J Korean Med Sci.
2005 Jun;20(3):499-501. 10.3346/jkms.2005.20.3.499.
A Novel Mutation (A148V) in the Glucose 6-phosphate Translocase (SLC37A4) Gene in a Korean Patient with Glycogen Storage Disease Type 1b
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jwonk@smc.samsung.co.kr
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine, Inha University, Inchon, Korea.
- 4Department of Radiology, College of Medicine, Inha University, Inchon, Korea.
- KMID: 1778514
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2005.20.3.499
Abstract
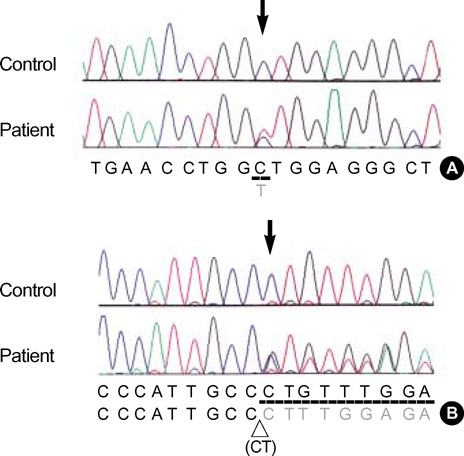
- We report a Korean patient with glycogen storage disease type 1b (GSD-1b) whose diagnosis was confirmed by liver biopsy and laboratory results. The patient presented with delay of puberty and short stature on admission and had typical clinical symptoms of GSD as well as chronic neutropenia and inflammatory bowel disease. Mutation analysis of the glucose 6-phosphate translocase 6-phosphate translocase (SLC37A4) gene revealed that the patient was a compound heterozygote of two different mutations including a deletion mutation (c.1042_1043delCT; L348fs) and a missense mutation (A148V). The L348fs mutation was inherited from the patient's father and has been reported in an Italian family with GSD-1b, while the A148V mutation was transmitted from the patient's mother and was a novel mutation. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of genetically confirmed case of GSD-1b in Korean.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Esophageal Stricture Secondary to Candidiasis in a Child with Glycogen Storage Disease 1b
Kyung Jae Lee, Shin Jie Choi, Woo Sun Kim, Sung-Sup Park, Jin Soo Moon, Jae Sung Ko
Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2016;19(1):71-75. doi: 10.5223/pghn.2016.19.1.71.Improvement of neutropenia in 2 adolescent cases treated with empagliflozin for glycogen storage disease type Ib
Hyunwoo Bae
Pediatr Emerg Med J. 2024;11(3):136-141. doi: 10.22470/pemj.2024.01011.
Reference
-
1. Gerin I, Veiga-da-Cunha M, Achouri Y, Collet JF, Van Schaftingen E. Sequence of a putative glucose 6-phosphate translocase, mutated in glycogen storage disease type Ib. FEBS Lett. 1997. 419:235–238.2. Veiga-da-Cunha M, Gerin I, Chen YT, de Barsy T, de Lonlay P, Dionisi-Vici C, Fenske CD, Lee PJ, Leonard JV, Maire I, McConkie-Rosell A, Schweitzer S, Vikkula M, Van Schaftingen E. A gene on chromosome 11q23 coding for a putative glucose-6-phosphate translocase is mutated in glycogen-storage disease types Ib and Ic. Am J Hum Genet. 1998. 63:976–983.3. Galli L, Orrico A, Marcolongo P, Fulceri R, Burchell A, Melis D, Parini R, Gatti R, Lam C, Benedetti A, Sorrentino V. Mutations in the glucose-6-phosphate transporter (G6PT) gene in patients with glycogen storage diseases type 1b and 1c. FEBS Lett. 1999. 459:255–258.
Article4. Veiga-da-Cunha M, Gerin I, Chen YT, Lee PJ, Leonard JV, Maire I, Wendel U, Vikkula M, Van Schaftingen E. The putative glucose 6-phosphate translocase gene is mutated in essentially all cases of glycogen storage disease type I non-a. Eur J Hum Genet. 1999. 7:717–723.
Article5. Lam CW, Sin SY, Lau ET, Lam YY, Poon P, Tong SF. Prenatal diagnosis of glycogen storage disease type 1b using denaturing high performance liquid chromatography. Prenat Diagn. 2000. 20:765–768.
Article6. Marcolongo P, Barone V, Priori G, Pirola B, Giglio S, Biasucci G, Zammarchi E, Parenti G, Burchell A, Benedetti A, Sorrentino V. Structure and mutation analysis of the glycogen storage disease type 1b gene. FEBS Lett. 1998. 436:247–250.
Article7. Chen YT, Bruchell A. Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D, editors. Glycogen storage disease. The Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease. 7th edn. McGraw-Hill;395–965.8. Lei KJ, Pan CJ, Shelly LL, Liu JL, Chou JY. Identification of mutations in the gene for glucose-6-phosphatase, the enzyme deficient in glycogen storage disease type 1a. J Clin Invest. 1994. 93:1994–1999.
Article9. Beaudet AL, Anderson DC, Michels VV, Arion WJ, Lange AJ. Neutropenia and impaired neutrophil migration in type IB glycogen storage disease. J Pediatr. 1980. 97:906–910.
Article10. Kure S, Suzuki Y, Matsubara Y, Sakamoto O, Shintaku H, Isshiki G, Hoshida C, Izumi I, Sakura N, Narisawa K. Molecular analysis of glycogen storage disease type Ib: identification of a prevalent mutation among Japanese patients and assignment of a putative glucose-6-phosphate translocase gene to chromosome 11. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998. 248:426–431.
Article11. Gerin I, Veiga-da-Cunha M, Noel G, Van Schaftingen E. Structure of the gene mutated in glycogen storage disease type Ib. Gene. 1999. 227:189–195.
Article12. Hiraiwa H, Pan CJ, Lin B, Moses SW, Chou JY. Inactivation of the glucose 6-phosphate transporter causes glycogen storage disease type 1b. J Biol Chem. 1999. 274:5532–5536.
Article13. Janecke AR, Bosshard NU, Mayatepek E, Schulze A, Gitzelmann R, Burchell A, Bartram CR, Janssen B. Molecular diagnosis of type 1c glycogen storage disease. Human Genet. 1999. 104:275–277.
Article14. Chen LY, Pan CJ, Shieh JJ, Chou JY. Structure-function analysis of the glucose-6 phosphate transporter deficient in glycogen storage disease type Ib. Hum Mol Genet. 2002. 11:3199–3207.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of glycogen storage disease type Ib
- Esophageal Stricture Secondary to Candidiasis in a Child with Glycogen Storage Disease 1b
- Improvement of neutropenia in 2 adolescent cases treated with empagliflozin for glycogen storage disease type Ib
- Novel SLC37A4 Mutations in Korean Patients With Glycogen Storage Disease Ib
- A case of multiple hepatic adenomas and gout with glycogen storage disease type Ia