J Korean Med Sci.
2010 Feb;25(2):197-202. 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.2.197.
Genetic Correlation of Community-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Strains from Carriers and from Patients with Clinical Infection in One Region of Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea. ttezebae@gmail.com
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea.
- 3Gyeonsang Institute of Health Science, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea.
- 4Department of Laboratory Medicine, Hallym Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Laboratory Medicine, Pusan National University, School of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 1779247
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2010.25.2.197
Abstract
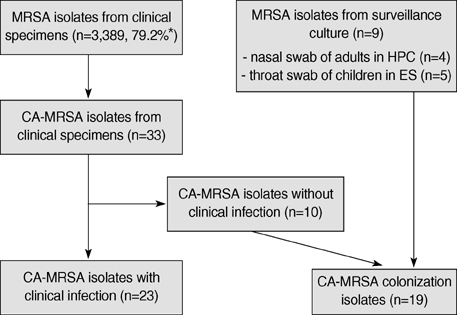
- Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA) is an increasingly common worldwide and colonizing S. aureus strains may serve as the causative pathogen for overt clinical infections. This study was performed to determine whether the pathogenic CA-MRSA isolate in clinical infections was genetically related to the MRSA isolates in community carriers. We prospectively collected a total of 42 CA-MRSA isolates (23 clinical infection isolates and 19 colonization isolates) in a local region of Korea. Antimicrobial susceptibility tests, staphylococcal toxin assays, SCCmec typing, multilocus sequence typing (MLST), and spa (staphylococcal protein A) typing were performed with all isolates. Thirty-four (81%) of 42 CA-MRSA isolates belonged to sequence type (ST) 72 in the MLST analysis. The distribution of STs did not differ significantly between colonization and clinical infection isolates (89.5% [17/19] vs. 73.9% [17/23], P=0.26). Among the ST72-MRSA isolates, spa type t664 (18, 52.9%) and t324 (8, 23.5%) were common in both groups. This study demonstrates that the community-associated MRSA strains from patients with clinical infections are closely related to the strains found in carriers from one local community.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Molecular Epidemiologic Study of a Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus Outbreak at a Newborn Nursery and Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
Hyun Mi Kang, Ki Cheol Park, Kyung-Yil Lee, Joonhong Park, Sun Hee Park, Dong-Gun Lee, Jong-Hyun Kim
Pediatr Infect Vaccine. 2019;26(3):148-160. doi: 10.14776/piv.2019.26.e23.Clinical Features of Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome Caused by Community-Associated Methicillin-Resistant
Staphylococcus aureus in Changwon City, Korea, during 2006 and 2015
Jun Hyeong Park, Min Chae Kim, Jin Han Kang, Jae Won Choi, Hak Sung Lee, Ju Hwa Shin, Je Chul Lee, Sang Hyuk Ma
Pediatr Infect Vaccine. 2019;26(1):42-50. doi: 10.14776/piv.2019.26.e5.
Reference
-
1. Kim HB, Park WB, Lee KD, Choi YJ, Park SW, Oh MD, Kim EC, Choe KW. Nationwide surveillance for Staphylococcus aureus with reduced susceptibility to vancomycin in Korea. J Clin Microbiol. 2003. 41:2279–2281.2. Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections--Michigan. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1981. 30:185–187.3. Herold BC, Immergluck LC, Maranan MC, Lauderdale DS, Gaskin RE, Boyle-Vavra S, Leitch CD, Daum RS. Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in children with no identified predisposing risk. JAMA. 1998. 279:593–598.4. Salmenlinna S, Lyytikainen O, Vuopio-Varkila J. Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Finland. Emerg Infect Dis. 2002. 8:602–607.5. Vandenesch F, Naimi T, Enright MC, Lina G, Nimmo GR, Heffernan H, Liassine N, Bes M, Greenland T, Reverdy ME, Etienne J. Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus carrying Panton-Valentine leukocidin genes: worldwide emergence. Emerg Infect Dis. 2003. 9:978–984.6. Fridkin SK, Hageman JC, Morrison M, Sanza LT, Como-Sabetti K, Jernigan JA, Harriman K, Harrison LH, Lynfield R, Farley MM. Active Bacterial Core Surveillance Program of the Emerging Infections Program Network. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus disease in three communities. N Engl J Med. 2005. 352:1436–1444.7. Zetola N, Francis JS, Nuermberger EL, Bishai WR. Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: an emerging threat. Lancet Infect Dis. 2005. 5:275–286.8. Tenover FC, McDougal LK, Goering RV, Killgore G, Projan SJ, Patel JB, Dunman PM. Characterization of a strain of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus widely disseminated in the United States. J Clin Microbiol. 2006. 44:108–118.9. Lina G, Piemont Y, Godail-Gamot F, Bes M, Peter MO, Gauduchon V, Vandenesch F, Etienne J. Involvement of Panton-Valentine leukocidin-producing Staphylococcus aureus in primary skin infections and pneumonia. Clin Infect Dis. 1999. 29:1128–1132.10. von Eiff C, Becker K, Machka K, Stammer H, Peters G. Nasal carriage as a source of Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. Study Group. N Engl J Med. 2001. 344:11–16.11. Kluytmans J, van Belkum A, Verbrugh H. Nasal carriage of Staphylococcus aureus: epidemiology, underlying mechanisms, and associated risks. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1997. 