Yonsei Med J.
2013 Jan;54(1):28-33. 10.3349/ymj.2013.54.1.28.
Evaluation of the Effect of Hemoglobin or Hematocrit Level on Dural Sinus Density Using Unenhanced Computed Tomography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, College of Medicine, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju, Korea. lsyrad@chungbuk.ac.kr
- 2Department of Neurology, College of Medicine, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju, Korea.
- KMID: 1776914
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2013.54.1.28
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To identify the relationship between hemoglobin (Hgb) or hematocrit (Hct) level and dural sinus density using unenhanced computed tomography (UECT).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
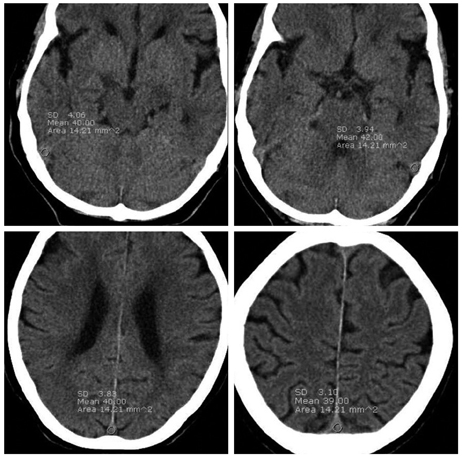
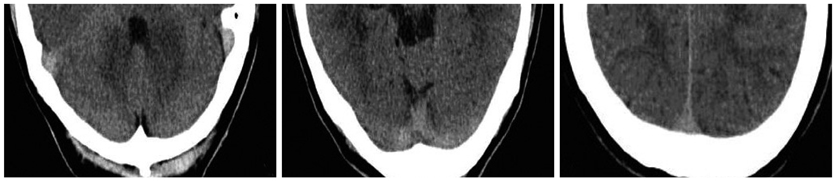
Patients who were performed UECT and had records of a complete blood count within 24 hours from UECT were included (n=122). We measured the Hounsfield unit (HU) of the dural sinus at the right sigmoid sinus, left sigmoid sinus and 2 points of the superior sagittal sinus. Quantitative measurement of dural sinus density using the circle regions of interest (ROI) method was calculated as average ROI values at 3 or 4 points. Simple regression analysis was used to evaluate the correlation between mean HU and Hgb or mean HU and Hct.
RESULTS
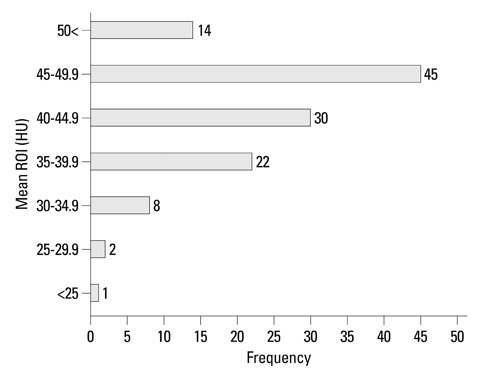
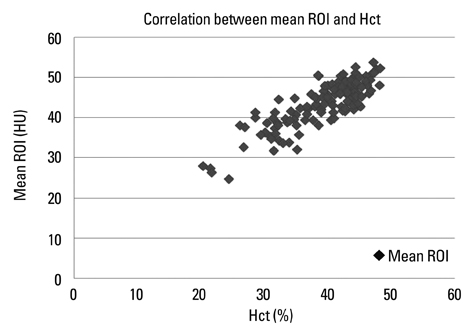
The mean densities of the dural sinuses ranged from 24.67 to 53.67 HU (mean, 43.28 HU). There was a strong correlation between mean density and Hgb level (r=0.832) and between mean density and Hct level (r=0.840).
CONCLUSION
Dural sinus density on UECT is closely related to Hgb and Hct levels. Therefore, the Hgb or Hct levels can be used to determine whether the dural sinus density is within the normal range or pathological conditions such as venous thrombosis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adolescent
Adult
Aged
Aged, 80 and over
Cranial Sinuses/pathology/*radiography
Female
*Hematocrit
Hemoglobins/*analysis
Hepatolenticular Degeneration/complications
Humans
Male
Middle Aged
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Complications
Radiographic Image Interpretation, Computer-Assisted
Reference Values
Regression Analysis
Superior Sagittal Sinus/pathology/*radiography
Tomography, X-Ray Computed/*methods
Young Adult
Hemoglobins
Figure
Reference
-
1. Linn J, Pfefferkorn T, Ivanicova K, Müller-Schunk S, Hartz S, Wiesmann M, et al. Noncontrast CT in deep cerebral venous thrombosis and sinus thrombosis: comparison of its diagnostic value for both entities. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009. 30:728–735.
