Korean J Gastroenterol.
2010 Mar;55(3):162-168. 10.4166/kjg.2010.55.3.162.
Clinical Significance of Incidentally Detected Eosinophilic Esophagitis with Pathologic Review
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. dhljohn@sunbh.org
- 2Department of Pathology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1775897
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2010.55.3.162
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/AIMS
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EE) is a chronic inflammatory disorder characterized by abnormal dense eosinophilic infiltration of esophageal mucosa and results in dysphasia and food impaction. EE is being increasingly recognized in adults. The prevalence is largely unknown. This study was performed to evaluate the detection rate of EE diagnosed based on pathologic criteria and to define the clinical characteristics of EE in Korea.
METHODS
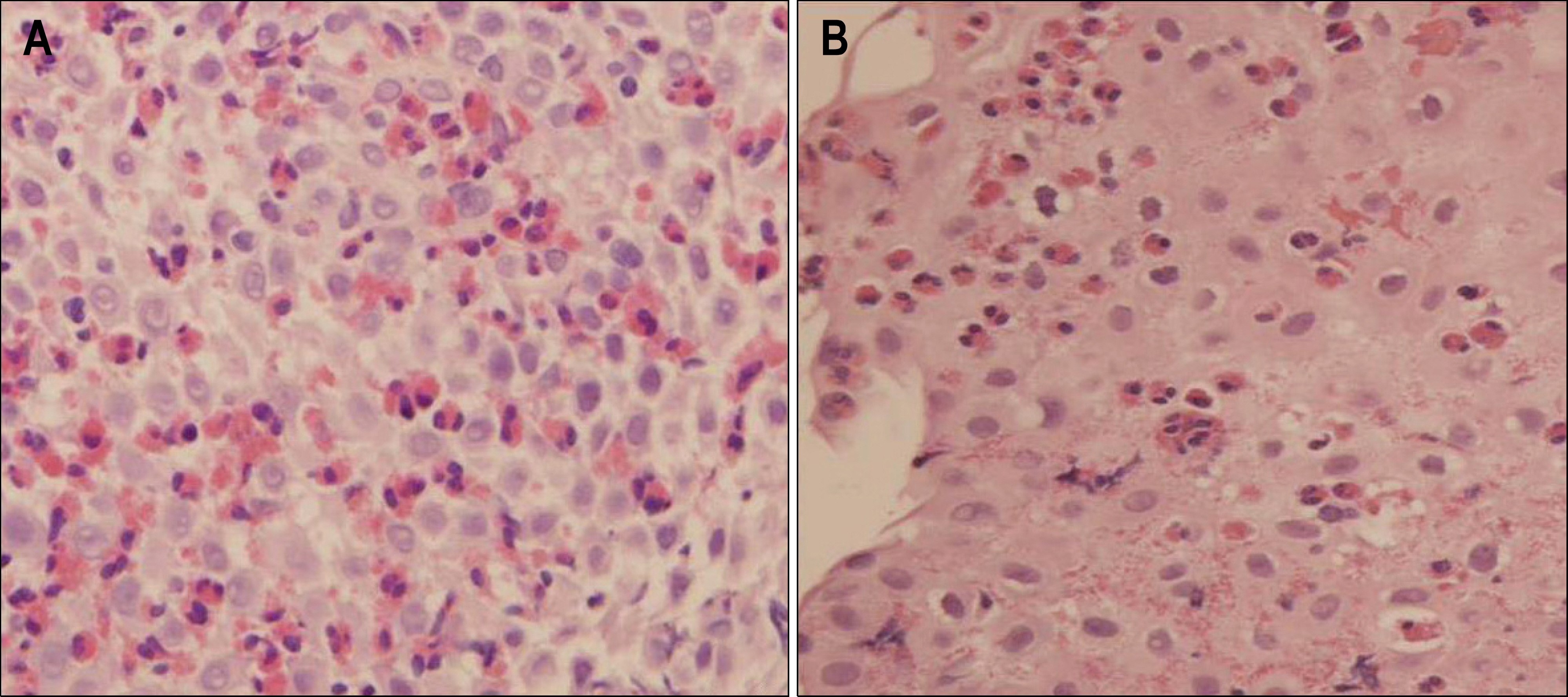
We reviewed biopsy specimen of the 1,609 patients who underwent esophageal biopsy from January 2006 till August 2008. The presence of more than 20 eosinophils per high power field in biopsy specimens was considered cases of EE. Clinical information and endoscopic findings were obtained.
