J Korean Med Sci.
2013 Nov;28(11):1661-1666. 10.3346/jkms.2013.28.11.1661.
Striatal Dopaminergic Functioning in Patients with Sporadic and Hereditary Spastic Paraplegias with Parkinsonism
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, College of Medicine, Chungbuk National University Hospital, Cheongju, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 3Department of Nuclear Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 4Department of Neurology, Ewha Woman's University, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Neurology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. brain@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1777666
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2013.28.11.1661
Abstract
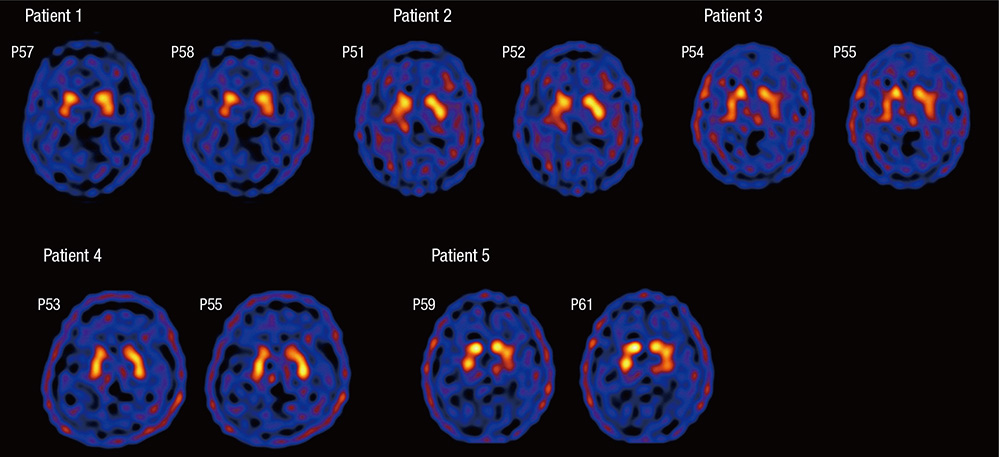
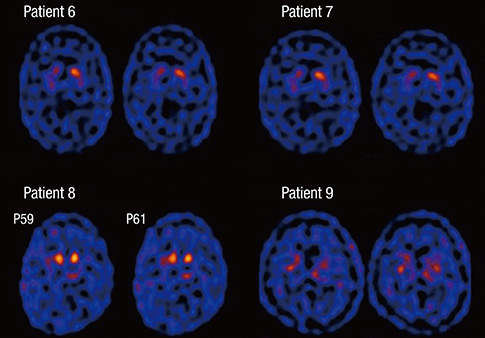
- Sporadic spastic paraplegia (SSP) and hereditary spastic paraplegia (HSP) belong to a clinical and genetically heterogeneous group of disorders characterized by progressive spasticity and weakness in the lower extremities. The symptoms are associated with pyramidal tract dysfunction and degeneration of the corticospinal tracts. Parkinsonism is uncommon in SSP/HSP patients. However, both disorders are associated with damage to the nigrostriatal dopaminergic system. In the present study, the clinical features of patients with SSP/HSP were investigated, and nigrostriatal dopaminergic binding potential was assessed using dopamine transporter (DAT) single-photon emission computer tomography (SPECT). Nine patients with spastic paraplegia participated in the present study. The subjects underwent DAT SPECT using the agent [2-[[2-[[[3-(4-chlorophenyl)-8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3,2,1]oct-2-yl]methyl](2-mercaptoethyl)amino]ethyl]amino]ethanethiolato (3-)-N2,N20,S2,S20]oxo-[IR-(exo-exo)])-[99mTc]technetium ([99mTc]TRODAT-1). The [99mTc]TRODAT-1 SPECT images of five patients appeared normal, whereas the images of four patients revealed reduced striatal ligand uptake. Among the four patients with reduced uptake, two had parkinsonism, and one exhibited periodic limb movements and restless leg syndrome. Our DAT SPECT imaging study shows that reduced DAT density may be observed in patients with parkinsonism. The results of the present study offer an explanation for the spectrum of spastic paraplegia symptoms and the progression of the disorder.
