J Korean Surg Soc.
2010 Jan;78(1):23-28. 10.4174/jkss.2010.78.1.23.
Early Experience of Doppler-Guided Hemorrhoidal Artery Ligation and Rectoanal Repair (DG-HAL & RAR) for the Treatment of Symptomatic Hemorrhoids
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Seoul Red Cross Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Surgery, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. gs3945@gmail.com
- KMID: 1775441
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2010.78.1.23
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: This study is to introduce our preliminary experience of the Doppler-guided hemorrhoidal artery ligation and Rectoanal repair (DG-HAL & RAR) as a new treatment for symptomatic or prolapsed hemorrhoids.
METHODS
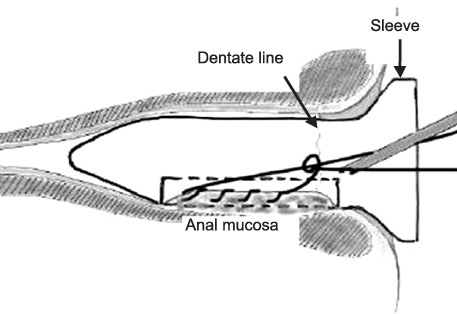
A Doppler probe incorporated proctoscope was inserted under the lithotomy position and the location of the hemorrhoidal artery was identified. The identified artery was ligated as a 'figure of eight' method with an absorbable suture into the submucosa. Then the prolapsed hemorrhoidal pile was lifted at the rectal mucosa by continuous suture to 5 mm above the dentate line and tied. The procedure was repeated at the 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, and 11 o'clock positions. We evaluated post-operative hospital stay, degree of pain, time to return to work, and recurrence.
RESULTS
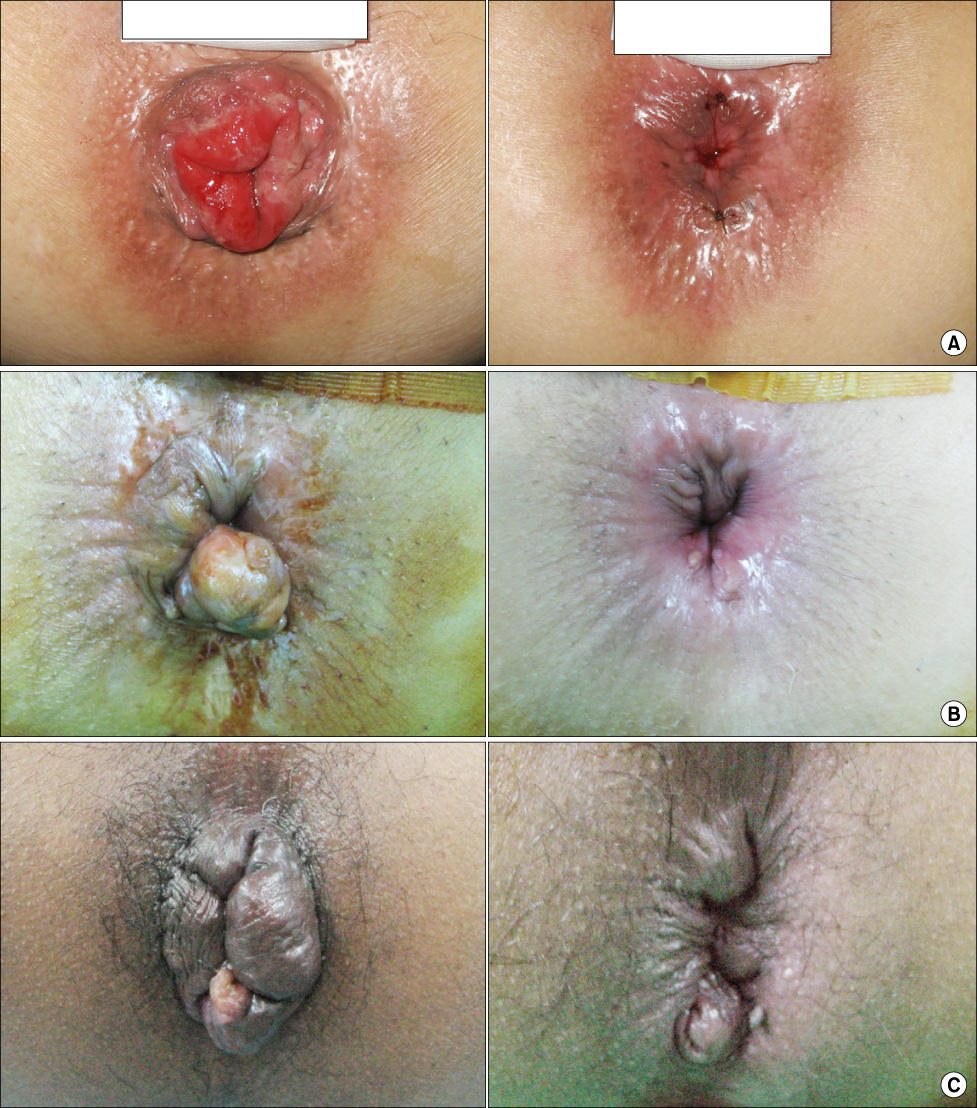
The patient's mean age was 50.2+/-15 years old and the mean follow-up time was 415+/-75 days. The constitution of the type of internal hemorrhoids was as follows: Grade II: 13, Grade III: 16, and Grade IV: 5. The mean operation time was 35 minutes and post-operative hospital stay was 1.4 days. The mean time it took to return to work was 1.8 days. There were no severe pains requiring injection of analgesics or other severe complications. So far, 2 patients have had recurrence of symptoms.
CONCLUSION
The DG-HAL & RAR is a safe and less painful procedure. The DG-HAL & RAR is an effective alternative for the treatment of symptomatic or prolapsed hemorrhoids.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Felice G, Privitera A, Ellul E, Klaumann M. Doppler-guided hemorrhoidal artery ligation: an alternative to hemorrhoidectomy. Dis Colon Rectum. 2005. 48:2090–2093.2. Scheyer M, Antonietti E, Rollinger G, Mall H, Arnold S. Doppler-guided hemorrhoidal artery ligation. Am J Surg. 2006. 191:89–93.3. Greenberg R, Karin E, Avital S, Skornick Y, Werbin N. First 100 cases with Doppler-guided hemorrhoidal artery ligation. Dis Colon Rectum. 2006. 49:485–489.4. Faucheron JL, Gangner Y. Doppler-guided hemorrhoidal artery ligation for the treatment of symptomatic hemorrhoids: early and three-year follow-up results in 100 consecutive patients. Dis Colon Rectum. 2008. 51:945–949.5. Longo A. Treatment of hemorrhoidal disease by reduction of mucosa and hemorrhoidalprolapse with a circular suturing device: a new procedure. 1998. In : Proceedings of 6th World Congress of Endoscopic Surgery; Jun 3~6; Rome, Italy: 777–784.6. Morinaga K, Hasuda K, Ikeda T. A novel therapy for internal hemorrhoids: ligation of the hemorrhoidal artery with a newly devised instrument (Moricorn) in conjunction with a Doppler flowmeter. Am J Gastroenterol. 1995. 90:610–613.7. Wallis de Vries BM, van der Beek ES, de Wijkerslooth LR, van der Zwet WC, van der Hoeven JA, Eeftinck Schattenkerk M, et al. Treatment of grade 2 and 3 hemorrhoids with Doppler-guided hemorrhoidal artery ligation. Dig Surg. 2007. 24:436–440.8. Bursics A, Morvay K, Kupcsulik P, Flautner L. Comparison of early and 1-year follow-up results of conventional hemorrhoidectomy and hemorrhoid artery ligation: a randomized study. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2004. 19:176–180.9. Hussein AM. Ligation-anopexy for treatment of advanced hemorrhoidal disease. Dis Colon Rectum. 2001. 44:1887–1890.10. Gupta PJ. Hemorrhoidal ablation and fixation: an alternative procedure for prolapsing hemorrhoids. Digestion. 2005. 72:181–188.11. Gupta PJ. Radioablation and suture fixation of advance grades of hemorrhoids. An effective alternative to staplers and Doppler guided ligation of hemorrhoids. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2006. 98:740–746.12. Aigner F, Bodner G, Conrad F, Mbaka G, Kreczy A, Fritsch H. The superior rectal artery and its branching pattern with regard to its clinical influence on ligation techniques for internal hemorrhoids. Am J Surg. 2004. 187:102–108.13. Walega P, Scheyer M, Kenig J, Herman RM, Arnold S, Nowak M, et al. Two-center experience in the treatment of hemorrhoidal disease using Doppler-guided hemorrhoidal artery ligation: functional results after 1-year follow-up. Surg Endosc. 2008. 22:2379–2383.14. Arnold S, Antonietti E, Rollinger G, Scheyer M. Doppler ultrasound assisted hemorrhoid artery ligation. A new therapy in symptomatic hemorrhoids. Chirurg. 2002. 73:269–273.15. Huang WS, Chin CC, Yeh CH, Lin PY, Wang JY. Randomized comparison between stapled hemorrhoidopexy and Ferguson hemorrhoidectomy for grade III hemorrhoids in Taiwan: a prospective study. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2007. 22:955–961.16. Bikhchandani J, Agarwal PN, Kant R, Malik VK. Randomized controlled trial to compare the early and mid-term results of stapled versus open hemorrhoidectomy. Am J Surg. 2005. 189:56–60.17. Wang JY, Lu CY, Tsai HL, Chen FM, Huang CJ, Huang YS, et al. Randomized controlled trial of LigaSure with submucosal dissection versus Ferguson hemorrhoidectomy for prolapsed hemorrhoids. World J Surg. 2006. 30:462–466.18. Gravie JF, Lehur PA, Huten N, Papillon M, Fantoli M, Descottes B, et al. Stapled hemorrhoidopexy versus milliganmorgan hemorrhoidectomy: a prospective, randomized, multicenter trial with 2-year postoperative follow up. Ann Surg. 2005. 242:29–35.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Early Experience of Treatment for Symptomatic Hemorrhoids with Doppler Guided Hemorrhoidal Artery Ligation and Recto-anal Repair
- One Year Follow-up Result of Doppler-guided Hemorrhoidal Artery Ligation and Recto-Anal Repair in 97 Consecutive Patients
- Early Experience with Doppler-guided Hemorrhoidal Artery Ligation
- Simple mucopexy and hemorrhoidal arterial ligation with and without Doppler guide: a randomized clinical trial for short-term outcome
- Minor Procedures of Hemorrhoids