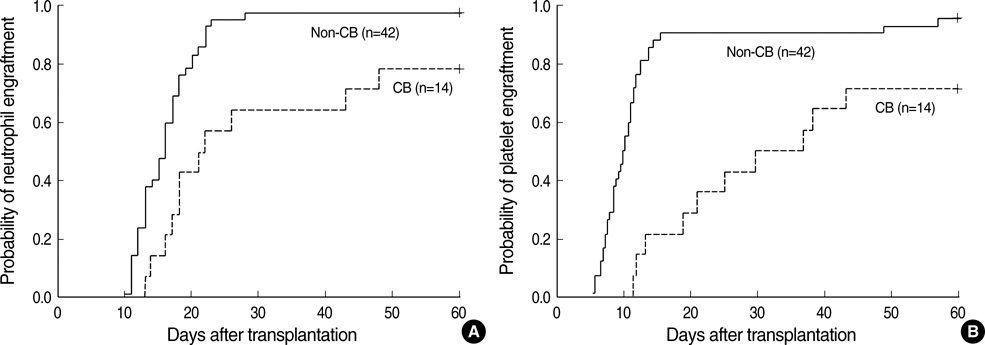
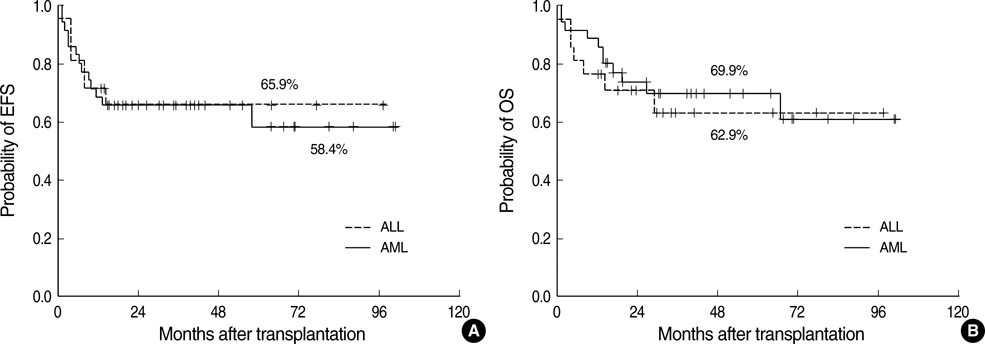
- We evaluate the outcomes in children with acute leukemia who received allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HCT) using unrelated donor. Fifty-six children in complete remission (CR) received HCT from unrelated donors between 2000 and 2007. Thirty-five had acute myeloid leukemia, and 21 had acute lymphoid leukemia. Stem cell sources included bone marrow in 38, peripheral blood in 4, and cord blood (CB) in 14. Four patients died before engraftment and 52 engrafted. Twenty patients developed grade II-IV acute graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) and 8 developed extensive chronic GVHD. With median follow-up of 39.1 months, event free survival and overall survival were 60.4% and 67.5%, respectively, at 5 yr. Events included relapse in 10 and treatment-related mortality (TRM) in 10. The causes of TRM included sepsis in 4, GVHD in 4 (1 acute GVHD and 3 chronic GVHD), veno-occlusive disease in 1 and fulminant hepatitis in 1. Patients transplanted with CB had event free survival of 57.1%, comparable to 63.2% for those transplanted with other than CB. In conclusion, HCT with unrelated donors is effective treatment modality for children with acute leukemia. In children with acute leukemia candidate for HCT but lack suitable sibling donor, unrelated HCT may be a possible treatment option at the adequate time of their disease.
MeSH Terms
-
Adolescent
Bone Marrow Transplantation
Child
Child, Preschool
Cord Blood Stem Cell Transplantation
Disease-Free Survival
Female
Graft vs Host Disease/etiology/immunology
*Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Humans
Infant
Leukemia, Myeloid, Acute/complications/mortality/*therapy
Male
Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Transplantation
Precursor Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia-Lymphoma/complications/mortality/*therapy
Risk Factors
Time Factors
Transplantation, Homologous
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chessells JM. Relapsed lymphoblastic leukaemia in children: a continuing challenge. Br J Haematol. 1998. 102:423–438.2. Pui CH, Evans WE. Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. N Engl J Med. 1998. 339:605–615.3. Heerema NA, Nachman JB, Sather HN, Sensel MG, Lee MK, Hutchinson R, Lange BJ, Steinherz PG, Bostrom B, Gaynon PS, Uckun F. Hypodiploidy with less than 45 chromosomes confers adverse risk in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a report from the children's cancer group. Blood. 1999. 94:4036–4045.4. Johansson B, Moorman AV, Haas OA, Watmore AE, Cheung KL, Swanton S, Secker-Walker LM. Hematologic malignancies with t(4;11q)(21q23)--a cytogenetic, morphologic, immunophenotypic and clinical study of 183 cases. European 11q23 Workshop participants. Leukemia. 1998. 12:779–787.5. Uckun FM, Nachman JB, Sather HN, Sensel MG, Kraft P, Steinherz PG, Lange B, Hutchinson R, Reaman GH, Gaynon PS, Heerema NA. Clinical significance of Philadelphia chromosome positive pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia in the context of contemporary intensive therapies: a report from the Children's Cancer Group. Cancer. 1998. 83:2030–2039.6. Ravindranath Y, Chang M, Steuber CP, Becton D, Dahl G, Civin C, Camitta B, Carroll A, Raimondi SC, Weinstein HJ. Pediatric Oncology Group. Pediatric Oncology Group (POG) studies of acute myeloid leukemia (AML): a review of four consecutive childhood AML trials conducted between 1981 and 2000. Leukemia. 2005. 19:2101–2116.
Article7. Gibson BE, Wheatley K, Hann IM, Stevens RF, Webb D, Hills RK, De Graaf SS, Harrison CJ. Treatment strategy and long-term results in paediatric patients treated in consecutive UK AML trials. Leukemia. 2005. 19:2130–2138.
Article8. Creutzig U, Zimmermann M, Ritter J, Reinhardt D, Hermann J, Henze G, Jürgens H, Kabisch H, Reiter A, Riehm H, Gadner H, Schellong G. Treatment strategies and long-term results in paediatric patients treated in four consecutive AML-BFM trials. Leukemia. 2005. 19:2030–2042.
Article9. Woods WG, Neudorf S, Gold S, Sanders J, Buckley JD, Barnard DR, Dusenbery K, DeSwarte J, Arthur DC, Lange BJ, Kobrinsky NL. Children's Cancer Group. A comparison of allogeneic bone marrow transplantation, autologous bone marrow transplantation, and aggressive chemotherapy in children with acute myeloid leukemia in remission. Blood. 2001. 97:56–62.10. Becton D, Dahl GV, Ravindranath Y, Chang MN, Behm FG, Raimondi SC, Head DR, Stine KC, Lacayo NJ, Sikic BI, Arceci RJ, Weinstein H. Pediatric Oncology Group. Randomized use of cyclosporin A (CsA) to modulate P-glycoprotein in children with AML in remission: Pediatric Oncology Group Study 9421. Blood. 2006. 107:1315–1324.
Article11. Kernan NA, Bartsch G, Ash RC, Beatty PG, Champlin R, Filipovich A, Gajewski J, Hansen JA, Henslee-Downey J, McCullough J, McGlave P, Perkins HA, Phillips GL, Sanders J, Stroncek D, Thomas ED, Blume KG. Analysis of 462 transplantations from unrelated donors facilitated by the national marrow donor program. N Engl J Med. 1993. 328:593–602.
Article12. Balduzzi A, Gooley T, Anasetti C, Sanders JE, Martin PJ, Petersdorf EW, Appelbaum FR, Buckner CD, Matthews D, Storb R, Sullivan KM, Hansen JA. Unrelated donor marrow transplantation in children. Blood. 1995. 86:3247–3256.
Article13. Davies SM, Wagner JE, Shu XO, Blazar BR, Katsanis E, Orchard PJ, Kersey JH, Dusenbery KE, Weisdorf DJ, McGlave PB, Ramsay NK. Unrelated donor bone marrow transplantation for children with acute leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 1997. 15:557–565.
Article14. Saarinen-Pihkala UM, Gustafsson G, Ringdén O, Heilmann C, Glomstein A, Lönnerholm G, Abrahamsson J, Bekassy AN, Schroeder H, Mellander L. Nordic Society of Pediatric Hematology and Oncology. No disadvantage in outcome of using matched unrelated donors as compared with matched sibling donors for bone marrow transplantation in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia in second remission. J Clin Oncol. 2001. 19:3406–3414.
Article15. Al-Kasim FA, Thornley I, Rolland M, Lau W, Tsang R, Freedman MH, Saunders EF, Calderwood S, Doyle JJ. Single-centre experience with allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in childhood: similar survival after matched-related and matched-unrelated donor transplants. Br J Haematol. 2002. 116:483–490.
Article16. Moore J, Nivison-Smith I, Goh K, Ma D, Bradstock K, Szer J, Durrant S, Schwarer A, Bardy P, Herrmann R, Dodds A. Equivalent survival for sibling and unrelated donor allogeneic stem cell transplantation for acute myelogenous leukemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2007. 13:601–607.
Article17. Dahlke J, Kröger N, Zabelina T, Ayuk F, Fehse N, Wolschke C, Waschke O, Schieder H, Renges H, Krüger W, Kruell A, Hinke A, Erttmann R, Kabisch H, Zander AR. Comparable results in patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia after related and unrelated stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2006. 37:155–163.
Article18. Neudorf S, Sanders J, Kobrinsky N, Alonzo TA, Buxton AB, Gold S, Barnard DR, Wallace JD, Kalousek D, Lange BJ, Woods WG. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for children with acute myelocytic leukemia in first remission demonstrates a role for graft versus leukemia in the maintenance of disease-free survival. Blood. 2004. 103:3655–3661.
Article19. Cox DR. Regression models and life tables. J R Stat Soc B. 1972. 34:187–220.20. Biondi A, Cimino G, Pieters R, Pui CH. Biological and therapeutic aspects of infant leukemia. Blood. 2000. 96:24–33.
Article21. Aricò M, Valsecchi MG, Camitta B, Schrappe M, Chessells J, Baruchel A, Gaynon P, Silverman L, Janka-Schaub G, Kamps W, Pui CH, Masera G. Outcome of treatment in children with Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2000. 342:998–1006.
Article22. Behm FG, Raimondi SC, Frestedt JL, Liu Q, Crist WM, Downing JR, Rivera GK, Kersey JH, Pui CH. Rearrangement of the MLL gene confers a poor prognosis in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia, regardless of presenting age. Blood. 1996. 87:2870–2877.
Article23. Badell I, Muñoz A, Ortega JJ, Martínez A, Madero L, Bureo E, Verdeguer A, Fernandez-Delgado R, Cubells J, Soledad-Maldonado M, Olivé T, Sastre A, Baro J, Díaz MA. Spanish Working Party for BMT in Children (GETMON). Long-term outcome of allogeneic or autologous haemopoietic cell transplantation for acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in second remission in children. GETMON experience 1983-1998. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2005. 35:895–901.
Article24. Michel G, Rocha V, Chevret S, Arcese W, Chan KW, Filipovich A, Takahashi TA, Vowels M, Ortega J, Bordigoni P, Shaw PJ, Yaniv I, Machado A, Pimentel P, Fagioli F, Verdeguer A, Jouet JP, Diez B, Ferreira E, Pasquini R, Rosenthal J, Sievers E, Messina C, Iori AP, Garnier F, Ionescu I, Locatelli F, Gluckman E. Eurocord Group. Unrelated cord blood transplantation for childhood acute myeloid leukemia: a Eurocord Group analysis. Blood. 2003. 102:4290–4297.
Article25. Rocha V, Cornish J, Sievers EL, Filipovich A, Locatelli F, Peters C, Remberger M, Michel G, Arcese W, Dallorso S, Tiedemann K, Busca A, Chan KW, Kato S, Ortega J, Vowels M, Zander A, Souillet G, Oakill A, Woolfrey A, Pay AL, Green A, Garnier F, Ionescu I, Wernet P, Sirchia G, Rubinstein P, Chevret S, Gluckman E. Comparison of outcomes of unrelated bone marrow and umbilical cord blood transplants in children with acute leukemia. Blood. 2001. 97:2962–2971.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- New therapeutic modalities on hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
- Chronic graft versus host disease with small bowel obstruction after unrelated hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in a patient with acute myeloid leukemia
- Pediatric Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Korea: April 2000: The Korean Society of Pediatric Hematology-Oncology
- Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Children with Leukemia: A Single Institution Experience with Respect to Donors
- Unusual isolated extramedullary relapse of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in the breast despite complete donor hematopoietic chimerism after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation