Korean J Lab Med.
2010 Dec;30(6):533-539. 10.3343/kjlm.2010.30.6.533.
Minimal Residual Disease Detection in Acute Leukemia Patients by Flow Cytometric Assay of Cross-lineage Antigen Expression
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. cjpark@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, University of Ulsan College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Laboratory Medicine, Eulji General Hospital, Eulji University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Laboratory Medicine, Gangneung Asan Hospital, Gangneung, Korea.
- KMID: 1781655
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/kjlm.2010.30.6.533
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
It has been demonstrated that flow cytometric detection of minimal residual disease (MRD) has a prognostic significance in the treatment of patients with acute leukemia. We investigated the significance of flow cytometric MRD detection for the first time in Korea.
METHODS
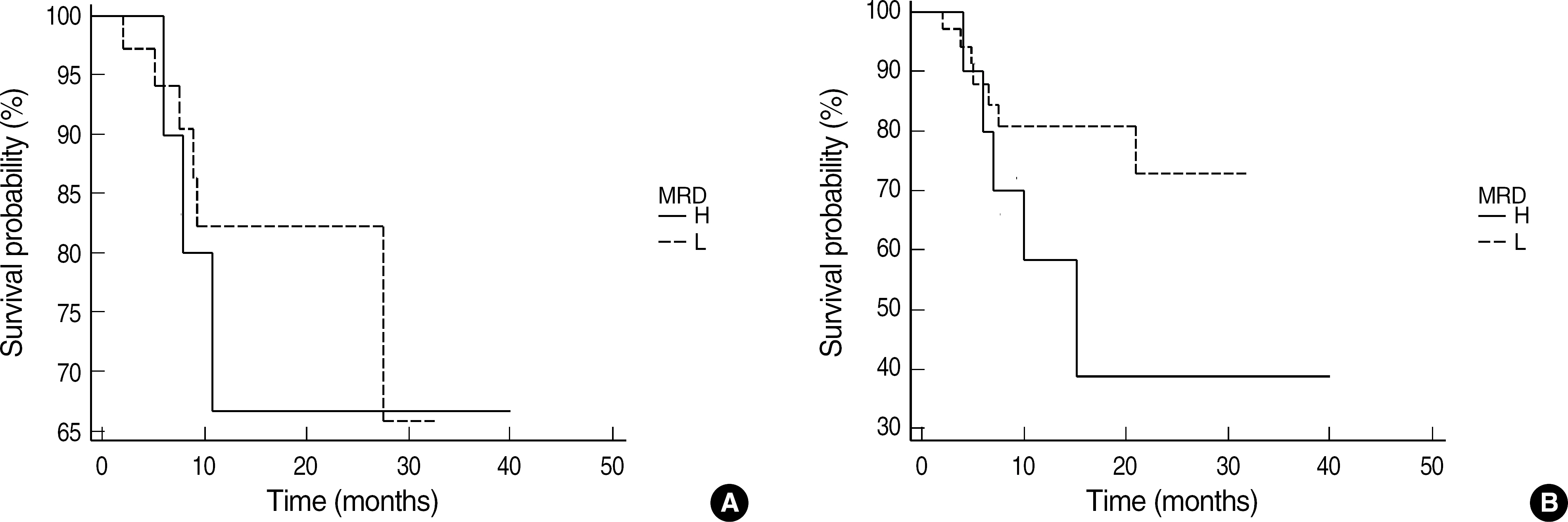
We analyzed the results of MRD detection in morphologically complete remission bone marrow aspirates from 89 patients with newly-diagnosed or relapsed acute leukemia, in which leukemic cells had cross-lineage antigen expression. Patients were grouped based on MRD frequencies: > or =1.0%, high MRD; <1.0%, low MRD.
RESULTS
Forty-seven ALL patients consisted of 10 with high and 37 with low MRD levels. Patients with high MRD levels showed a tendency of more frequent relapse than those with low MRD levels (40.0% and 13.5%, respectively) (P=0.08). High MRD group showed a tendency of short relapse-free survival (RFS) and overall survival (OS), although the differences were not statistically significant. Forty-two AML patients consisted of 16 with high and 26 with low MRD levels. There were no correlations between the MRD levels and relapse rate, RFS or OS. AML patients with high MRD levels showed significantly higher rate of unfavorable cytogenetic risk categories and lower rate of favorable risk categories (P=0.03).
CONCLUSIONS
MRD detection by flow cytometric assay of cross-lineage antigen expression would be useful in predicting treatment outcome in patients with ALL rather than AML. We expect that the establishment of the standardization of methods, time to test or antibody combination would be achieved through further trials in this country.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Acute Disease
Adolescent
Adult
Aged
Antigens/*metabolism
Antigens, CD/metabolism
Bone Marrow/metabolism
Child
Child, Preschool
Disease-Free Survival
Female
*Flow Cytometry
Humans
Infant
Leukemia, Myeloid, Acute/*diagnosis/mortality/therapy
Male
Middle Aged
Neoplasm, Residual/diagnosis
Precursor Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia-Lymphoma/*diagnosis/mortality/therapy
Recurrence
Survival Rate
Figure
Reference
-
1.Vidriales MB., San-Miguel JF., Orfao A., Coustan-Smith E., Campana D. Minimal residual disease monitoring by flow cytometry. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2003. 16:599–612.
Article2.Chung NG., Buxhofer-Ausch V., Radich JP. The detection and significance of minimal residual disease in acute and chronic leukemia. Tissue Antigens. 2006. 68:371–85.
Article3.Kern W., Haferlach C., Haferlach T., Schnittger S. Monitoring of minimal residual disease in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer. 2008. 112:4–16.
Article4.Campana D. Status of minimal residual disease testing in childhood haematological malignancies. Br J Haematol. 2008. 143:481–9.
Article5.Al-Mawali A., Gillis D., Lewis I. The role of multiparameter flow cytometry for detection of minimal residual disease in acute myeloid leukemia. Am J Clin Pathol. 2009. 131:16–26.
Article6.Ciudad J., San Miguel JF., Lopez-Berges MC., Vidriales B., Valverde B., Ocqueteau M, et al. Prognostic value of immunophenotypic detection of minimal residual disease in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 1998. 16:3774–81.
Article7.Coustan-Smith E., Sancho J., Hancock ML., Boyett JM., Behm FG., Raimondi SC, et al. Clinical importance of minimal residual disease in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2000. 96:2691–6.
Article8.Coustan-Smith E., Sancho J., Behm FG., Hancock ML., Razzouk BI., Ribeiro RC, et al. Prognostic importance of measuring early clearance of leukemic cells by flow cytometry in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2002. 100:52–8.
Article9.Dworzak MN., Froschl G., Printz D., Mann G., Potschger U., Muhlegger N, et al. Prognostic significance and modalities of flow cytometric minimal residual disease detection in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2002. 99:1952–8.
Article10.Coustan-Smith E., Gajjar A., Hijiya N., Razzouk BI., Ribeiro RC., Rivera GK, et al. Clinical significance of minimal residual disease in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia after first relapse. Leukemia. 2004. 18:499–504.
Article11.Coustan-Smith E., Ribeiro RC., Stow P., Zhou Y., Pui CH., Rivera GK, et al. A simplified flow cytometric assay identifies children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia who have a superior clinical outcome. Blood. 2006. 108:97–102.
Article12.Borowitz MJ., Devidas M., Hunger SP., Bowman WP., Carroll AJ., Carroll WL, et al. Clinical significance of minimal residual disease in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia and its relationship to other prognostic factors: a Children's Oncology Group study. Blood. 2008. 111:5477–85.
Article13.San Miguel JF., Martinez A., Macedo A., Vidriales MB., Lopez-Berges C., Gonzalez M, et al. Immunophenotyping investigation of minimal residual disease is a useful approach for predicting relapse in acute myeloid leukemia patients. Blood. 1997. 90:2465–70.
Article14.Venditti A., Buccisano F., Del Poeta G., Maurillo L., Tamburini A., Cox C, et al. Level of minimal residual disease after consolidation therapy predicts outcome in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2000. 96:3948–52.
Article15.Plata E., Choremi-Papadopoulou H., Viglis V., Yataganas X. Flow-cytometric detection of minimal residual disease with atypical antigen combinations in patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia. Ann Hematol. 2000. 79:543–6.
Article16.San Miguel JF., Vidriales MB., Lopez-Berges C., Diaz-Mediavilla J., Gutierrez N., Canizo C, et al. Early immunophenotypical evaluation of minimal residual disease in acute myeloid leukemia identifies different patient risk groups and may contribute to postinduction treatment stratification. Blood. 2001. 98:1746–51.
Article17.Venditti A., Tamburini A., Buccisano F., Del Poeta G., Maurillo L., Panetta P, et al. Clinical relevance of minimal residual disease detection in adult acute myeloid leukemia. J Hematother Stem Cell Res. 2002. 11:349–57.
Article18.Coustan-Smith E., Ribeiro RC., Rubnitz JE., Razzouk BI., Pui CH., Pounds S, et al. Clinical significance of residual disease during treatment in childhood acute myeloid leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 2003. 123:243–52.
Article19.Kern W., Voskova D., Schoch C., Hiddemann W., Schnittger S., Haferlach T. Determination of relapse risk based on assessment of minimal residual disease during complete remission by multiparameter flow cytometry in unselected patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2004. 104:3078–85.
Article20.Kern W., Voskova D., Schoch C., Schnittger S., Hiddemann W., Haferlach T. Prognostic impact of early response to induction therapy as assessed by multiparameter flow cytometry in acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica. 2004. 89:528–40.21.Feller N., van der Pol MA., van Stijn A., Weijers GW., Westra AH., Evertse BW, et al. MRD parameters using immunophenotypic detection methods are highly reliable in predicting survival in acute myeloid leukaemia. Leukemia. 2004. 18:1380–90.
Article22.Buccisano F., Maurillo L., Gattei V., Del Poeta G., Del Principe MI., Cox MC, et al. The kinetics of reduction of minimal residual disease impacts on duration of response and survival of patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2006. 20:1783–9.
Article23.Shin S., Kahng J., Kim M., Lim J., Kim Y., Han K. Distribution of antigenic aberration in the bone marrow of acute leukemia in complete remission. Korean J Lab Med. 2008. 28:1–7. (신소영, 강지민, 김명신, 임지향, 김용구, 한경자. 급성백혈병 완전 관해 골수에서 항원형 이상 세포의분포. 대한진단검사의학회지 2008;28:1-7.).
Article24.Kern W., Danhauser-Riedl S., Ratei R., Schnittger S., Schoch C., Kolb HJ, et al. Detection of minimal residual disease in unselected patients with acute myeloid leukemia using multiparameter flow cytometry for definition of leukemia-associated immunophenotypes and determination of their frequencies in normal bone marrow. Haematologica. 2003. 88:646–53.25.Mrozek K., Heerema NA., Bloomfield CD. Cytogenetics in acute leukemia. Blood Rev. 2004. 18:115–36.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Distribution of Antigenic Aberration in the Bone Marrow of Acute Leukemia in Complete Remission
- Prognostic significance of minimal residual disease detected by a simplified flow cytometric assay during remission induction chemotherapy in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Measurements of treatment response in childhood acute leukemia
- Unusual Antigen Expression of Acute Leukemia
- Immunotherapeutic potential of JL1, a thymocyte surface protein, for leukemia