J Korean Med Sci.
2014 Apr;29(4):550-555. 10.3346/jkms.2014.29.4.550.
Seasonal Variation in Hemoglobin A1c in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ymchomd@snu.ac.kr
- 2Institute of Medical and Biological Engineering, Medical Research Center, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Interdisciplinary Program for Bioengineering, Graduate School, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics Seoul National University College of Medicine and Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Biomedical Engineering, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1774461
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2014.29.4.550
Abstract
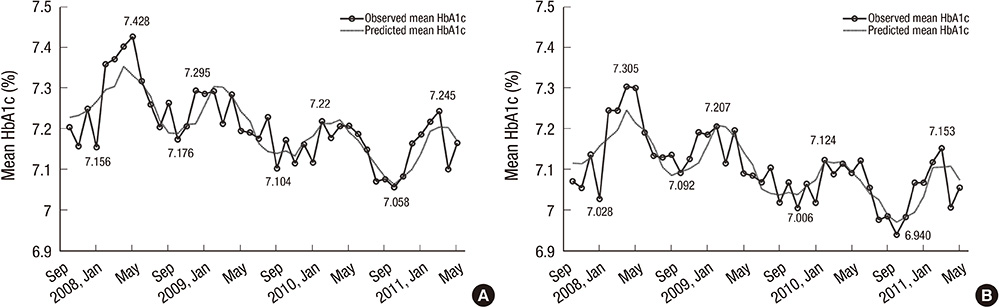
- A seasonal variation of glucose homeostasis in humans has been reported in various geographic regions. In this study, we examined seasonal variations in hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) in patients with type 2 diabetes living in Korea. We analyzed 57,970 HbA1c values from 4,191 patients and the association of these values with ambient temperature for 3.5 yr. Overall, HbA1c exhibited its highest values from February to March and its lowest values from September to October (coefficient for cos t = -0.0743, P = 0.058) and the difference between the peak and nadir in a year was 0.16%-0.25%. A statistically significant seasonal variation was observed in the patients who were taking oral anti-diabetic drugs (OADs) without insulin treatment (coefficient for cos t = -0.0949, P < 0.05). The Spearman correlation coefficient between daily HbA1c values and the corresponding 3-month moving average ambient temperature was -0.2154 (95% confidence interval [CI]: -0.2711, -0.1580; P < 0.05). In conclusion, HbA1c values exhibited a seasonal variation in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes, with the highest values during the cold season, particularly in those who were treated with OADs, which should be taken into account in clinical practice for stable glucose control during the cold season.
MeSH Terms
-
Anti-Bacterial Agents/therapeutic use
Asian Continental Ancestry Group
Bacterial Infections/prevention & control
Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2/*diagnosis/drug therapy
Hemoglobin A, Glycosylated/*analysis
Humans
Hypoglycemic Agents/therapeutic use
Insulin/therapeutic use
Republic of Korea
Seasons
Temperature
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Hemoglobin A, Glycosylated
Hypoglycemic Agents
Insulin
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Year-Long Trend in Glycated Hemoglobin Levels in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Jonghwa Jin, Seong Wook Lee, Won-Ki Lee, Jae-Han Jeon, Jung-Guk Kim, In-Kyu Lee, Yeon-Kyung Choi, Keun-Gyu Park
Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(5):1142-1146. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2021.1154.
Reference
-
1. Panda S, Hogenesch JB, Kay SA. Circadian rhythms from flies to human. Nature. 2002; 417:329–335.2. Reppert SM, Weaver DR. Coordination of circadian timing in mammals. Nature. 2002; 418:935–941.3. Bechtold DA, Loudon AS. Hypothalamic clocks and rhythms in feeding behaviour. Trends Neurosci. 2013; 36:74–82.4. Ziv E, Kalman R, Hershkop K, Barash V, Shafrir E, Bar-On H. Insulin resistance in the NIDDM model Psammomys obesus in the normoglycaemic, normoinsulinaemic state. Diabetologia. 1996; 39:1269–1275.5. Laraki M, Reusens B, Issoual D, Remacle C. Seasonal variations in the function of the endocrine pancreas in Psammomys obesus. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1998; 112:255–261.6. Sacks DB, Arnold M, Bakris GL, Bruns DE, Horvath AR, Kirkman MS, Lernmark A, Metzger BE, Nathan DM. Guidelines and recommendations for laboratory analysis in the diagnosis and management of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2011; 34:e61–e99.7. Mianowska B, Fendler W, Szadkowska A, Baranowska A, Grzelak-Agaciak E, Sadon J, Keenan H, Mlynarski W. HbA(1c) levels in schoolchildren with type 1 diabetes are seasonally variable and dependent on weather conditions. Diabetologia. 2011; 54:749–756.8. Hinde FR, Standen PJ, Mann NP, Johnston DI. Seasonal variation of haemoglobin A1 in children with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Eur J Pediatr. 1989; 148:597–599.9. Tseng CL, Brimacombe M, Xie M, Rajan M, Wang H, Kolassa J, Crystal S, Chen TC, Pogach L, Safford M. Seasonal patterns in monthly hemoglobin A1c values. Am J Epidemiol. 