Korean Circ J.
2011 Dec;41(12):759-762. 10.4070/kcj.2011.41.12.759.
Spontaneous Spinal Epidural Hematomas Associated With Acute Myocardial Infarction Treatment
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurological Surgery, College of Medicine, Chung-Ang University, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurological Surgery, Chung-Ang University Graduate School, Seoul, Korea. nscharisma@hanmail.net
- 3Department of Neurosurgery, Spine Center, Chuncheon Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University Medical Center, Hallym University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 4Department of Neurosurgery, Kyungpook National University Hospital, Daegu, Korea.
- 5Division of Cardiology, College of Medicine, Chung-Ang University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1776254
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2011.41.12.759
Abstract
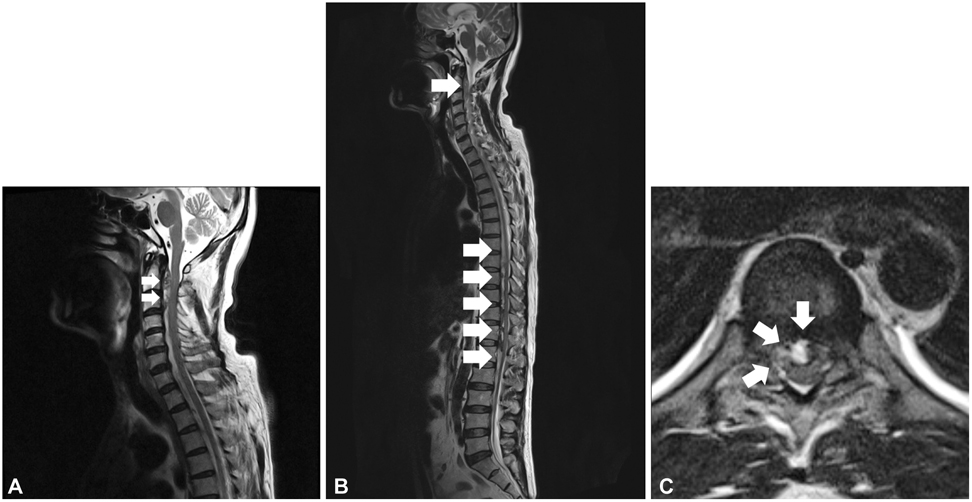
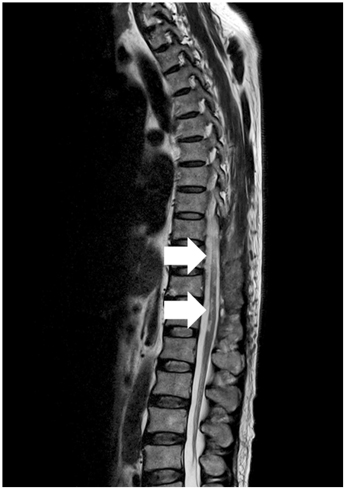
- Many studies have reported spontaneous spinal epidural hematoma (SSEH). Although most cases are idiopathic, several are associated with thrombolytic therapy or anticoagulants. We report a case of SSEH coincident with acute myocardial infarction (AMI), which caused serious neurological deficits. A 56 year old man presented with chest pain accompanied with back and neck pain, which was regarded as an atypical symptom of AMI. He was treated with nitroglycerin, aspirin, low molecular weight heparin, and clopidogrel. A spinal magnetic resonance image taken after paraplegia developed 3 days after the initial symptoms revealed an epidural hematoma at the cervical and thoracolumbar spine. Despite emergent decompressive surgery, paraplegia has not improved 7 months after surgery. A SSEH should be considered when patients complain of abrupt, strong, and non-traumatic back and neck pain, particularly if they have no spinal pain history.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chan KC, Wu DJ, Ueng KC, et al. Spinal epidural hematoma following tissue plasminogen activator and heparinization for acute myocardial infarction. Jpn Heart J. 2002. 43:417–421.2. Subbiah M, Avadhani A, Shetty AP, Rajasekaran S. Acute spontaneous cervical epidural hematoma with neurological deficit after low-molecular-weight heparin therapy: role of conservative management. Spine J. 2010. 10:e11–e15.3. Akhtar MM, Iqbal YH, Kaski JC. Managing unstable angina and non-ST elevation MI. Practitioner. 2010. 254:25–30.4. Kumar A, Cannon CP. Acute coronary syndromes: diagnosis and management, part I. Mayo Clin Proc. 2009. 84:917–938.5. Riegel B, Hanlon AL, McKinley S, et al. Differences in mortality in acute coronary syndrome symptom clusters. Am Heart J. 2010. 