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Aged
Brain/*radionuclide imaging
Dopamine Plasma Membrane Transport Proteins/metabolism
Female
Humans
Male
Middle Aged
Organotechnetium Compounds/diagnostic use
Paraplegia/diagnosis/genetics/*radionuclide imaging
Parkinsonian Disorders/complications/genetics/*radionuclide imaging
Pyramidal Tracts
Radiopharmaceuticals/diagnostic use
Spastic Paraplegia, Hereditary/diagnosis/genetics/*radionuclide imaging
Tomography, Emission-Computed, Single-Photon
Dopamine Plasma Membrane Transport Proteins
Organotechnetium Compounds
Radiopharmaceuticals
Figure
Reference
-
1. Harding AE. Classification of the hereditary ataxias and paraplegias. Lancet. 1983; 1:1151–1155.2. Dion PA, Daoud H, Rouleau GA. Genetics of motor neuron disorders: new insights into pathogenic mechanisms. Nat Rev Genet. 2009; 10:769–782.3. Sakai T, Kawakami H. Machado-Joseph disease: a proposal of spastic paraplegic subtype. Neurology. 1996; 46:846–847.4. Kaneko A, Narabayashi Y, Itokawa K, Nakazato Y, Hosokawa T, Iwasaki S, Ohno R, Hamaguchi K, Ikeda M, Nomura M. A case of Machado-Joseph disease presenting with spastic paraparesis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1997; 62:542–543.5. Teive HA, Iwamoto FM, Camargo CH, Lopes-Cendes I, Werneck LC. Machado-Joseph disease versus hereditary spastic paraplegia: case report. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2001; 59:809–811.6. Micheli F, Cersósimo MG, Zúñiga Ramírez C. Hereditary spastic paraplegia associated with dopa-responsive parkinsonism. Mov Disord. 2006; 21:716–717.7. Guidubaldi A, Piano C, Santorelli FM, Silvestri G, Petracca M, Tessa A, Bentivoglio AR. Novel mutations in SPG11 cause hereditary spastic paraplegia associated with early-onset levodopa-responsive Parkinsonism. Mov Disord. 2011; 26:553–556.8. Kang SY, Lee MH, Lee SK, Sohn YH. Levodopa-responsive parkinsonism in hereditary spastic paraplegia with thin corpus callosum. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2004; 10:425–427.9. Dick AP, Stevenson CJ. Hereditary spastic paraplegia; report of a family with associated extrapyramidal signs. Lancet. 1953; 1:921–923.10. Hedera P. Hereditary spastic paraplegia or spinocerebellar ataxia? not always as easy as it seems. Eur J Neurol. 2009; 16:887–888.11. Wang YG, Du J, Wang JL, Chen J, Chen C, Luo YY, Xiao ZQ, Jiang H, Yan XX, Xia K, et al. Six cases of SCA3/MJD patients that mimic hereditary spastic paraplegia in clinic. J Neurol Sci. 2009; 285:121–124.12. Anheim M, Lagier-Tourenne C, Stevanin G, Fleury M, Durr A, Namer IJ, Denora P, Brice A, Mandel JL, Koenig M, et al. SPG11 spastic paraplegia: a new cause of juvenile parkinsonism. J Neurol. 2009; 256:104–108.13. Lee Y, Paik D, Bang S, Kang J, Chun B, Lee S, Bae E, Chung J, Kim J. Loss of spastic paraplegia gene atlastin induces age-dependent death of dopaminergic neurons in Drosophila. Neurobiol Aging. 2008; 29:84–94.14. Albin RL, Koeppe RA, Rainier S, Fink JK. Normal dopaminergic nigrostriatal innervation in SPG3A hereditary spastic paraplegia. J Neurogenet. 2008; 22:289–294.15. Kim JY, Kim SY, Kim JM, Kim YK, Yoon KY, Kim JY, Lee BC, Kim JS, Paek SH, Park SS, et al. Spinocerebellar ataxia type 17 mutation as a causative and susceptibility gene in parkinsonism. Neurology. 2009; 72:1385–1389.16. Booij J, Speelman JD, Horstink MW, Wolters EC. The clinical benefit of imaging striatal dopamine transporters with [123I]FP-CIT SPET in differentiating patients with presynaptic parkinsonism from those with other forms of parkinsonism. Eur J Nucl Med. 2001; 28:266–272.17. Iranzo A, Valldeoriola F, Lomeña F, Molinuevo JL, Serradell M, Salamero M, Cot A, Ros D, Pavía J, Santamaria J, et al. Serial dopamine transporter imaging of nigrostriatal function in patients with idiopathic rapid-eye-movement sleep behaviour disorder: a prospective study. Lancet Neurol. 2011; 10:797–805.18. Albin RL, Koeppe RA, Chervin RD, Consens FB, Wernette K, Frey KA, Aldrich MS. Decreased striatal dopaminergic innervation in REM sleep behavior disorder. Neurology. 2000; 55:1410–1412.19. Eisensehr I, Linke R, Noachtar S, Schwarz J, Gildehaus FJ, Tatsch K. Reduced striatal dopamine transporters in idiopathic rapid eye movement sleep behaviour disorder: comparison with Parkinson's disease and controls. Brain. 2000; 123:1155–1160.20. Stiasny-Kolster K, Doerr Y, Möller JC, Höffken H, Behr TM, Oertel WH, Mayer G. Combination of 'idiopathic' REM sleep behaviour disorder and olfactory dysfunction as possible indicator for alpha-synucleinopathy demonstrated by dopamine transporter FP-CIT-SPECT. Brain. 2005; 128:126–137.21. Wharton SB, McDermott CJ, Grierson AJ, Wood JD, Gelsthorpe C, Ince PG, Shaw PJ. The cellular and molecular pathology of the motor system in hereditary spastic paraparesis due to mutation of the spastin gene. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2003; 62:1166–1177.22. Seidel K, De Vos R, Derksen L, Bauer P, Riess O, den Dunnen W, Deller T, Hageman G, Rüb U. Widespread thalamic and cerebellar degeneration in a patient with a complicated hereditary spastic paraplegia (HSP). Ann Anat. 2009; 191:203–211.23. Kuru S, Sakai M, Konagaya M, Yoshida M, Hashizume Y. Autopsy case of hereditary spastic paraplegia with thin corpus callosum showing severe gliosis in the cerebral white matter. Neuropathology. 2005; 25:346–352.24. Trotta N, Orso G, Rossetto MG, Daga A, Broadie K. The hereditary spastic paraplegia gene, spastin, regulates microtubule stability to modulate synaptic structure and function. Curr Biol. 2004; 14:1135–1147.25. Salinas S, Carazo-Salas RE, Proukakis C, Schiavo G, Warner TT. Spastin and microtubules: functions in health and disease. J Neurosci Res. 2007; 85:2778–2782.