2005; 161:565–574.10. Sakura H, Tanaka Y, Iwamoto Y. Seasonal fluctuations of glycated hemoglobin levels in Japanese diabetic patients. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2010; 88:65–70.11. Higgins T, Saw S, Sikaris K, Wiley CL, Cembrowski GC, Lyon AW, Khajuria A, Tran D. Seasonal variation in hemoglobin A1c: is it the same in both hemispheres? J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2009; 3:668–671.12. Maguire GA, Edwards OM. Seasonal variation in glycated haemoglobin in diabetics. Ann Clin Biochem. 2001; 38:59–60.13. Garde AH, Hansen AM, Skovgaard LT, Christensen JM. Seasonal and biological variation of blood concentrations of total cholesterol, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate, hemoglobin A(1c), IgA, prolactin, and free testosterone in healthy women. Clin Chem. 2000; 46:551–559.14. Norman AW. Sunlight, season, skin pigmentation, vitamin D, and 25-hydroxyvitamin D: integral components of the vitamin D endocrine system. Am J Clin Nutr. 1998; 67:1108–1110.15. Reiter RJ. The melatonin rhythm: both a clock and a calendar. Experientia. 1993; 49:654–664.16. Chiu KC, Chu A, Go VL, Saad MF. Hypovitaminosis D is associated with insulin resistance and beta cell dysfunction. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004; 79:820–825.17. Scragg R, Sowers M, Bell C. Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D, diabetes, and ethnicity in the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Diabetes Care. 2004; 27:2813–2818.18. Liu E, Meigs JB, Pittas AG, McKeown NM, Economos CD, Booth SL, Jacques PF. Plasma 25-hydroxyvitamin d is associated with markers of the insulin resistant phenotype in nondiabetic adults. J Nutr. 2009; 139:329–334.19. Rapuri PB, Kinyamu HK, Gallagher JC, Haynatzka V. Seasonal changes in calciotropic hormones, bone markers, and bone mineral density in elderly women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002; 87:2024–2032.20. Pévet P. Melatonin: from seasonal to circadian signal. J Neuroendocrinol. 2003; 15:422–426.21. Peschke E, Bähr I, Mühlbauer E. Melatonin and pancreatic islets: interrelationships between melatonin, insulin and glucagon. Int J Mol Sci. 2013; 14:6981–7015.22. Cagnacci A, Arangino S, Renzi A, Paoletti AM, Melis GB, Cagnacci P, Volpe A. Influence of melatonin administration on glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity of postmenopausal women. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2001; 54:339–346.23. McMullan CJ, Schernhammer ES, Rimm EB, Hu FB, Forman JP. Melatonin secretion and the incidence of type 2 diabetes. JAMA. 2013; 309:1388–1396.24. Chen HS, Jap TS, Chen RL, Lin HD. A prospective study of glycemic control during holiday time in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care. 2004; 27:326–330.25. Pivarnik JM, Reeves MJ, Rafferty AP. Seasonal variation in adult leisure-time physical activity. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2003; 35:1004–1008.26. Dasgupta K, Chan C, Da Costa D, Pilote L, De Civita M, Ross N, Strachan I, Sigal R, Joseph L. Walking behaviour and glycemic control in type 2 diabetes: seasonal and gender differences-study design and methods. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2007; 6:1.27. Shahar DR, Yerushalmi N, Lubin F, Froom P, Shahar A, Kristal-Boneh E. Seasonal variations in dietary intake affect the consistency of dietary assessment. Eur J Epidemiol. 2001; 17:129–133.28. Visscher TL, Seidell JC. Time trends (1993-1997) and seasonal variation in body mass index and waist circumference in the Netherlands. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2004; 28:1309–1316.29. Holman RR, Paul SK, Bethel MA, Matthews DR, Neil HA. 10-year follow-up of intensive glucose control in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008; 359:1577–1589.30. Committee of clinical practice guideline: treatment guideline for diabetes. 1st ed. Seoul: MMK Communications; Korean Diabetes Association;2007.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Performance Evaluation of the ARKRAY ADAMS A1c HA-8180
- The Optimal Cutoff Value of Glycated Hemoglobin for Detection of Diabetic Retinopathy
- Factors Associated with Hemoglobin A1c among Patient Aged 40 years over with Diabetes Mellitus: 2012 Korea Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Relationship between Glycemic Control and Diabetic Retinopathy
- The Glycated Albumin to Glycated Hemoglobin Ratio Might Not Be Associated with Carotid Atherosclerosis in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes