Clinical and Epidemiological Comparison of Human Metapneumovirus and Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Seoul, Korea, 2003-2008
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Asthma and Allergy Center, Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital, Seoul, Korea. kimck@paik.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Laboratory Medicine, Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1778026
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2010.25.3.342
Abstract
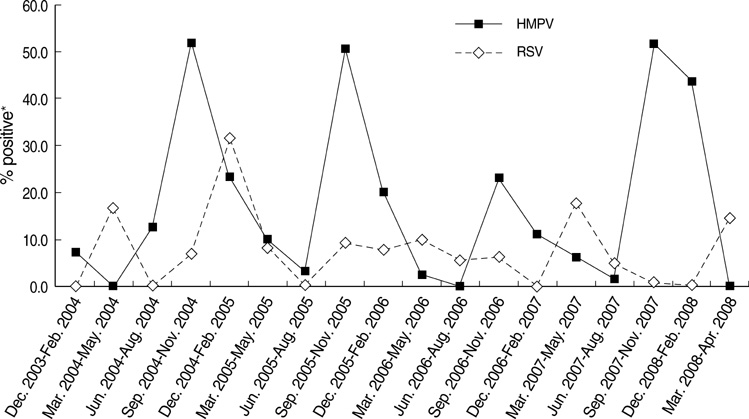
- Human metapneumovirus (HMPV) shares clinical and epidemiological characteristics with well-known respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). The aim of this study was to investigate the clinical and epidemiological differences between HMPV- and RSV-induced wheezing illnesses. A total of 1,008 nasopharyngeal aspirate specimens was collected from 1,008 pediatric patients hospitalized with acute respiratory tract infection at Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital from December 2003 to April 2008, and tested for seven common respiratory viruses. Conditions classified as wheezing illness were bronchiolitis, reactive airways disease, and bronchial asthma. HMPV caused a significantly lower proportion of wheezing illness when compared to RSV (48.1% vs. 82.2%, P<0.05). HMPV-induced wheezing illness occurred predominantly in older patients when compared to RSV patients (P<0.001). RSV infections peaked in the fall and winter followed by peaks of HMPV infection in winter and spring. Eosinophil counts were significantly higher (P<0.01) in RSV patients when compared to HMPV patients. These results show that human metapneumovirus patients exhibit several different clinical and epidemiological characteristics, such as higher proportion of wheezing illness, age and seasonal incidence, and eosinophil counts, when compared to RSV patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Bronchiolitis/physiopathology/virology
Child
Child, Preschool
Female
Humans
Infant
Korea/epidemiology
Male
Metapneumovirus/pathogenicity
Nasopharynx/virology
Paramyxoviridae Infections/*epidemiology/*physiopathology/virology
Respiratory Sounds/*physiopathology
Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infections/*epidemiology/*physiopathology/virology
Respiratory Syncytial Viruses/pathogenicity
Retrospective Studies
Seasons
Figure
Cited by 9 articles
-
Clinical Manifestations of Respiratory Viruses in Hospitalized Children with Acute Viral Lower Respiratory Tract Infections from 2010 to 2011 in Busan and Gyeongsangnam-do, Korea
Hye-Young Kim, Kyoung Min Kim, Seong Heon Kim, Seung Kook Son, Hee Ju Park
Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2012;22(3):265-272. doi: 10.7581/pard.2012.22.3.265.A Case of Human Metapneumovirus Pneumonia in an Immunocompetent Adult Patient Mimicking with Influenza (A/H1N1-2009) Pandemic
Jin Young Yoo, Jun Young Eun, Eun Jung Lee, Tae Hyong Kim, Eun Ju Choo, Min Hyuk Jeon
Infect Chemother. 2011;43(2):217-221. doi: 10.3947/ic.2011.43.2.217.Trend in Viral Infectious Diseases in Children
Sung Hee Oh
Infect Chemother. 2011;43(6):435-442. doi: 10.3947/ic.2011.43.6.435.Clinical and Epidemiological Characteristics of Human Metapneumovirus Infections, in Comparison with Respiratory Syncytial Virus A and B
Soo Young Kang, Che Ry Hong, Hyun Mi Kang, Eun Young Cho, Hyun Ju Lee, Eun Hwa Choi, Hoan Jong Lee
Korean J Pediatr Infect Dis. 2013;20(3):168-177. doi: 10.14776/kjpid.2013.20.3.168.Comparison of respiratory disease by human metapneumovirus and respiratory syncytial virus in children
Woo Jin Chung, Sung Shil Kang, Kyong Won Bang, Yoon Hong Chun, Jong-Seo Yoon, Hyun Hee Kim, Jin Tack Kim, Joon Sung Lee
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2013;1(2):157-163. doi: 10.4168/aard.2013.1.2.157.Comparison of nasal cytokine profiles of human metapneumovirus and respiratory syncytial virus
Jin-Sung Park, Young-Ho Kim, Eunmi Kwon, Zak Callaway, Takao Fujisawa, Chang-Keun Kim
Asia Pac Allergy. 2017;7(4):206-212. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2017.7.4.206.Viral Infections and Associated Factors That Promote Acute Exacerbations of Asthma
Chang-Keun Kim, Zak Callaway, James E. Gern
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2018;10(1):12-17. doi: 10.4168/aair.2018.10.1.12.Infection, eosinophilia and childhood asthma
Chang-Keun Kim, Zak Callaway, Takao Fujisawa
Asia Pac Allergy. 2012;2(1):3-14. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2012.2.1.3.Literature review and future strategies of childhood respiratory diseases in Korea
Man Yong Han, Hai Lee Chung, Young Min Ahn, Jung Yeon Shim
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2018;6(Suppl 1):S66-S76. doi: 10.4168/aard.2018.6.S1.S66.
Reference
-
1. Peret TC, Boivin G, Li Y, Couillard M, Humphrey C, Osterhaus AD, Erdman DD, Anderson LJ. Characterization of human metapneumoviruses isolated from patients in North America. J Infect Dis. 2002. 185:1660–1663.
Article2. Jartti T, van den Hoogen B, Garofalo RP, Osterhaus AD, Ruuskanen O. Metapneumovirus and acute wheezing in children. Lancet. 2002. 360:1393–1394.
Article3. Chung JY, Han TH, Kim BE, Kim CK, Kim SW, Hwang ES. Human metapneumovirus infection in hospitalized children with acute respiratory disease in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2006. 21:838–842.
Article4. Madhi SA, Ludewick H, Abed Y, Klugman KP, Boivin G. Human metapneumovirus-associated lower respiratory tract infections among hospitalized human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1)-infected and HIV-1-uninfected African infants. Clin Infect Dis. 2003. 37:1705–1710.
Article5. van den Hoogen BG, de Jong JC, Groen J, Kuiken T, de Groot R, Fouchier RA, Osterhaus AD. A newly discovered human pneumovirus isolated from young children with respiratory tract disease. Nat Med. 2001. 7:719–724.
Article6. Glezen P, Denny FW. Epidemiology of acute lower respiratory disease in children. N Engl J Med. 1973. 288:498–505.
Article7. Boivin G, Abed Y, Pelletier G, Ruel L, Moisan D, Cote S, Peret TC, Erdman DD, Anderson LJ. Virological features and clinical manifestations associated with human metapneumovirus: a new paramyxovirus responsible for acute respiratory tract infections in all age groups. J Infect Dis. 2002. 186:1330–1334.8. Sigurs N, Bjarnason R, Sigurbergsson F, Kjellman B. Respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis in infancy is an important risk factor for asthma and allergy at age 7. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000. 161:1501–1507.
Article9. Jartti T, Lehtinen P, Vuorinen T, Osterback R, van den Hoogen B, Osterhaus AD, Ruuskanen O. Respiratory picornaviruses and respiratory syncytial virus as causative agents of acute expiratory wheezing in children. Emerg Infect Dis. 2004. 10:1095–1101.
Article10. Williams JV, Tollefson SJ, Heymann PW, Carper HT, Patrie J, Crowe JE. Human metapneumovirus infection in children hospitalized for wheezing. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005. 115:1311–1312.
Article11. Freymouth F, Vabret A, Legrand L, Eterradossi N, Lafay-Delaire F, Brouard J, Guillois B. Presence of the new human metapneumovirus in French children with bronchiolitis. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2003. 22:92–94.12. Chung JY, Han TH, Kim SW, Kim CK, Hwang ES. Detection of viruses identified recently in children with acute wheezing. J Med Virol. 2007. 79:1238–1243.
Article13. Rawlinson WD, Waliuzzaman Z, Carter IW, Belessis YC, Gilbert KM, Morton JR. Asthma exacerbations in children associated with rhinovirus but not human metapneumovirus infection. J Infect Dis. 2003. 187:1314–1318.
Article14. Mahalingam S, Schwarze J, Zaid A, Nissen M, Sloots T, Tauro S, Storer J, Alvarez R. Perspective on the host response to human metapneumovirus infection: what can we learn from respiratory syncytial virus infections? Microbes Infect. 2006. 8:285–293.
Article15. van den Hoogen BG, Osterhaus DM, Fouchier RA. Clinical impact and diagnosis of human metapneumovirus infection. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2004. 23:Suppl 1. S25–S32.
Article16. Garcia-Garcia ML, Calvo C, Perez-Brena P, De Cea JM, Acosta B, Casas I. Prevalence and clinical characteristics of human metapneumovirus infections in hospitalized infants in Spain. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2006. 41:863–871.17. Crowe JE Jr, Williams JV. Immunology of viral respiratory tract infection in infancy. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2003. 4:112–119.
Article18. Mertsola J, Ziegler T, Ruuskanen O, Vanto T, Koivikko A, Halonen P. Recurrent wheezy bronchitis and respiratory infections. Arch Dis Child. 1991. 66:124–129.19. Esper F, Boucher D, Weibel C, Martinello RA, Kahn JS. Human metapneumovirus infection in the United States: clinical manifestations associated with a newly emerging respiratory infection in children. Pediatrics. 2003. 111:1407–1410.
Article20. Garcia-Garcia ML, Calvo C, Casas I, Bracamonte T, Rellan A, Gozalo F, Tenorio T, Perez-Brena P. Human metapneumovirus bronchiolitis in infancy is an important risk factor for asthma at age 5. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2007. 42:458–464.21. Manoha C, Espinosa S, Aho SL, Huet F, Pothier P. Epidemiological and clinical features of hMPV, RSV and RVs infections in young children. J Clin Virol. 2007. 38:221–226.
Article22. von Linstow ML, Larsen HH, Eugen-Olsen J, Koch A, Nordmann Winther T, Meyer AM, Westh H, Lundgren B, Melbye M, Hogh B. Human metapneumovirus and respiratory syncytial virus in hospitalized Danish children with acute respiratory tract infection. Scand J Infect Dis. 2004. 36:578–584.23. Kim YK, Kim JW, Wee YS, Yoo EG, Han MY. Clinical features of Human [Metapneumovirus and Respiratory Syncytial Virus infection in hospitalized children.]. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2009. 19:12–19.24. Kahn JS. Epidemiology of human metapneumovirus. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006. 19:546–557.
Article25. Baer G, Schaad UB, Heininger U. Clinical findings and unusual epidemiologic characteristics of human metapneumovirus infections in children in the region of Basel, Switzerland. Eur J Pediatr. 2008. 167:63–69.
Article26. Williams JV, Harris PA, Tollefson SJ, Halburnt-Rush LL, Pingsterhaus JM, Edwards KM, Wright PF, Crowe JE Jr. Human metapneumovirus and lower respiratory tract disease in otherwise healthy infants and children. N Engl J Med. 2004. 350:443–450.
Article27. Ehlenfield DR, Cameron K, Welliver RC. Eosinophilia at the time of respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis predicts childhood reactive airway disease. Pediatrics. 2000. 105:79–83.
Article28. Gerna G, Campanini G, Rovida F, Sarasini A, Lilleri D, Paolucci S, Marchi A, Baldanti F, Revello MG. Changing circulation rate of human metapneumovirus strains and types among hospitalized pediatric patients during three consecutive winter-spring seasons. Brief report. Arch Virol. 2005. 150:2365–2375.29. Ebihara T, Endo R, Ma X, Ishiguro N, Kikuta H. Detection of human metapneumovirus antigens in nasopharyngeal secretions by an immunofluorescent-antibody test. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. 43:1138–1141.
Article30. Berman S. Epidemiology of acute respiratory infections in children of developing countries. Rev Infect Dis. 1991. 13:Suppl 6. S454–S462.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical and Epidemiological Characteristics of Human Metapneumovirus Infections, in Comparison with Respiratory Syncytial Virus A and B
- Clinical Features of Human Metapneumovirus and Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection in Hospitalized Children
- Viral Agents Involved in Wheezing and Asthma in Children
- Detection of Respiratory Viruses and Atypical Bacterial Pathogens in Infants with Acute Respiratory Infections Using Multiplex PCR
- A Case of Severe Human Metapneumovirus Pneumonia Requiring Mechanical Ventilation in an Immunocompetent Adult