J Korean Med Sci.
2013 Oct;28(10):1468-1473. 10.3346/jkms.2013.28.10.1468.
A Reverse Dipping Pattern Predicts Cardiovascular Mortality In a Clinical Cohort
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Sung Ae Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Preventive Medicine, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 3Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jhs2003@hanyang.ac.kr
- KMID: 1777683
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2013.28.10.1468
Abstract
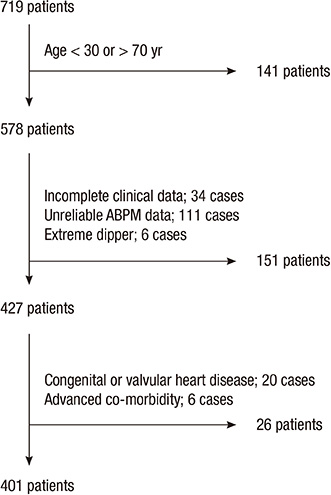
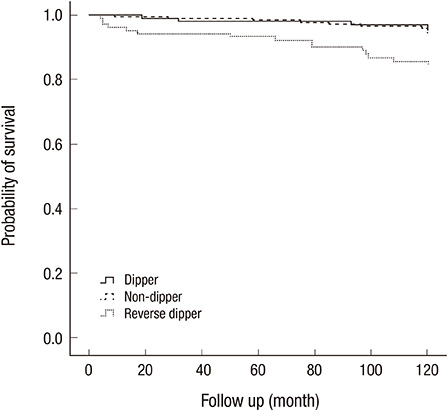
- An abnormal dipping pattern in ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) is a cardiovascular (CV) risk factor. However, its impact on CV mortality has not been investigated sufficiently in clinical practice to be considered a standard parameter. We assessed the association between abnormal dipping patterns and increased CV mortality in a tertiary hospital in Korea. Our retrospective cohort study included 401 patients who underwent ABPM between 1994 and 1996 in Hanyang University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. The patients were classified as risers (<0% drop in systolic BP; n=107), and others included dippers and non-dippers (> or =0% drop, n=294). The follow-up period was 120 months. The frequency of CV mortality was 14.0% in risers and 5.8% in others. A Cox regression analysis found a significant association between dipping pattern and CV mortality, after adjusting for age, gender, body mass index, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, smoking and hypercholesterolemia. Risers were at greater risk of CV death than others (RR, 3.02, P=0.022), but there was no difference in event rates between dippers and non-dippers. The reverse dipping pattern may be more frequent in clinical settings than in the population at large, and it is strongly associated with increased risk of CV mortality in Korea.
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Age Factors
Aged
Blood Pressure/*physiology
Blood Pressure Monitoring, Ambulatory
Body Mass Index
Cardiovascular Diseases/*mortality
Cohort Studies
Female
Humans
Hypertension/complications
Kaplan-Meier Estimate
Male
Middle Aged
Predictive Value of Tests
Regression Analysis
Retrospective Studies
Risk Factors
Sex Factors
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ben-Dov IZ, Kark JD, Ben-Ishay D, Mekler J, Ben-Arie L, Bursztyn M. Predictors of all-cause mortality in clinical ambulatory monitoring: unique aspects of blood pressure during sleep. Hypertension. 2007; 49:1235–1241.2. Staessen JA, Thijs L, Fagard R, O'Brien ET, Clement D, de Leeuw PW, Mancia G, Nachev C, Palatini P, Parati G, et al. Predicting cardiovascular risk using conventional vs ambulatory blood pressure in older patients with systolic hypertension: Systolic hypertension in Europe trial investigators. JAMA. 1999; 282:539–546.3. Dolan E, Stanton A, Thijs L, Hinedi K, Atkins N, McClory S, Den Hond E, McCormack P, Staessen JA, O'Brien E. Superiority of ambulatory over clinic blood pressure measurement in predicting mortality: the Dublin Outcome Study. Hypertension. 2005; 46:156–161.4. Kim SG. Clinical implications of ambulatory and home blood pressure monitoring. Korean Circ J. 2010; 40:423–431.5. Verdecchia P, Porcellati C, Schillaci G, Borgioni C, Ciucci A, Battistelli M, Guerrieri M, Gatteschi C, Zampi I, Santucci A, et al. Ambulatory blood pressure: an independent predictor of prognosis in essential hypertension. Hypertension. 1994; 24:793–801.6. Kim BK, Lim YH, Lee HT, Lee JU, Kim KS, Kim SG, Kim JH, Lim HK, Shin J. Non-dipper pattern is a determinant of the inappropriateness of left ventricular mass in essential hypertensive patients. Korean Circ J. 2011; 41:191–197.7. Routledge FS, McFetridge-Durdle JA, Dean CR. Canadian Hypertension Society. Night-time blood pressure patterns and target organ damage: a review. Can J Cardiol. 2007; 23:132–138.8. Fagard RH, Celis H, Thijs L, Staessen JA, Clement DL, De Buyzere ML, De Bacquer DA. Daytime and nighttime blood pressure as predictors of death and cause-specific cardiovascular events in hypertension. Hypertension. 2008; 51:55–61.9. Ohkubo T, Imai Y, Tsuji I, Nagai K, Watanabe N, Minami N, Kato J, Kikuchi N, Nishiyama A, Aihara A, et al. Relation between nocturnal decline in blood pressure and mortality: the Ohasama Study. Am J Hypertens. 1997; 10:1201–1207.10. Shin JH, Lee KJ, Lee J, Choi JH, Lee JU, Kim KS, Kim SK. Significance of nocturnal blood pressure changes by ambulatory blood pressure monitoring. Hanyang J Med. 1997; 17:133–142.11. O'Brien E, Asmar R, Beilin L, Imai Y, Mallion JM, Mancia G, Mengden T, Myers M, Padfield P, Palatini P, et al. European Society of Hypertension recommendations for conventional, ambulatory and home blood pressure measurement. J Hypertens. 2003; 21:821–848.12. Imai Y, Sasaki S, Minami N, Munakata M, Hashimoto J, Sakuma H, Sakuma M, Watanabe N, Imai K, Sekino H, et al. The accuracy and performance of the A&D TM 2421, a new ambulatory blood pressure monitoring device based on the cuff-oscillometric method and the Korotkoff sound technique. Am J Hypertens. 1992; 5:719–726.13. O'Brien E, Atkins N, Staessen J. State of the market: a review of ambulatory blood pressure monitoring devices. Hypertension. 1995; 26:835–842.14. Liniger C, Favre L, Assal JP. Twenty-four hour blood pressure and heart rate profiles of diabetic patients with abnormal cardiovascular reflexes. Diabet Med. 1991; 8:420–427.15. Nakano S, Fukuda M, Hotta F, Ito T, Ishii T, Kitazawa M, Nishizawa M, Kigoshi T, Uchida K. Reversed circadian blood pressure rhythm is associated with occurrences of both fatal and nonfatal vascular events in NIDDM subjects. Diabetes. 1998; 47:1501–1506.16. Ohkubo T, Hozawa A, Yamaguchi J, Kikuya M, Ohmori K, Michimata M, Matsubara M, Hashimoto J, Hoshi H, Araki T, et al. Prognostic significance of the nocturnal decline in blood pressure in individuals with and without high 24-h blood pressure: the Ohasama Study. J Hypertens. 2002; 20:2183–2189.17. Boggia J, Li Y, Thijs L, Hansen TW, Kikuya M, Björklund-Bodegård K, Richart T, Ohkubo T, Kuznetsova T, Torp-Pedersen C, et al. Prognostic accuracy of day versus night ambulatory blood pressure: a cohort study. Lancet. 2007; 370:1219–1229.18. Fagard RH. Dipping pattern of nocturnal blood pressure in patients with hypertension. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2009; 7:599–605.19. Fagard RH, Thijs L, Staessen JA, Clement DL, De Buyzere ML, De Bacquer DA. Prognostic significance of ambulatory blood pressure in hypertensive patients with history of cardiovascular disease. Blood Press Monit. 2008; 13:325–332.20. Fagard RH, Thijs L, Staessen JA, Clement DL, De Buyzere ML, De Bacquer DA. Night-day blood pressure ratio and dipping pattern as predictors of death and cardiovascular events in hypertension. J Hum Hypertens. 2009; 23:645–653.21. Redon J, Lurbe E. Nocturnal blood pressure versus nondipping pattern: what do they mean? Hypertension. 2008; 51:41–42.22. Cuspidi C, Vaccarella A, Leonetti G, Sala C. Ambulatory blood pressure and diabetes: targeting nondipping. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2010; 6:111–115.23. Hermida RC, Ayala DE, Mojón A, Fernández JR. Effects of time of antihypertensive treatment on ambulatory blood pressure and clinical characteristics of subjects with resistant hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 2010; 23:432–439.24. De la Sierra A, Redon J, Banegas JR, Segura J, Parati G, Gorostidi M, de la Cruz JJ, Sobrino J, Llisterri JL, Alonso J, et al. Prevalence and factors associated with circadian blood pressure patterns in hypertensive patients. Hypertension. 2009; 53:466–472.25. Palatini P, Mormino P, Canali C, Santonastaso M, De Venuto G, Zanata G, Pessina AC. Factors affecting ambulatory blood pressure reproducibility: results of the HARVEST Trial: hypertension and ambulatory recording venetia study. Hypertension. 1994; 23:211–216.26. Staessen J, Bulpitt CJ, O'Brien E, Cox J, Fagard R, Stanton A, Thijs L, Van Hulle S, Vyncke G, Amery A. The diurnal blood pressure profile: a population study. Am J Hypertens. 1992; 5:386–392.27. Parati G, Staessen JA. Day-night blood pressure variations: mechanisms, reproducibility and clinical relevance. J Hypertens. 2007; 25:2377–2380.28. Manning G, Rushton L, Donnelly R, Millar-Craig MW. Variability of diurnal changes in ambulatory blood pressure and nocturnal dipping status in untreated hypertensive and normotensive subjects. Am J Hypertens. 2000; 13:1035–1038.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Diabetic Neuropathy and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease
- Clinical and life style factors related to the nighttime blood pressure, nighttime dipping and their phenotypes in Korean hypertensive patients
- Abrupt Decline in Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate after Initiating Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors Predicts Clinical Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Age-period-cohort Analysis of Cardiovascular Disease Mortality in Japan, 1995-2018
- Asian Cohort Studies on Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Childhood