Lab Med Online.
2014 Jul;4(3):164-167. 10.3343/lmo.2014.4.3.164.
Performance Evaluation of the ARKRAY ADAMS A1c HA-8180
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Konyang University Hospital, College of Medicine, Konyang University, Daejeon, Korea. hjchomd@kyuh.ac.kr
- KMID: 1706854
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/lmo.2014.4.3.164
Abstract
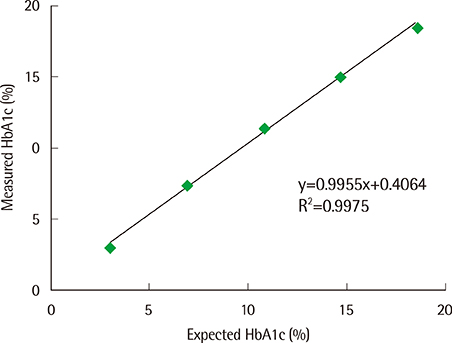
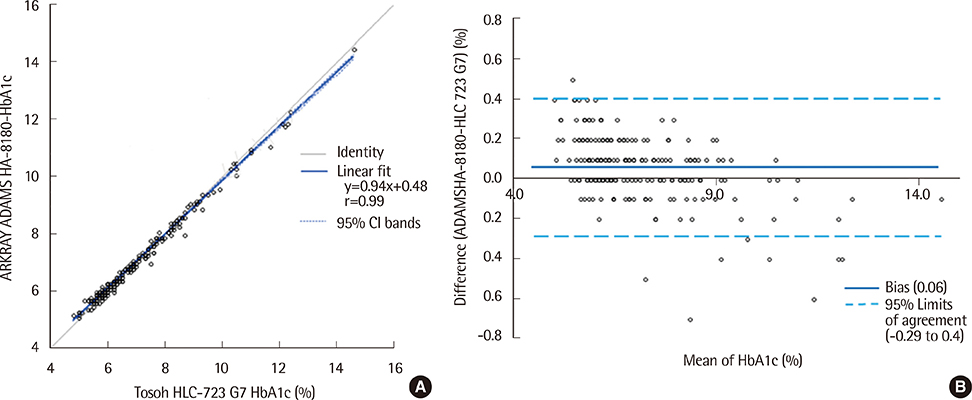
- The hemoglobin A1c (Hb A1c) test is widely used to diagnose diabetes mellitus and monitor glycemic control in patients with diabetes. We evaluated the performance of the ARKRAY ADAMS A1c HA-8180 (ARKRAY KDK, Japan), an automated, HPLC-based Hb A1c analyzer. The ARKRAY ADAMS A1c HA-8180 was evaluated for its linearity and precision and compared to the HLC-723 G7 (Tosoh Corporation, Japan), according to the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute's guidelines. The coefficients of variation (CVs) for within-run precision at low and high levels were 0.6% and 0.3%, respectively, and the total CVs at low and high levels were 0.8% and 0.6%, respectively. The coefficient of determination (R2) was 0.9975, with linearity in the range of 3.0-18.5%. A comparison between the ARKRAY ADAMS A1c HA-8180 and HLC-723 G7 revealed a good correlation (r=0.9955) in the range of 4.8-14.6%. The runtime was 57 s per sample. The ARKRAY ADAMS A1c HA-8180 showed good analytical performance and high throughput. Therefore, it is suitable for routine use for clinical measurements of Hb A1c.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim SG, Choi DS. The present state of diabetes mellitus in Korea. J Korean Med Assoc. 2008; 51:791–798.