RESULTS
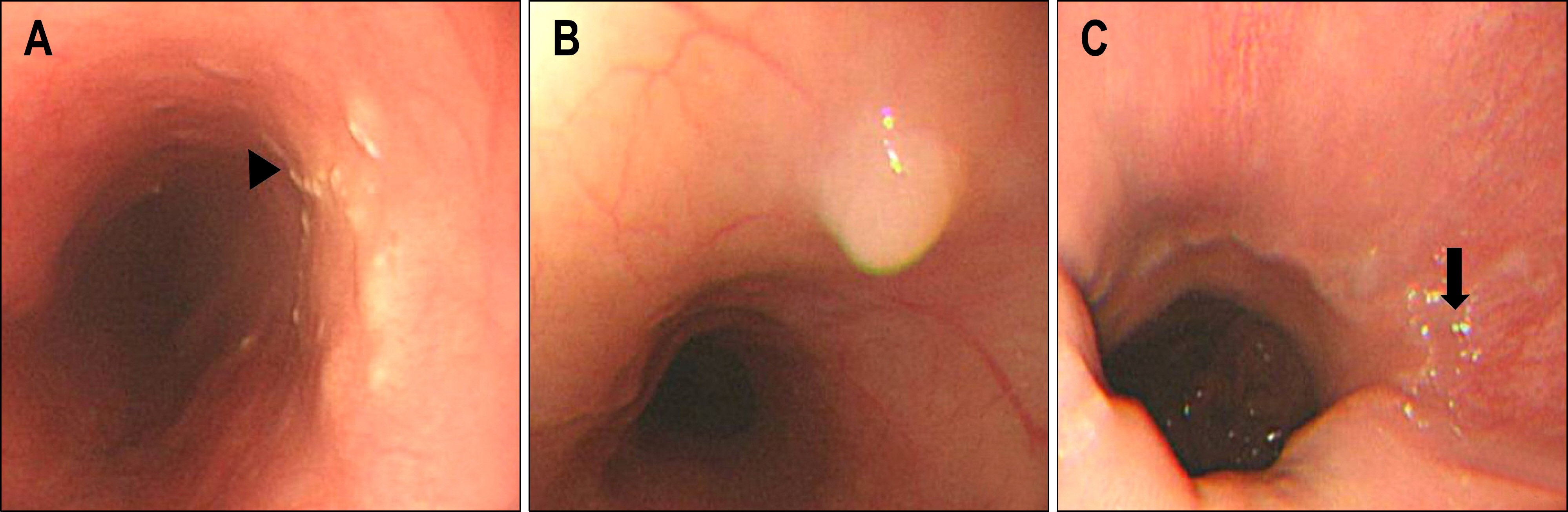
7 (0.4%) patients were diagnosed as EE based on pathologic criteria retrospectively. Clinical symptoms were epigastric pain (43%), regurgitation (29%), dyspepsia (14%), and no symptom (14%). Endoscopic findings were whitish exudates or granules (57%), esophageal polyp (29%), and hyperemic change (14%). Two patients received treatment. One patient with bronchial asthma improved after treatment with inhaled corticosteroid, and one patient improved after 8 week proton pump inhibitor therapy.
CONCLUSIONS
Eosinophilic esophagitis was found in 0.4% of the total esophageal biopsied cases. Our results suggest that Korean patients with eosinophilic esophagitis showed symptoms mimicking gastroesophageal reflux disease and atypical endoscopic findings. Therefore, regardless of the gross appearance of the mucosa, meticulous diagnostic approaches are needed for patients with swallowing difficulty and lack of response to proton pump inhibitor.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Landres RT, Kuster GG, Strum WB. Eosinophilic esophagitis in a patient with vigorous achalasia. Gastroenterology. 1978; 74:1298–1301.
Article2. Liacouras CA, Wenner WJ, Brown K, Ruchelli E. Primary eosinophilic esophagitis in children: successful treatment with oral corticosteroids. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1998; 26:380–385.
Article3. Walsh SV, Antonioli DA, Goldman H, et al. Allergic esophagitis in children: a clinicopathological entity. Am J Surg Pathol. 1999; 23:390–396.4. Orenstein SR, Shalaby TM, Di Lorenzo C, et al. The spec-trum of pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis beyond infancy: a clinical series of 30 children. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000; 95:1422–1430.
Article5. Attwood SE, Smyrk TC, Demeester TR, Jones JB. Esophageal eosinophilia with dysphagia. A distinct clinicopathologic syndrome. Dig Dis Sci. 1993; 38:109–116.6. Sgouros SN, Bergele C, Mantides A. Eosinophilic esophagitis in adults: a systematic review. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006; 18:211–217.
Article7. Croese J, Fairley SK, Masson JW, et al. Clinical and endoscopic features of eosinophilic esophagitis in adults. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003; 58:516–522.
Article8. Kapel RC, Miller JK, Torres C, Aksoy S, Lash R, Katzka DA. Eosinophilic esophagitis: a prevalent disease in the United States that affects all age groups. Gastroenterology. 2008; 134:1316–1321.
Article9. Arora AS, Yamazaki K. Eosinophilic esophagitis: asthma of the esophagus? Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004; 2:523–530.
Article10. Dellon ES, Aderoju A, Woosley JT, Sandler RS, Shaheen NJ. Variability in diagnostic criteria for eosinophilic esophagitis: a systematic review. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007; 102:2300–2313.
Article11. Kim JW, Park JS, Kim YH, et al. Secondary achalasia by eosionphilic esophagitis. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 2002; 25:198–202.12. Lee BJ, Park HJ, Yoon HS, Kim HK, Kim HS. Three cases of eosinophilic esophagitis with dysphagia as a chief com-plaint. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 2008; 36:145–149.13. Lee HC, Cho HJ, Park KS, et al. The comparison of eosinophilic esophagitis and gastroesophageal reflux disease. Chonnam Med J. 2007; 43:177–180.14. Yu YH, Jo YJ, Jung MY, et al. Prevalence of eosinophilic esophagitis with dysphagia and reflux related symptoms in Korean patients. Korean J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2009; 15:15–22.15. Noel RJ, Putnam PE, Rothenberg ME. Eosinophilic esophagitis. N Engl J Med. 2004; 351:940–941.
Article16. Ronkainen J, Talley NJ, Aro P, et al. Prevalence of oesopha-geal eosinophils and eosinophilic oesophagitis in adults: the population-based Kalixanda study. Gut. 2007; 56:615–620.
Article17. Whitney-Miller CL, Katzka D, Furth EE. Eosinophilic esophagitis: a retrospective review of esophageal biopsy specimens from 1992 to 2004 at an adult academic medical center. Am J Clin Pathol. 2009; 131:788–792.18. Veerappan GR, Perry JL, Duncan TJ, et al. Prevalence of eosinophilic esophagitis in an adult population undergoing upper endoscopy: a prospective study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009; 7:420–426.
Article19. Park HJ. Eosinophilic esophagitis. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2007; 50:286–291.20. Zink DA, Amin M, Gebara S, Desai TK. Familial dysphagia and eosinophilia. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 65:330–334.
Article21. Faubion WA Jr, Perrault J, Burgart LJ, Zein NN, Clawson M, Freese DK. Treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis with inhaled corticosteroids. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1998; 27:90–93.
Article22. Spergel JM, Brown-Whitehorn T, Beausoleil JL, Shuker M, Liacouras CA. Predictive values for skin prick test and atopy patch test for eosinophilic esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007; 119:509–511.
Article23. Kagalwalla AF, Sentongo TA, Ritz S, et al. Effect of six- food elimination diet on clinical and histologic outcomes in eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006; 4:1097–1102.24. Straumann A, Spichtin HP, Grize L, Bucher KA, Beglinger C, Simon HU. Natural history of primary eosinophilic esophagitis: a follow-up of 30 adult patients for up to 11.5 years. Gastroenterology. 2003; 125:1660–1669.
Article25. Basavaraju KP, Wong T. Eosinophilic oesophagitis: a common cause of dysphagia in young adults? Int J Clin Pract. 2008; 62:1096–1107.
Article26. Moawad FJ, Veerappan GR, Wong RK. Eosinophilic esophagitis. Dig Dis Sci. 2009; 54:1818–1828.
Article27. Straumann A, Spichtin HP, Bucher KA, Heer P, Simon HU. Eosinophilic esophagitis: red on microscopy, white on endoscopy. Digestion. 2004; 70:109–116.
Article28. Rothenberg ME, Mishra A, Collins MH, Putnam PE. Patho-genesis and clinical features of eosinophilic esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001; 108:891–894.
Article29. Ruchelli E, Wenner W, Voytek T, Brown K, Liacouras C. Severity of esophageal eosinophilia predicts response to con-ventional gastroesophageal reflux therapy. Pediatr Dev Pathol. 1999; 2:15–18.
Article30. Furuta GT, Liacouras CA, Collins MH, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis in children and adults: a systematic review and consensus recommendations for diagnosis and treatment. Gastroenterology. 2007; 133:1342–1363.
Article31. Shah A, Kagalwalla AF, Gonsalves N, Melin-Aldana H, Li BU, Hirano I. Histopathologic variability in children with eosinophilic esophagitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009; 104:716–721.
Article32. Arora AS, Perrault J, Smyrk TC. Topical corticosteroid treatment of dysphagia due to eosinophilic esophagitis in adults. Mayo Clin Proc. 2003; 78:830–835.
Article33. Stein ML, Collins MH, Villanueva JM, et al. Anti-IL-5 (me-polizumab) therapy for eosinophilic esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006; 118:1312–1319.
Article34. Attwood SE, Lewis CJ, Bronder CS, Morris CD, Armstrong GR, Whittam J. Eosinophilic oesophagitis: a novel treatment using Montelukast. Gut. 2003; 52:181–185.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Review of Eosinophilic Esophagitis
- A Case of Eosinophilic Esophagitis Found Incidentally during the Evaluation of a Gastric Submucosal Tumor
- CT Findings of Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Case Report
- Three Cases of Eosinophilic Esophagitis with Dysphagia as a Chief Complaint
- Emerging Issues in Esophageal Motility Diseases