Ann Lab Med.
2013 May;33(3):221-224. 10.3343/alm.2013.33.3.221.
A Novel Mutation (c.200T>C) in the NAGLU Gene of a Korean Patient with Mucopolysaccharidosis IIIB
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. nayadoo@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jindk@skku.edu
- KMID: 1781332
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2013.33.3.221
Abstract
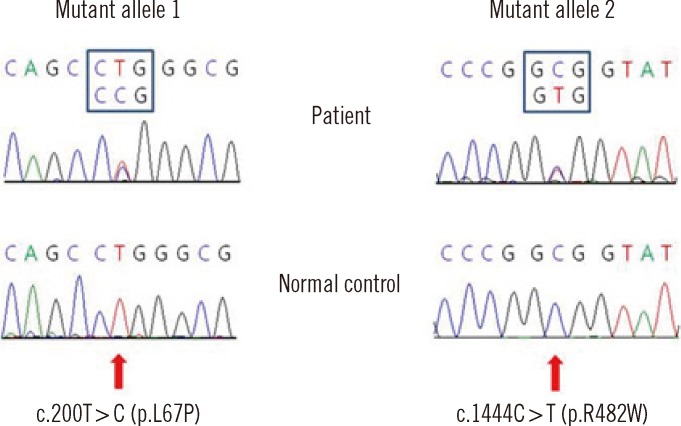
- Mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS) IIIB is a lysosomal storage disorder (LSD) caused by abnormalities of the enzyme alpha-N-acetylglucosaminidase (NAGLU) that is required for degradation of heparan sulfate. The patient in this study was a 4-yr-old boy. He presented with normal height and weight, pectus carinatum, and multiple persistent Mongolian spots on his back. He had mild dysmorphic features with prominent speech developmental delays and, to a lesser extent, motor developmental delays. The cetylpyridinium chloride precipitation test revealed excessive mucopolysacchariduria (657.2 mg glycosaminoglycan/g creatinine; reference range, <175 mg glycosaminoglycan/g creatinine). Thin layer chromatography showed urinary heparan sulfate excretion. NAGLU enzyme activity was significantly decreased in leukocytes (not detected; reference range, 0.9-1.51 nmol/hr/mg protein) as well as in plasma (0.14 nmol/hr/mg protein; reference range, 22.3-60.9 nmol/hr/mg protein). PCR and direct sequencing analysis of the NAGLU gene showed that the patient was a compound heterozygote for 2 mutations: c.200T>C (p.L67P) and c.1444C>T (p.R482W). The c.200T>C mutation was a novel finding. This is the first report of a Korean patient with MPS IIIB who was confirmed by molecular genetic analyses and biochemical investigation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Acetylglucosaminidase/blood/*genetics
Alleles
Asian Continental Ancestry Group/*genetics
Child, Preschool
Chromatography, Thin Layer
Heterozygote
Humans
Leukocytes/metabolism
Male
Mucopolysaccharidosis III/diagnosis/*genetics
Mutation
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Republic of Korea
Sequence Analysis, DNA
Acetylglucosaminidase
Figure
Reference
-
1. Saudubray JM, Berghe VG, Walter JH, editors. Inborn metabolic disease. 2012. 5th ed. Berlin: Springer;p. 580–590.2. Valstar MJ, Bruggenwirth HT, Olmer R, Wevers RA, Verheijen FW, Poorthuis BJ, et al. Mucopolysaccharidosis type IIIB may predominantly present with an attenuated clinical phenotype. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2010; 33:759–767. PMID: 20852935.
Article3. Verhoeven WM, Csepán R, Marcelis CL, Lefeber DJ, Egger JI, Tuinier S. Sanfilippo B in an elderly female psychiatric patient: a rare but relevant diagnosis in presenile dementia. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2010; 122:162–165. PMID: 20040070.
Article4. Zhao HG, Li HH, Bach G, Schmidtchen A, Neufeld EF. The molecular basis of Sanfilippo syndrome type B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996; 93:6101–6105. PMID: 8650226.
Article5. Weber B, Blanch L, Clements PR, Scott HS, Hopwood JJ. Cloning and expression of the gene involved in Sanfilippo B syndrome (mucopolysaccharidosis III B). Hum Mol Genet. 1996; 5:771–777. PMID: 8776591.
Article6. Sohn WY, Lee JH, Paik KH, Kwon EK, Kim AH, Jin DK. Clinical and laboratory features of Korean mucopolysaccharidoses (MPSs). Korean J Pediatr. 2005; 48:1132–1138.7. Ng PC. Predicting deleterious amino acid substitutions. Genome Res. 2001; 11:863–874. PMID: 11337480.
Article8. Ramensky V, Bork P, Sunyaev S. Human non-synonymous SNPs: server and survey. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002; 30:3894–3900. PMID: 12202775.
Article9. Bunge S, Knigge A, Steglich C, Kleijer WJ, van Diggelen OP, Beck M, et al. Mucopolysaccharidosis type IIIB (Sanfilippo B): identification of 18 novel alpha-N-acetylglucosaminidase gene mutations. J Med Genet. 1999; 36:28–31. PMID: 9950362.10. Tanaka A, Kimura M, Lan HT, Takaura N, Yamano T. Molecular analysis of the alpha-N-acetylglucosaminidase gene in seven Japanese patients from six unrelated families with mucopolysaccharidosis IIIB (Sanfilippo type B), including two novel mutations. J Hum Genet. 2002; 47:484–487. PMID: 12202988.11. Valstar MJ, Ruijter GJ, van Diggelen OP, Poorthuis BJ, Wijburg FA. Sanfilippo syndrome: A mini-review. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2008; 31:240–252. PMID: 18392742.
Article12. Lin HY, Lin SP, Chuang CK, Niu DM, Chen MR, Tsai FJ, et al. Incidence of the mucopolysaccharidoses in Taiwan, 1984-2004. Am J Med Genet A. 2009; 149A:960–964. PMID: 19396827.
Article13. Héron B, Mikaeloff Y, Froissart R, Caridade G, Maire I, Caillaud C, et al. Incidence and natural history of mucopolysaccharidosis type III in France and comparison with United Kingdom and Greece. Am J Med Genet A. 2011; 155A:58–68. PMID: 21204211.
Article14. Poorthuis BJ, Wevers RA, Kleijer WJ, Groener JE, de Jong JG, van Weely S, et al. The frequency of lysosomal storage diseases in The Netherlands. Hum Genet. 1999; 105:151–156. PMID: 10480370.
Article15. Baehner F, Schmiedeskamp C, Krummenauer F, Miebach E, Bajbouj M, Whybra C, et al. Cumulative incidence rates of the mucopolysaccharidoses in Germany. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2005; 28:1011–1017. PMID: 16435194.
Article16. Weber B, Guo XH, Kleijer WJ, van de, Poorthuis BJ, Hopwood JJ. Sanfilippo type B syndrome (mucopolysaccharidosis III B): allelic heterogeneity corresponds to the wide spectrum of clinical phenotypes. Eur J Hum Genet. 1999; 7:34–44. PMID: 10094189.
Article17. Yogalingam G. Molecular genetics of mucopolysaccharidosis type IIIA and IIIB: Diagnostic, clinical, and biological implications. Hum Mutat. 2001; 18:264–281. PMID: 11668611.
Article18. van de Kamp JJ, Niermeijer MF, von Figura K, Giesberts MA. Genetic heterogeneity and clinical variability in the Sanfilippo syndrome (types A, B, and C). Clin Genet. 1981; 20:152–160. PMID: 6796310.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Long-term clinical course of a patient with mucopolysaccharidosis type IIIB
- Birth of a healthy baby after preimplantation genetic diagnosis in a carrier of mucopolysaccharidosis type II: The first case in Korea
- Comparative Study of p53 Mutation and Oncoprotein Expression in Gastric Adenocarcinoma
- A Case of Mucopolysaccharidosis Type I with Spinal Cord Compression
- Germline Mutation of Rb1 Gene in Korean Retinoblastoma Patients