Article2. National Health Insurance Corporation Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service. 2011 National Health Insurance Statistical Yearbook. http://www.nhic.or.kr/portal/site/main/menuitem.74b68c0b767ded38b31148b4062310a0.3. American Diabetes Association. Executive summary: Standards of medical care in diabetes--2010. Diabetes Care. 2010; 33:Suppl 1. S4–S10.4. Song J, Kwon KC, Kim JH, Kim JW, Min WK, Lee SY, et al. Annual report on external quality assessment in metabolic disorders in Korea (2008). J Lab Med Qual Assur. 2009; 31:143–159.5. Ko SH, Kim DJ, Oh SJ, Lee HJ, Shim KH, Woo MH, et al. 2011 Clinical practice guidelines for type 2 diabetes in Korea. J Korean Diabetes. 2011; 12:183–189.
Article6. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Evaluation of precision performance of quantitative measurement methods; Approved guideline -Second edition. EP5-A2. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2004.7. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Evaluation of the linearity of quantitative measurement procedures; A statistical approach; Approved guideline. EP6-A. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2003.8. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Method comparison and bias estimation using patient samples; Approved guideline-Second edition. EP9-A2. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2002.9. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Defining, establishing, and verifying reference intervals in the clinical laboratory; Approved guideline-Thrid edition. C28-A3. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2008.10. Marshall SM, Barth JH. Standardization of HbA1c measurements: a consensus statement. Ann Clin Biochem. 2000; 37:45–46.
Article11. Goodall I, Colman PG, Schneider HG, McLean M, Barker G. Desirable performance standards for HbA(1c) analysis - precision, accuracy and standardisation: consensus statement of the Australasian Association of Clinical Biochemists (AACB), the Australian Diabetes Society (ADS), the Royal College of Pathologists of Australasia (RCPA), Endocrine Society of Australia (ESA), and the Australian Diabetes Educators Association (ADEA). Clin Chem Lab Med. 2007; 45:1083–1097.
Article12. Westgard J. Minimum specifications from biological variation database. Updated on 2014. http://www.westgard.com/minimum-biodatabase1.htm.13. Lim J, Kim JM, Koo SH, Kwon KC. Evaluation of the performance of ARKRAY ADAMS HA-8180 Hb A1c Analyzer. Lab Med Online. 2012; 2:126–130.
Article14. Choi Q, Han M, Chang HE, Song SH, Park KU, Song J. Performance evaluation of the ADAMS A1c HA-8180 Analyzer for Hb A1c. J Lab Med Qual Assur. 2012; 34:25–30.15. Nakanishi K, Siga S, Mori N, Ishida A, Masuda K, Yamasita S, et al. Basic Investigation of ADAMS A1c HA-8180, a new Hb A1c measuring instrument using high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). JJCLA. 2010; 35:243–249.16. The Korean Association of Quality Assurance for Clinical Laboratory. Updated on 2013-02-28. http://www.labqa.org/sub/catalog.php?boardid=board_seminar&mode=view&no=259&start=0&search_str=&val=&CatNo=43.17. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Verification of comparability of patient results within one health care system; Proposed guideline. C54-P. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2007.18. Lee SY, Kim JW. Evaluation of the Tosoh HLC-723 G7 Hemoglobin A1c Analyzer. Korean J Lab Med. 2003; 23:180–185.19. Jeong GY, Lee MK, Kim JW. Performance evaluation of TOSOH automated glycohemoglobin analyzer HLC-723GHb V A1c 2.2TM. Korean J Clin Pathol. 1999; 19:36–39.20. Bry L, Chen PC, Sacks DB. Effects of hemoglobin variants and chemically modified derivatives on assays for glycohemoglobin. Clin Chem. 2001; 47:153–163.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of the Performance of ARKRAY ADAMS HA-8180 HbA1c Analyzer
- Performance Evaluation of the ARKRAY ADAMS Bridge System Comprising Glucose GA-1171 and HbA1c HA-8180 Analyzers
- Performance Evaluation of the ADAMS A1c HA-8180 Analyzer for HbA1c
- Performance Evaluation of TOSOH Automated Glycohemoglobin Analyzer HLC-723GHb V A1c 2.2TM
- Evaluation of VARIANTTM II Hemoglobin A1c Autoanalyzer