J Korean Med Sci.
2014 Apr;29(4):570-575. 10.3346/jkms.2014.29.4.570.
Assessment of Hepatic Fibrosis Regression by Transient Elastography in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Treated with Oral Antiviral Agents
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Liver Cirrhosis Clinical Research Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yh.paik@skku.edu
- KMID: 1774464
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2014.29.4.570
Abstract
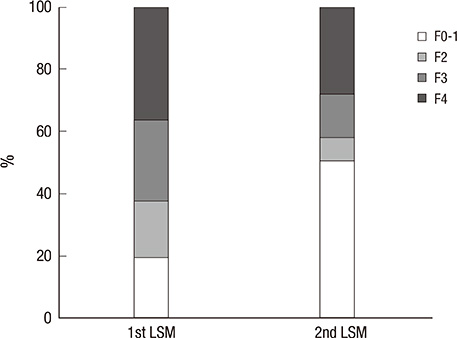
- Transient elastography (TE) has been used as a non-invasive method for liver stiffness measurement (LSM) in patients with chronic liver disease. This study was performed to assess the change of LSM by TE and to assess its clinical usefulness during long-term oral antiviral therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB). We retrospectively reviewed 83 CHB patients. The mean interval between two LSM was 411.5 +/- 149.5 days. Initial and follow-up LSM was 16.15 +/- 12.41 kPa and 11.26 +/- 7.36 kPa, respectively (P < 0.001). The degree of regression of liver stiffness was -2.03 +/- 0.36% per month. The fibrosis stage classified by LSM value improved in 37 (44.6%) patients during oral antiviral therapy. Of the 30 (36.1%) patients with LSM > or = 14.1 kPa (cirrhosis) at 1st LSM, 12 (40%) proved to no longer have cirrhosis (> or = 1 decrease in fibrosis stage) at 2nd LSM. LSM significantly decreased in both baseline high (> upper limit of normal [ULN] x 2) and low (< or = ULN x 2) alanine aminotransferase groups during antiviral therapy (P < 0.001; P = 0.001, respectively). Long-term oral antiviral therapy resulted in the improvement of liver stiffness in a substantial portion of patients with CHB. TE may be used a useful clinical tool to assess disease progression in CHB patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Administration, Oral
Adult
Aged
Alanine Transaminase/blood
Antiviral Agents/*therapeutic use
Elasticity Imaging Techniques
Female
Hepatitis B, Chronic/*drug therapy
Humans
Liver/ultrasonography
Liver Cirrhosis/*ultrasonography
Male
Middle Aged
Retrospective Studies
Severity of Illness Index
Antiviral Agents
Alanine Transaminase
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chen CJ, Iloeje UH, Yang HI. Long-term outcomes in hepatitis B: the REVEAL-HBV study. Clin Liver Dis. 2007; 11:797–816.2. Chisari FV, Ferrari C. Hepatitis B virus immunopathogenesis. Annu Rev Immunol. 1995; 13:29–60.3. Friedman SL. Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. Gastroenterology. 2008; 134:1655–1669.4. Kisseleva T, Brenner DA. Hepatic stellate cells and the reversal of fibrosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006; 21:S84–S87.5. Dienstag JL, Goldin RD, Heathcote EJ, Hann HW, Woessner M, Stephenson SL, Gardner S, Gray DF, Schiff ER. Histological outcome during long-term lamivudine therapy. Gastroenterology. 2003; 124:105–117.6. Chang TT, Liaw YF, Wu SS, Schiff E, Han KH, Lai CL, Safadi R, Lee SS, Halota W, Goodman Z, et al. Long-term entecavir therapy results in the reversal of fibrosis/cirrhosis and continued histological improvement in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2010; 52:886–893.7. Liaw YF, Sung JJ, Chow WC, Farrell G, Lee CZ, Yuen H, Tanwandee T, Tao QM, Shue K, Keene ON, et al. Lamivudine for patients with chronic hepatitis B and advanced liver disease. N Engl J Med. 2004; 351:1521–1531.8. Schiff E, Simsek H, Lee WM, Chao YC, Sette H Jr, Janssen HL, Han SH, Goodman Z, Yang J, Brett-Smith H, et al. Efficacy and safety of entecavir in patients with chronic hepatitis B and advanced hepatic fibrosis or cirrhosis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2008; 103:2776–2783.9. Iloeje UH, Yang HI, Su J, Jen CL, You SL, Chen CJ. Risk Evaluation of Viral Load Elevation and Associated Liver Disease/Cancer-In HBV (the REVEAL-HBV) Study Group. Predicting cirrhosis risk based on the level of circulating hepatitis B viral load. Gastroenterology. 