10:505–520.12. Enright MC, Day NP, Davies CE, Peacock SJ, Spratt BG. Multilocus sequence typing for characterization of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible clones of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 2000. 38:1008–1015.13. Harmsen D, Claus H, Witte W, Rothganger J, Turnwald D, Vogel U. Typing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a university hospital setting by using novel software for spa repeat determination and database management. J Clin Microbiol. 2003. 41:5442–5448.14. McDougal LK, Steward CD, Killgore GE, Chaitram JM, McAllister SK, Tenover FC. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis typing of oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from the United States: establishing a national database. J Clin Microbiol. 2003. 41:5113–5120.15. Zhang K, McClure JA, Elsayed S, Louie T, Conly JM. Novel multiplex PCR assay for characterization and concomitant subtyping of staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec types I to V in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. 43:5026–5033.16. Murchan S, Kaufmann ME, Deplano A, de Ryck R, Struelens M, Zinn CE, Fussing V, Salmenlinna S, Vuopio-Varkila J, El Solh N, Cuny C, Witte W, Tassios PT, Legakis N, van Leeuwen W, van Belkum A, Vindel A, Laconcha I, Garaizar J, Haeggman S, Olsson-Liljequist B, Ransjo U, Coombes G, Cookson B. Harmonization of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis protocols for epidemiological typing of strains of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a single approach developed by consensus in 10 European laboratories and its application for tracing the spread of related strains. J Clin Microbiol. 2003. 41:1574–1585.17. Aires-de-Sousa M, Boye K, de Lencastre H, Deplano A, Enright MC, Etienne J, Friedrich A, Harmsen D, Holmes A, Huijsdens XW, Kearns AM, Mellmann A, Meugnier H, Rasheed JK, Spalburg E, Strommenger B, Struelens MJ, Tenover FC, Thomas J, Vogel U, Westh H, Xu J, Witte W. High interlaboratory reproducibility of DNA sequence-based typing of bacteria in a multicenter study. J Clin Microbiol. 2006. 44:619–621.
Article18. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing: 17th informational supplement. 2007. Wayne, PA: CLSI.19. Peacock SJ, Moore CE, Justice A, Kantzanou M, Story L, Mackie K, O'Neill G, Day NP. Virulent combinations of adhesin and toxin genes in natural populations of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 2002. 70:4987–4996.20. Oliveira DC, de Lencastre H. Multiplex PCR strategy for rapid identification of structural types and variants of the mec element in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002. 46:2155–2161.21. Shopsin B, Gomez M, Montgomery SO, Smith DH, Waddington M, Dodge DE, Bost DA, Riehman M, Naidich S, Kreiswirth BN. Evaluation of protein A gene polymorphic region DNA sequencing for typing of Staphylococcus aureus strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1999. 37:3556–3563.22. Wang CC, Lo WT, Chu ML, Siu LK. Epidemiological typing of community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from children in Taiwan. Clin Infect Dis. 2004. 39:481–487.23. Ma SH, Lee YS, Lee SH, Kim HK, Jin JS, Shin EK, Lee JC. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clones with distinct clinical and microbiological features in a Korean community. J Med Microbiol. 2007. 56:866–868.24. Kim ES, Song JS, Lee HJ, Choe PG, Park KH, Cho JH, Park WB, Kim SH, Bang JH, Kim DM, Park KU, Shin S, Lee MS, Choi HJ, Kim NJ, Kim EC, Oh MD, Kim HB, Choe KW. A survey of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Korea. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2007. 60:1108–1114.25. Cha HY, Moon DC, Choi CH, Oh JY, Jeong YS, Lee YC, Seol SY, Cho DT, Chang HH, Kim SW, Lee JC. Prevalence of the ST239 clone of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and differences in antimicrobial susceptibilities of ST239 and ST5 clones identified in a Korean hospital. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. 43:3610–3614.26. Gustafsson EB, Ringberg H, Johansson PJ. MRSA in children from foreign countries adopted to Swedish families. Acta Paediatr. 2007. 96:105–108.
Article27. Ko KS, Park S, Peck KR, Shin EJ, Oh WS, Lee NY, Song JH. Molecular characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus spread by neonates transferred from primary obstetrics clinics to a tertiary care hospital in Korea. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2006. 27:593–597.28. Gillet Y, Issartel B, Vanhems P, Fournet JC, Lina G, Bes M, Vandenesch F, Piémont Y, Brousse N, Floret D, Etienne J. Association between Staphylococcus aureus strains carrying gene for Panton-Valentine leukocidin and highly lethal necrotising pneumonia in young immunocompetent patients. Lancet. 2002. 359:753–759.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Infection in Neonates
- A case of multiple furunculosis caused by methicillin-resistant staphylococcs aureus
- A Survey for Methicillin - Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus
- Community-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Nosocomial Infections
- Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA)