Clinicopathological Characteristics of Mucinous Carcinoma of the Breast in Korea: Comparison with Invasive Ductal Carcinoma-Not Otherwise Specified
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. bwpark@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Pathology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Surgery, Pochon CHA University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 1778029
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2010.25.3.361
Abstract
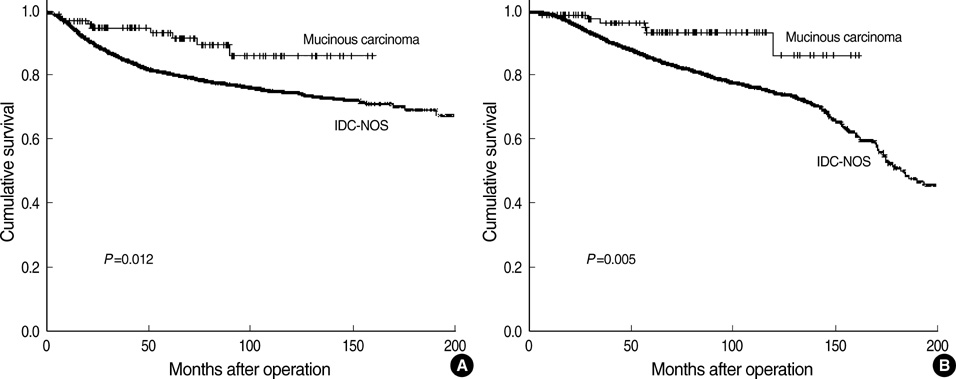
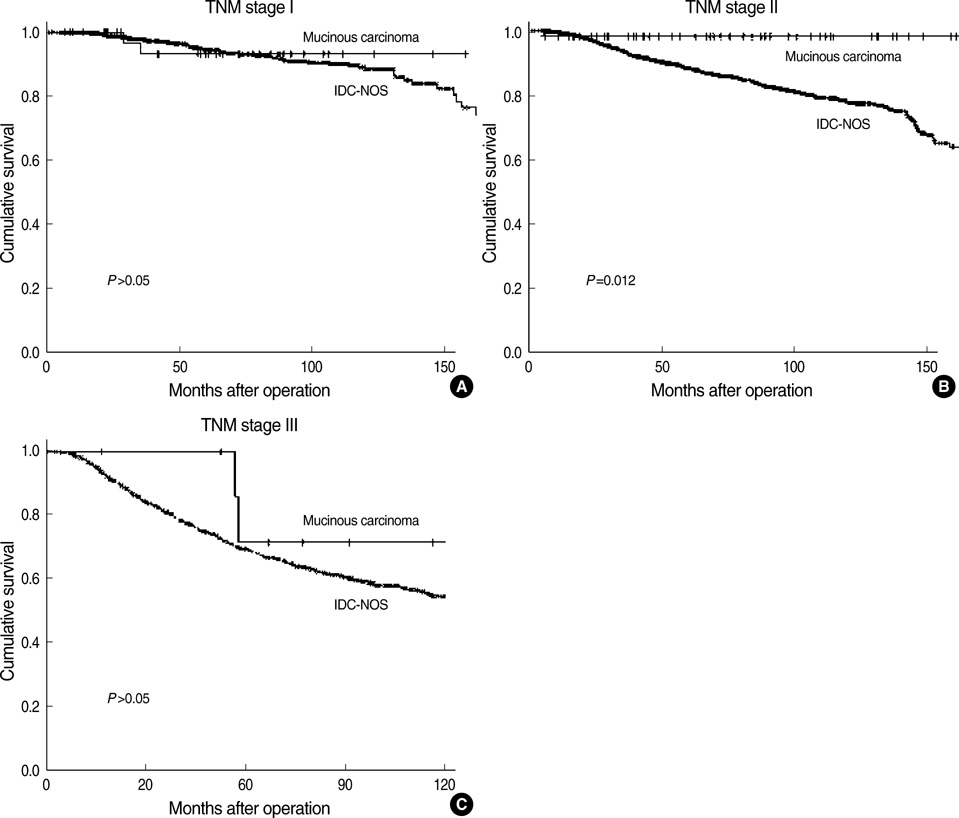
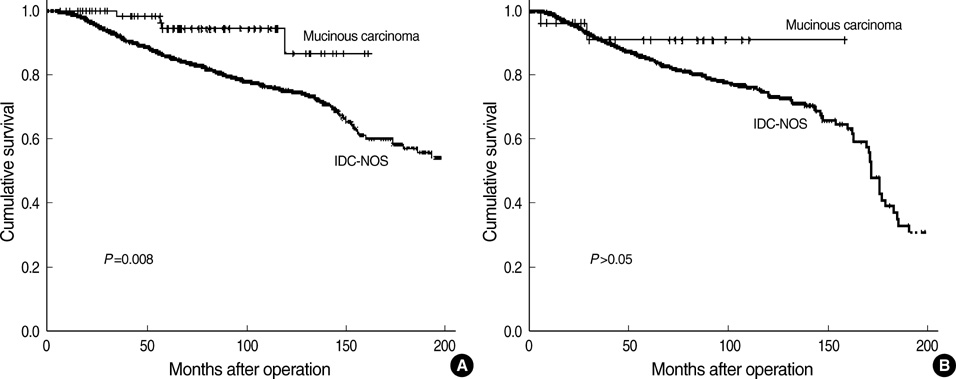
- Clinicopathological characteristics and prognostic factors of mucinous carcinoma (MC) were compared with invasive ductal carcinoma-not otherwise specified (IDC-NOS). Clinicopathological characteristics and survivals of 104 MC patients were retrospectively reviewed and compared with those of 3,936 IDC-NOS. The median age at diagnosis was 45 yr in MC and 47 yr in IDC-NOS, respectively. The sensitivity of mammography and sonography for pure MC were 76.5% and 94.7%, respectively. MC showed favorable characteristics including less involvement of lymph node, lower stage, more expression of estrogen receptors, less HER-2 overexpression and differentiated grade, and better 10-yr disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS) (86.1% and 86.3%, respectively) than IDC-NOS (74.7% and 74.9%, respectively). Ten-year DFS of pure and mixed type was 90.2% and 68.8%, respectively. Nodal status and stage were statistically significant factors for survival. MC in Koreans showed similar features to Western populations except for a younger age of onset than in IDC-NOS. Since only pure MC showed better prognosis than IDC-NOS, it is important to differentiate mixed MC from pure MC. Middle-aged Korean women presenting breast symptoms should be examined carefully and evaluated with an appropriate diagnostic work-up because some patients present radiologically benign-like lesions.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adenocarcinoma, Mucinous/diagnosis/genetics/*pathology
Adult
Aged
Aged, 80 and over
Breast/pathology
Breast Neoplasms/classification/diagnosis/genetics/*pathology
Carcinoma, Ductal/diagnosis/genetics/*pathology
Disease-Free Survival
Female
Genes, erbB-2
Humans
Korea
Lymphatic Metastasis
Mammography
Middle Aged
Prognosis
Retrospective Studies
Sensitivity and Specificity
Survival Rate
Young Adult
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Mucinous Carcinoma of the Breast in Comparison with Invasive Ductal Carcinoma: Clinicopathologic Characteristics and Prognosis
Soo Youn Bae, Min-Young Choi, Dong Hui Cho, Jeong Eon Lee, Seok Jin Nam, Jung-Hyun Yang
J Breast Cancer. 2011;14(4):308-313. doi: 10.4048/jbc.2011.14.4.308.Comparison of the Distribution Pattern of 21-Gene Recurrence Score between Mucinous Breast Cancer and Infiltrating Ductal Carcinoma in Chinese Population: A Retrospective Single-Center Study
Jiayi Wu, Shuning Ding, Lin Lin, Xiaochun Fei, Caijin Lin, Lisa Andriani, Chihwan Goh, Jiahui Huang, Jin Hong, Weiqi Gao, Siji Zhu, Hui Wang, Ou Huang, Xiaosong Chen, Jianrong He, Yafen Li, Kunwei Shen, Weiguo Chen, Li Zhu
Cancer Res Treat. 2020;52(3):671-679. doi: 10.4143/crt.2019.387.
Reference
-
1. Louwman MW, Vriezen M, van Beek MW, Nolthenius-Puylaert MC, van der Sangen MJ, Roumen RM, Kiemeney LA, Coebergh JW. Uncommon breast tumors in perspective: incidence, treatment and survival in the Netherlands. Int J Cancer. 2007. 121:127–135.
Article2. Andre S, Cunha F, Bernardo M, Meneses e Sousa J, Cortez F, Soares J. Mucinous carcinoma of the breast: a pathologic study of 82 cases. J Surg Oncol. 1995. 58:162–167.3. Li CI, Uribe DJ, Daling JR. Clinical characteristics of different histologic types of breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 2005. 93:1046–1052.
Article4. Diab SG, Clark GM, Osborne CK, Libby A, Allred DC, Elledge RM. Tumor characteristics and clinical outcome of tubular and mucinous breast carcinomas. J Clin Oncol. 1999. 17:1442–1448.
Article5. Tan PH, Tse GM, Bay BH. Mucinous breast lesions: diagnostic challenges. J Clin Pathol. 2008. 61:11–19.
Article6. Di Saverio S, Gutierrez J, Avisar E. A retrospective review with long term follow up of 11,400 cases of pure mucinous breast carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2008. 111:541–547.
Article7. Komenaka IK, El-Tamer MB, Troxel A, Hamele-Bena D, Joseph KA, Horowitz E, Ditkoff BA, Schnabel FR. Pure mucinous carcinoma of the breast. Am J Surg. 2004. 187:528–532.
Article8. Page DL. Special types of invasive breast cancer, with clinical implications. Am J Surg Pathol. 2003. 27:832–835.
Article9. Silverberg SG, Kay S, Chitale AR, Levitt SH. Colloid carcinoma of the breast. Am J Clin Pathol. 1971. 55:355–363.
Article10. Capella C, Eusebi V, Mann B, Azzopardi JG. Endocrine differentiation in mucoid carcinoma of the breast. Histopathology. 1980. 4:613–630.
Article11. Ahn SH. Clinical characteristics of breast cancer patients in Korea in 2000. Arch Surg. 2004. 139:27–31.12. Jung J. The Korean Breast Cancer Society. Nationwide Korean breast cancer data of 2004 using breast cancer registration program. J Breast Cancer. 2006. 9:151–161.13. Wolff AC, Hammond ME, Schwartz JN, Hagerty KL, Allred DC, Cote RJ, Dowsett M, Fitzgibbons PL, Hanna WM, Langer A, Mc-Shane LM, Paik S, Pegram MD, Perez EA, Press MF, Rhodes A, Sturgeon C, Taube SE, Tubbs R, Vance GH, van de Vijver M, Wheeler TM, Hayes DF. American Society of Clinical Oncology. College of American Pathologists. American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for human epidermal growth factor 2 testing in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2007. 25:118–145.14. Shin HR, Jung KW, Won YJ, Park JG. 2002 Annual report of the Korea Central Cancer Registry: based on registered data from 139 hospitals. Cancer Res Treat. 2004. 36:103–114.
Article15. Son BH, Kwak BS, Kim JK, Kim HJ, Hong SJ, Lee JS, Hwang UK, Yoon HS, Ahn SH. Changing patterns in the clinical characteristics of Korean patients with breast cancer during the last 15 years. Arch Surg. 2006. 141:155–160.
Article16. Ahn SH, Yoo KY. Chronological changes of clinical characteristics in 31,115 new breast cancer patients among Koreans during 1996-2004. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2006. 99:209–214.
Article17. Smith RA, Cokkinides V, Brawley OW. Cancer screening in the United States, 2008: a review of current American Cancer Society guidelines and cancer screening issues. CA Cancer J Clin. 2008. 58:161–179.
Article18. Lee SY, Jeong SH, Kim J, Jung SH, Song KB, Nam CM. Scheduling mammography screening for the early detection of breast cancer in Korean women. J Med Screen. 2007. 14:205–209.
Article19. Dhillon R, Depree P, Metcalf C, Wylie E. Screen-detected mucinous breast carcinoma: potential for delayed diagnosis. Clin Radiol. 2006. 61:423–430.
Article20. Memis A, Ozdemir N, Parildar M, Ustun EE, Erhan Y. Mucinous (colloid) breast cancer: mammographic and US features with histologic correlation. Eur J Radiol. 2000. 35:39–43.
Article21. Matsuda M, Yoshimoto M, Iwase T, Takahasi K, Kasumi F, Akiyama F, Sakamoto G. Mammographic and clinicopathological features of mucinous carcinoma of the breast. Breast Cancer. 2000. 7:65–70.
Article22. Margolese R. Screening mammography in young women: a different perspective. Lancet. 1996. 347:881–882.
Article23. Houssami N, Irwig L, Simpson JM, McKessar M, Noakes J. Sydney Breast Imaging Accuracy Study: comparative sensitivity and specificity of mammography and sonography in young women with symptoms. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003. 180:935–940.24. Foxcroft LM, Evans EB, Porter AJ. The diagnosis of breast cancer in women younger than 40. Breast. 2004. 13:297–306.
Article25. Kim HJ, Kim SW, Chung KW, Chang MC, Youn YK, Oh SK, Choe KJ, Noh DY. Clinicopathologic characteristics of mucinous carcinoma of the breast. J Korean Surg Soc. 2001. 61:266–272.26. Scopsi L, Andreola S, Pilotti S, Bufalino R, Baldini MT, Testori A, Rilke F. Mucinous carcinoma of the breast. A clinicopathologic, histochemical, and immunocytochemical study with special reference to neuroendocrine differentiation. Am J Surg Pathol. 1994. 18:702–711.27. Komaki K, Sakamoto G, Sugano H, Morimoto T, Monden Y. Mucinous carcinoma of the breast in Japan. A prognostic analysis based on morphologic features. Cancer. 1988. 61:989–996.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinicopathologic Characteristics of Apocrine Breast Carcinoma
- MR Imaging of Mucinous Carcinoma of the Breast Associated with Ductal Carcinoma In Situ: Case Report
- Mucinous carcinoma of the breast: distinctive histopathologic and genetic characteristics
- Mucinous precursor lesions of mucinous carcinoma in breast: Incidence and histopathologic features
- Clinicopathologic Analysis of 40 Mucinous Breast Carcinomas