2006; 130:678–686.10. Chen CJ, Yang HI, Su J, Jen CL, You SL, Lu SN, Huang GT, Iloeje UH. REVEAL-HBV Study Group. Risk of hepatocellular carcinoma across a biological gradient of serum hepatitis B virus DNA level. JAMA. 2006; 295:65–73.11. Guido M, Rugge M. Liver biopsy sampling in chronic viral hepatitis. Semin Liver Dis. 2004; 24:89–97.12. Martínez SM, Crespo G, Navasa M, Forns X. Noninvasive assessment of liver fibrosis. Hepatology. 2011; 53:325–335.13. Sandrin L, Fourquet B, Hasquenoph JM, Yon S, Fournier C, Mal F, Christidis C, Ziol M, Poulet B, Kazemi F, et al. Transient elastography: a new noninvasive method for assessment of hepatic fibrosis. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2003; 29:1705–1713.14. Kim BK, Kim SU, Kim HS, Park JY, Ahn SH, Chon CY, Cho IR, Joh DH, Park YN, Han KH, et al. Prospective validation of FibroTest in comparison with liver stiffness for predicting liver fibrosis in Asian subjects with chronic hepatitis B. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e35825.15. Park SH. Trends in the seroprevalence of hepatitis B surface antigen in the South Korean population. Int J Infect Dis. 2012; 16:e669–e672.16. Yoo BC, Park JW, Kim HJ, Lee DH, Cha YJ, Park SM. Precore and core promoter mutations of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B in Korea. J Hepatol. 2003; 38:98–103.17. Lok AS, McMahon BJ. Chronic hepatitis B: update 2009. Hepatology. 2009; 50:661–662.18. Poynard T, Mathurin P, Lai CL, Guyader D, Poupon R, Tainturier MH, Myers RP, Muntenau M, Ratziu V, Manns M, et al. A comparison of fibrosis progression in chronic liver diseases. J Hepatol. 2003; 38:257–265.19. Jung KS, Kim SU, Ahn SH, Park YN, Kim do Y, Park JY, Chon CY, Choi EH, Han KH. Risk assessment of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma development using liver stiffness measurement (FibroScan). Hepatology. 2011; 53:885–894.20. Bedossa P, Dargère D, Paradis V. Sampling variability of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2003; 38:1449–1457.21. Ganne-Carrié N, Ziol M, de Ledinghen V, Douvin C, Marcellin P, Castera L, Dhumeaux D, Trinchet JC, Beaugrand M. Accuracy of liver stiffness measurement for the diagnosis of cirrhosis in patients with chronic liver diseases. Hepatology. 2006; 44:1511–1517.22. Friedrich-Rust M, Ong MF, Martens S, Sarrazin C, Bojunga J, Zeuzem S, Herrmann E. Performance of transient elastography for the staging of liver fibrosis: a meta-analysis. Gastroenterology. 2008; 134:960–974.23. Chon YE, Choi EH, Song KJ, Park JY, Kim do Y, Han KH, Chon CY, Ahn SH, Kim SU. Performance of transient elastography for the staging of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B: a meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e44930.24. Coco B, Oliveri F, Maina AM, Ciccorossi P, Sacco R, Colombatto P, Bonino F, Brunetto MR. Transient elastography: a new surrogate marker of liver fibrosis influenced by major changes of transaminases. J Viral Hepat. 2007; 14:360–369.25. Kim SU, Seo YS, Cheong JY, Kim MY, Kim JK, Um SH, Cho SW, Paik SK, Lee KS, Han KH, et al. Factors that affect the diagnostic accuracy of liver fibrosis measurement by Fibroscan in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2010; 32:498–505.26. Chan HL, Wong GL, Choi PC, Chan AW, Chim AM, Yiu KK, Chan FK, Sung JJ, Wong VW. Alanine aminotransferase-based algorithms of liver stiffness measurement by transient elastography (Fibroscan) for liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B. J Viral Hepat. 2009; 16:36–44.27. Marcellin P, Gane E, Buti M, Afdhal N, Sievert W, Jacobson IM, Washington MK, Germanidis G, Flaherty JF, Schall RA, et al. Regression of cirrhosis during treatment with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for chronic hepatitis B: a 5-year open-label follow-up study. Lancet. 2013; 381:468–475.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Current role of transient elastography in the management of chronic hepatitis B patients
- Clinical applications of transient elastography
- Prediction of fibrosis progression in chronic viral hepatitis
- Differential Diagnosis of Diffuse Liver Disease
- New antiviral agents for treatment of chronic hepatitis B