J Korean Med Sci.
2009 Aug;24(4):747-750. 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.4.747.
A Case of Wernicke's Encephalopathy Following Fluorouracil-based Chemotherapy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Hematology-Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea. oncolee@ewha.ac.kr
- KMID: 1779215
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2009.24.4.747
Abstract
- The pyrimidine antimetabolite 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) is a chemotherapeutic agent used widely for various tumors. Common side effects of 5-FU are related to its effects on the bone marrow and gastrointestinal epithelium. Neurotoxicity caused by 5-FU is uncommon, although acute and delayed forms have been reported. Wernicke's encephalopathy is an acute, neuropsychiatric syndrome resulting from thiamine deficiency, and has significant morbidity and mortality. Central nervous system neurotoxicity such as Wernicke's encephalopathy following chemotherapy with 5-FU has been reported rarely, although it has been suggested that 5-FU can produce adverse neurological effects by causing thiamine deficiency. We report a patient with Wernicke's encephalopathy, reversible with thiamine therapy, associated with 5-FU-based chemotherapy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Acute Disease
Antimetabolites, Antineoplastic/*adverse effects
Female
Fluorouracil/*adverse effects
Humans
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Middle Aged
Nasopharyngeal Neoplasms/drug therapy/radiotherapy
Thiamine/therapeutic use
Thiamine Deficiency/*complications/diagnosis
Wernicke Encephalopathy/*chemically induced/diagnosis
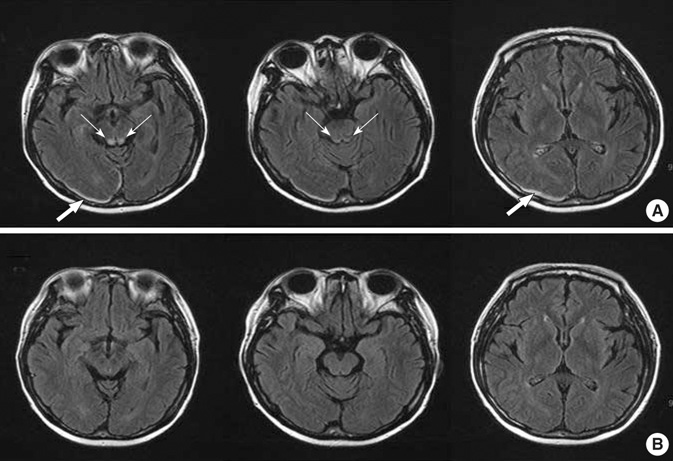
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Two Cases of Wernicke's Encephalopathy That Developed during Total Parenteral Nutrition in Colon Cancer Patients Treated with 5-Fluorouracil-based Chemotherapy
Kyung Pyo Cho, Jae Sung Lee, Ji Seok Seong, Yong Moon Woo, Young Jun Cho, Beom Jin Jeong, Jee Hoon Sohn, Su-Jung Kim
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2014;64(3):158-163. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2014.64.3.158.A Case of 5-Fluorouracil Induced Encephalopathy
Kyung A Kwon, Hyuk-Chan Kwon, Min Chan Kim, Sung-Hyun Kim, Sung Yong Oh, Suee Lee, Hyo-Jin Kim
Cancer Res Treat. 2010;42(2):118-120. doi: 10.4143/crt.2010.42.2.118.
Reference
-
1. Kummar S, Noronha V, Chu E. Devita VT, Hellman S, Rosenberg SA, editors. Antimetabolites. Cancer: principles and practice of oncology. 2005. volume 1:7th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;361–364.2. Sausville EA, Longo DL. Kasper DL, Braunwald E, Fauci AS, Hauser SL, Longo DL, Jameson JL, editors. Principles of cancer treatment: surgery, chemotherapy and biologic therapy. Harrison's principles of internal medicine. 2005. volume 1:16th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill;476.3. Pirzada NA, Ali II, Dafer RM. Fluorouracil-induced neurotoxicity. Ann Pharmacother. 2000. 34:35–38.
Article4. Kim YA, Chung HC, Choi HJ, Rha SY, Seong JS, Jeung HC. Intermediate dose 5-fluorouracil-induced encephalopathy. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2006. 36:55–59.
Article5. Yeh KH, Cheng AL. High-dose 5-fluorouracil infusional therapy is associated with hyperammonaemia, lactic acidosis and encephalopathy. Br J Cancer. 1997. 75:464–465.
Article6. Sechi G, Serra A. Wernicke's encephalopathy: new clinical settings and recent advances in diagnosis and management. Lancet Neurol. 2007. 6:442–455.
Article7. Attard O, Dietemann JL, Diemunsch P, Pottecher T, Meyer A, Calon BL. Wernicke encephalopathy: a complication of parenteral nutrition diagnosed by magnetic resonance imaging. Anesthesiology. 2006. 105:847–848.
Article8. Merkin-Zaborsky H, Ifergane G, Frisher S, Valdman S, Herishanu Y, Wirguin I. Thiamine-responsive acute neurological disorders in nonalcoholic patients. Eur Neurol. 2001. 45:34–37.
Article9. Chiossi G, Neri I, Cavazzuti M, Basso G, Facchinetti F. Hyperemesis gravidarum complicated by Wernicke encephalopathy: background, case report, and review of the literature. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 2006. 61:255–268.
Article10. Seo IS, Lee SH, Kim SH, Kim WS, Lee KS, Song SK, Lee WG, Kim EH, Choi YW, Lee YU. A case of acute coma & respiratory arrest in Wernicke's encephalopathy caused by malnutrition . Korean J Med. 1998. 55:137–144.11. Kondo K, Fujiwara M, Murase M, Kodera Y, Akiyama S, Ito K, Takagi H. Severe acute metabolic acidosis and Wernicke's encephalopathy following chemotherapy with 5-fluorouracil and cisplatin: case report and review of the literature. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 1996. 26:234–236.
Article12. Aksoy M, Basu TK, Brient J, Dickerson JW. Thiamin status of patients treated with drug combinations containing 5-fluorouracil. Eur J Cancer. 1980. 16:1041–1045.
Article13. Steeghs N, de Jongh FE, Sillevis Smitt PA, van den Bent MJ. Cisplatin-induced encephalopathy and seizures. Anticancer Drugs. 2003. 14:443–446.
Article14. Hong SH, Kim ES, Roh YW, Jung SK, Chung C, Kong HS, Yun CB, Kang SS, Lee SK, Hwang HY, Bang SM, Cho EK, Shin DB, Lee JH. A case of iatrogenic Wernicke's encephalopathy following chemotherapy and total parenteral nutrition. Korean J Hematol. 2001. 36:95–99.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Two Cases of Wernicke's Encephalopathy with Hyperemesis Gravidarum
- A Case of Bilateral Sudden Deafness Caused by Wernicke Encephalopathy
- A Case of Wernicke's Encephalopathy Associated with Hyperemesis Gravidarum
- Wernicke Encephalopathy in a Homeless Patient With Delusions: A Case Report
- A Case of Wernicke's Encephalopathy Associated with Hyperemesis Gravidarum