Article2. Bogousslavsky J, Pierre P. Ischemic stroke in patients under age 45. Neurol Clin. 1992. 10:113–124.
Article3. Linn J, Ertl-Wagner B, Seelos KC, Strupp M, Reiser M, Brückmann H, et al. Diagnostic value of multidetector-row CT angiography in the evaluation of thrombosis of the cerebral venous sinuses. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007. 28:946–952.4. Tehindrazanarivelo AD, Bousser MG. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension and cerebral dural sinus thrombosis. Am J Med. 1994. 97:200–201.
Article5. Leker RR, Steiner I. Features of dural sinus thrombosis simulating pseudotumor cerebri. Eur J Neurol. 1999. 6:601–604.
Article6. Renowden S. Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis. Eur Radiol. 2004. 14:215–226.
Article7. Ferro JM, Canhão P, Stam J, Bousser MG, Barinagarrementeria F. ISCVT Investigators. Prognosis of cerebral vein and dural sinus thrombosis: results of the International Study on Cerebral Vein and Dural Sinus Thrombosis (ISCVT). Stroke. 2004. 35:664–670.
Article8. Sidani CA, Ballourah W, El Dassouki M, Muwakkit S, Dabbous I, Dahoui H, et al. Venous sinus thrombosis leading to stroke in a patient with sickle cell disease on hydroxyurea and high hemoglobin levels: treatment with thrombolysis. Am J Hematol. 2008. 83:818–820.
Article9. Wendling LR. Intracranial venous sinus thrombosis: diagnosis suggested by computed tomography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1978. 130:978–980.
Article10. Patronas NJ, Duda EE, Mirfakhraee M, Wollmann RL. Superior sagittal sinus thrombosis diagnosed by computed tomography. Surg Neurol. 1981. 15:11–14.
Article11. Virapongse C, Cazenave C, Quisling R, Sarwar M, Hunter S. The empty delta sign: frequency and significance in 76 cases of dural sinus thrombosis. Radiology. 1987. 162:779–785.
Article12. Fanous R, Leung A, Karlik S. Quantitative assessment of the superior sagittal sinus on unenhanced computed tomography. Eur J Radiol. 2010. 75:336–342.
Article13. Osborn AG, Anderson RE, Wing SD. The false falx sign. Radiology. 1980. 134:421–425.
Article14. Black DF, Rad AE, Gray LA, Campeau NG, Kallmes DF. Cerebral venous sinus density on noncontrast CT correlates with hematocrit. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011. 32:1354–1357.
Article15. Morita S, Ueno E, Masukawa A, Suzuki K, Machida H, Fujimura M. Hyperattenuating signs at unenhanced CT indicating acute vascular disease. Radiographics. 2010. 30:111–125.
Article16. New PF, Aronow S. Attenuation measurements of whole blood and blood fractions in computed tomography. Radiology. 1976. 121(3 Pt. 1):635–640.
Article17. Swensen SJ, McLeod RA, Stephens DH. CT of extracranial hemorrhage and hematomas. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1984. 143:907–912.
Article18. Collins AJ, Gillespie S, Kelly BE. Can computed tomography identify patients with anaemia? Ulster Med J. 2001. 70:116–118.19. Doppman JL, Rienmuller R, Lissner J. The visualized interventricular septum on cardiac computed tomography: a clue to the presence of severe anemia. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1981. 5:157–160.20. Foster M, Nolan RL, Lam M. Prediction of anemia on unenhanced computed tomography of the thorax. Can Assoc Radiol J. 2003. 54:26–30.21. Title RS, Harper K, Nelson E, Evans T, Tello R. Observer performance in assessing anemia on thoracic CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005. 185:1240–1244.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effects of Lead Exposure on Hematocrit and Hemoglobin
- Dural sinus thrombosis identified by point-of-care ultrasound
- Giant Arachnoid Granulation Misdiagnosed as Transverse Sinus Thrombosis
- A Case of Dural Carotid-Cavernous Sinus Fistula Associated with Ophthalmic Manifestations
- Contralateral Transverse Sinus Occlusion After Treatment of Transverse-Sigmoid Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula: A Case Report