159:392–398.6. Lee HO. Typical and atypical clinical signs and symptoms of myocardial infarction and delayed seeking of professional care among blacks. Am J Crit Care. 1997. 6:7–13.7. McSweeney JC, Cody M, O'Sullivan P, Elberson K, Moser DK, Garvin BJ. Women's early warning symptoms of acute myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2003. 108:2619–2623.8. Lee H, Bahler R, Park OJ, Kim CJ, Lee HY, Kim YJ. Typical and atypical symptoms of myocardial infarction among African-Americans, whites, and Koreans. Crit Care Nurs Clin North Am. 2001. 13:531–539.9. Løvlien M, Schei B, Hole T. Women with myocardial infarction are less likely than men to experience chest symptoms. Scand Cardiovasc J. 2006. 40:342–347.10. Atypical presentation of myocardial infarction in the outpatient setting, a lapse in clinical knowledge and inadequate data transfer constitute a potentially fatal error. Int J Qual Health Care. 2003. 15:179. doi: 10.1093/intqhc/mzg027.11. Liu Z, Jiao Q, Xu J, Wang X, Li S, You C. Spontaneous spinal epidural hematoma: analysis of 23 cases. Surg Neurol. 2008. 69:253–260.12. Kitagawa RS, Mawad ME, Whitehead WE, Curry DJ, Luersen TG, Jea A. Paraspinal arteriovenous malformations in children. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2009. 3:425–428.13. Sung JH, Hong JT, Son BC, Lee SW. Clopidogrel-induced spontaneous spinal epidural hematoma. J Korean Med Sci. 2007. 22:577–579.14. Dimou J, Jithoo R, Morokoff A. Spontaneous spinal epidural haematoma in a geriatric patient on aspirin. J Clin Neurosci. 2010. 17:142–144.15. Deger SM, Emmez H, Bahadirli K, et al. A spontaneous spinal epidural hematoma in a hemodialysis patient: a rare entity. Intern Med. 2009. 48:2115–2118.16. Tagaya A, Miyajima Y, Sakamoto M, et al. Spontaneous spinal epidural hematoma in an infant with undiagnosed hemophilia A. Pediatr Int. 2010. 52:296–298.17. Cultrera F, Passanisi M, Giliberto O, Giuffrida M, Mancuso P, Ventura F. Spinal epidural hematoma following coronary thrombolysis: a case report. J Neurosurg Sci. 2004. 48:43–47.18. Groen RJ, van Alphen HA. Operative treatment of spontaneous spinal epidural hematomas: a study of the factors determining postoperative outcome. Neurosurgery. 1996. 39:494–508. discussion 508-9.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Spontaneous Cervical Epidural Hematomas in Healthy Young Adults: Case Report
- Spontaneous Spinal Epidural Hematoma
- Thoracolumbar Epidural Hematoma Complicated by Cauda Equina Syndrome : Complication of Systemic Heparinization Following Epidural Anesthesia: A case report
- Nontraumatic Spinal Epidural Hematoma - An Analysis of The Etiology -
- Surgical Treatment of Spontaneous Cervicothoracic Spine Epidural Hematoma without Risk Factors: A Case Report