Korean J Radiol.
2005 Dec;6(4):208-213. 10.3348/kjr.2005.6.4.208.
Simple Pulmonary Eosinophilia Evaluated by Means of FDG PET: the Findings of 14 Cases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Korea. hykim@ncc.re.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, National Cancer Center, Korea.
- 3Center for Nuclear Medicine, National Cancer Center, Korea.
- KMID: 1777277
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2005.6.4.208
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
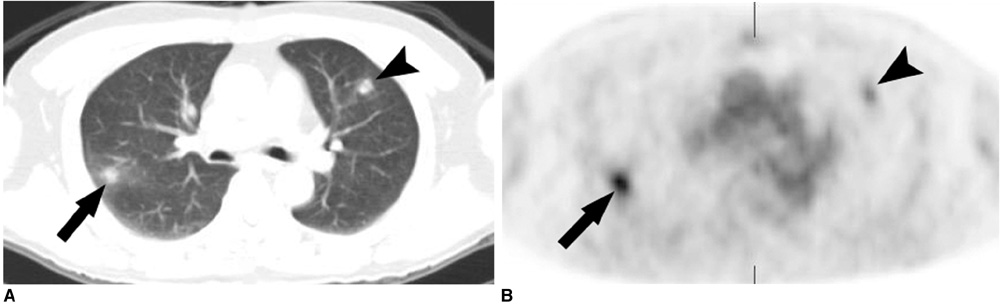
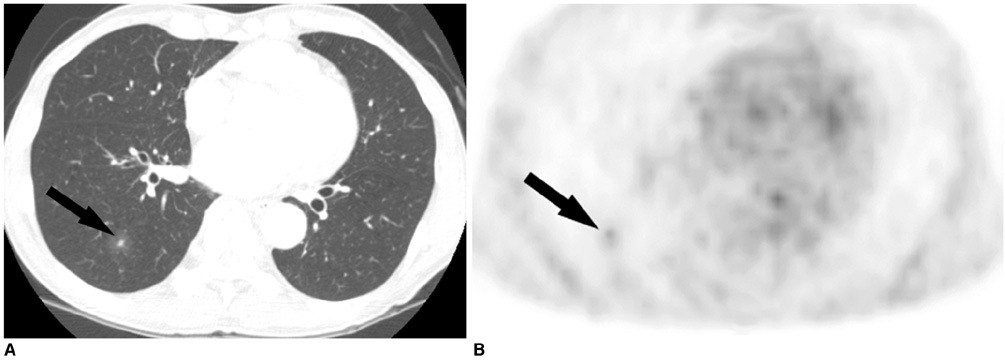
We wanted to describe the findings of simple pulmonary eosinophilia with using 18 fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography (PET). MATERIALS AND METHODS: We analysed the findings of 14 patients who underwent thoracic computed tomography (CT) and PET, and then they were subsequently proven to have simple pulmonary eosinophilia. PET studies were performed in four patients with malignancy to evaluate for cancer metastasis, and PET scans were also done in 10 healthy subjects who underwent volunteer cancer screening. The PET scans were evaluated by using the maximum standardized uptake values (SUVs). The subjects' CT findings also were reviewed and correlated with the PET findings. RESULTS: A total of 42 nodules were detected on the CT scans. There were single nodules in three patients and multiple nodules in 11 patients (mean number of nodules: 3, range: 1-10, mean diameter: 9.5 mm+/-4.7). Twelve of 42 (28.6%) nodules showed FDG uptake and their mean maximum SUV was 2.5+/-1.6 (range: 0.6-5.3). Five of six solid nodules showed FDG uptake (2.2+/-1.1, range: 0.9-3.6), six of 11 semisolid nodules showed FDG uptake (3.1+/-1.8, range: 0.6-5.3) and one of 25 pure ground-glass opacity nodule showed a maximum SUV of 0.8. The maximum SUVs of seven nodules in five patients were greater than 2.5. The maximum SUVs were significantly different according to the nodule types (p < 0.001). CONCLUSION: Simple pulmonary eosinophilia commonly causes an increase in FDG uptake. Therefore, correlation of the PET findings with the CT findings or the peripheral eosinophil counts can help physicians arrive at the correct diagnosis of simple pulmonary eosinophilia.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Computer-Aided Differential Diagnosis of the Pulmonary Nodule: Towards an Understanding of the Medical Imaging Basics and Experiences in the Field
Matvey V. Sprindzuk, Kovalev V. Alekseevich, Snezhko E. Vitalévich, Kharuzhyk S. Anatolévich
J Lung Cancer. 2009;8(2):78-91. doi: 10.6058/jlc.2009.8.2.78.
Reference
-
1. Lowe VJ, Duhalongsed FG, Patz EF, Delong DM, Hoffman JM, Wolfe WG, et al. Pulmonary abnormalities and PET data analysis: A retrospective study. Radiology. 1997. 202:435–439.2. Lowe VJ, Hoffman JM, DeLong DM, Patz EF, Coleman RE. Semiquantitative and visual analysis of FDG-PET images in pulmonary abnormalities. J Nucl Med. 1994. 35:1771–1776.3. Goo JM, Im JG, Do KH, Kim KW, Chung JW, Park JH, et al. Pulmonary tuberculoma evaluated by means of FDG PET: findings in 10 cases. Radiology. 2000. 216:117–121.4. Hubner KF, Buonocor E, Singh SK, Gould HR, Cotten DW. Characterization of chest masses by FDG positron emission tomography. Clin Nucl Med. 1995. 20:293–298.5. Shin L, Katz DS, Yung E. Hypermetabolism on F-18 FDG PET of multiple pulmonary nodules resulting from bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia. Clin Nucl Med. 2004. 29:654–656.6. Gotway MB, Storto ML, Golden JA, Reddy GP, Webb WR. Incidental detection of thoracic sarcoidosis on whole-body 18 fluorine-2-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose positron emission tomography. J Thorac Imaging. 2000. 15:201–204.7. Konishi J, Yamazaki K, Tsukamoto E, Tamaki N, Onodera Y, Otake T, et al. Mediastinal lymph node staging by FDG-PET in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: analysis of false-positive FDG-PET findings. Respiration. 2003. 70:500–506.8. Allen JN, Davis WB. Eosinophilic lung diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994. 150:1423–1438.9. Jung KJ, Lee KS, Kim TS, Chung MP, Choi DC, Kwon OJ. Simple pulmonary eosinophilia (Loeffler's syndrome): chest radiographic and CT findings. J Korean Radiol Soc. 2000. 42:83–90.10. Kim CK, Gupta NC, Chandramouli B, Alavi A. Standardized uptake values of FDG: body surface area correction is preferable to body weight correction. J Nucl Med. 1994. 35:164–167.11. Kim Y, Lee KS, Choi DC, Primack SL, Im JG. The spectrum of eosinophilic lung disease: radiologic findings. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1997. 21:920–930.12. Deichen JT, Prante O, Gack M, Schmiedehausen K, Kuwert T. Uptake of [18F] fluorodeoxyglucose in human monocyte-macrophages in vitro. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2003. 30:267–273.13. Kapucu LO, Meltzer CC, Townsend DW, Keenan RJ, Luketich JD. Fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose uptake in pneumonia. J Nucl Med. 1998. 39:1267–1269.14. Travis WD, Garg K, Franklin WA, Wistuba II, Sabloff B, Noguchi M, et al. Evolving concepts in the pathology and computed tomography imaging of lung adenocarcinoma and bronchioloalveolar carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2005. 23:3279–3287.15. Nomori H, Watanabe K, Ohtsuka T, Naruke T, Suemasu K, Uno K. Evaluation of F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET scanning for pulmonary nodules less than 3 cm in diameter, with special reference to the CT images. Lung Cancer. 2004. 45:19–27.16. Dewan NA, Gupta NC, Redepenning LS, Phalen JJ, Frick MP. Diagnostic efficacy of PET-FDG imaging in solitary pulmonary nodules. Potential role in evaluation and management. Chest. 1993. 104:997–1002.17. Higashi K, Ueda Y, Seki H, Yuasa K, Oguchi M, Noguchi T, et al. Fluorine-18-FDG PET imaging is negative in bronchioloalveolar lung carcinoma. J Nucl Med. 1998. 39:1016–1020.18. Coleman RE. PET in lung cancer. J Nucl Med. 1999. 40:814–820.19. Stumpe KD, Dazzi H, Schaffner A, von Schulthess GK. Infection imaging using whole-body FDG-PET. Eur J Nucl Med. 2000. 27:822–832.20. Bedrossian CW, Greenberg SD, Williams LJ Jr. Ultrastructure of the lung in Loeffler's pneumonia. Am J Med. 1975. 58:438–443.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- F-18 FDG PET Scan findings in Patients with Pulmonary Involvement in the Hypereosinophilic Syndrome
- F-18 FDG PET/CT Finding in Solid Pseudo-papillary Tumor of the Pancreas 6 years After Initial Diagnosis
- Diagnostic Efficacy of FDG-PET Imaging in Solitary Pulmonary Nodule
- Diagnostic Efficacy of FDG-PET in Solitary Pulmonary Nodule
- The Clinical Role of FDG PET in Malignant Lymphoma