J Korean Fract Soc.
2015 Jan;28(1):93-101. 10.12671/jkfs.2015.28.1.93.
Diagnosis and Management of Acute Compartment Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. kbleeos@chonnam.ac.kr
- KMID: 1774103
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2015.28.1.93
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
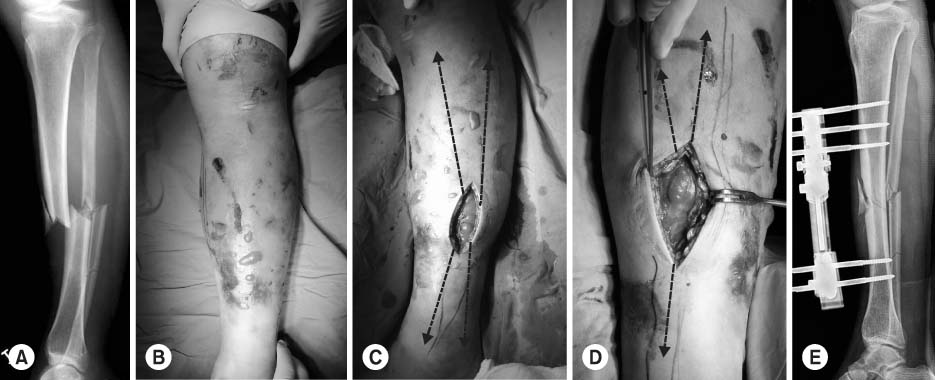
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Clinical Outcomes of Fasciotomy for Acute Compartment Syndrome
Ji Yong Park, Young Chang Kim, Ji Wan Kim
J Korean Fract Soc. 2015;28(4):223-229. doi: 10.12671/jkfs.2015.28.4.223.Compartment Syndrome of the Gluteus Medius Occurred without Bleeding or Trauma: A Case Report
Gyu-Min Kong, Yong-Uk Kwon, Jun-Ho Park
Hip Pelvis. 2015;27(4):278-282. doi: 10.5371/hp.2015.27.4.278.Surgical Timing of Treating Adult Trauma: Emergency/Urgency
Dong-Hyun Kang, Kyu Hyun Yang
J Korean Fract Soc. 2015;28(2):139-145. doi: 10.12671/jkfs.2015.28.2.139.
Reference
-
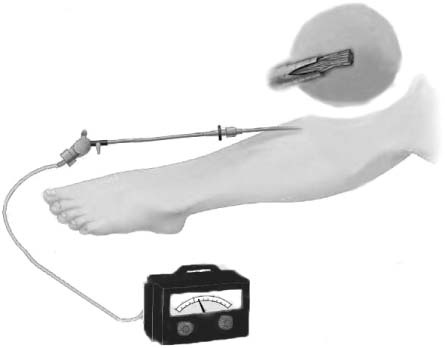
1. Mubarak SJ, Hargens AR, Owen CA, Garetto LP, Akeson WH. The wick catheter technique for measurement of intramuscular pressure. A new research and clinical tool. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1976; 58:1016–1020.
Article2. Matsen FA 3rd. Compartmental syndrome. An unified concept. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1975; (113):8–14.3. Volkmann R. Die ischaemischem Muskellamungen und Kontrakturen. Zentralbl Chir. 1881; 8:801.4. Holden CE. The pathology and prevention of Volkmann's ischaemic contracture. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1979; 61:296–300.
Article5. Seddon HJ. Volkmann's ischaemia in the lower limb. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1966; 48:627–636.
Article6. McQueen MM. Acute compartment syndrome. In : Court-Brown CM, Heckman JD, McQueen MM, Ricci WM, Tornetta P, editors. Rockwood and Green's fractures in adults. 8th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health;2014. p. 895–913.7. Uliasz A, Ishida JT, Fleming JK, Yamamoto LG. Comparing the methods of measuring compartment pressures in acute compartment syndrome. Am J Emerg Med. 2003; 21:143–145.
Article8. Whitesides TE, Heckman MM. Acute compartment syndrome: update on diagnosis and treatment. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 1996; 4:209–218.
Article9. The Korean Fracture Society. Principles of fracture management. 1st ed. Seoul: Pan Mun Education;2013.10. Finkemeier CG, Schmidt AH, Kyle RF, Templeman DC, Varecka TF. A prospective, randomized study of intramedullary nails inserted with and without reaming for the treatment of open and closed fractures of the tibial shaft. J Orthop Trauma. 2000; 14:187–193.
Article11. Ritenour AE, Dorlac WC, Fang R, et al. Complications after fasciotomy revision and delayed compartment release in combat patients. J Trauma. 2008; 64:S153–S161.
Article12. Ebraheim NA, Hoeflinger MJ, Savolaine ER, Jackson WT. Anterior compartment syndrome of the thigh as a complication of blunt trauma in a patient on prolonged anticoagulation therapy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991; (263):180–184.
Article13. McQueen MM, Gaston P, Court-Brown CM. Acute compartment syndrome. Who is at risk? J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2000; 82:200–203.14. Fitzgerald AM, Gaston P, Wilson Y, Quaba A, McQueen MM. Long-term sequelae of fasciotomy wounds. Br J Plast Surg. 2000; 53:690–693.
Article15. Hope MJ, McQueen MM. Acute compartment syndrome in the absence of fracture. J Orthop Trauma. 2004; 18:220–224.
Article16. Court-Brown CM, McBirnie J. The epidemiology of tibial fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1995; 77:417–421.
Article17. Harrington P, Bunola J, Jennings AJ, Bush DJ, Smith RM. Acute compartment syndrome masked by intravenous morphine from a patient-controlled analgesia pump. Injury. 2000; 31:387–389.
Article18. Hargens AR, Akeson WH, Mubarak SJ, et al. Fluid balance within the canine anterolateral compartment and its relationship to compartment syndromes. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1978; 60:499–505.
Article19. Heckman MM, Whitesides TE Jr, Grewe SR, Judd RL, Miller M, Lawrence JH 3rd. Histologic determination of the ischemic threshold of muscle in the canine compartment syndrome model. J Orthop Trauma. 1993; 7:199–210.
Article20. Matava MJ, Whitesides TE Jr, Seiler JG 3rd, Hewan-Lowe K, Hutton WC. Determination of the compartment pressure threshold of muscle ischemia in a canine model. J Trauma. 1994; 37:50–58.
Article21. Hayes G, Liauw S, Romaschin AD, et al. Separation of reperfusion injury from ischaemia induced necrosis. Surg Forum. 1988; 39:306–308.22. Labbe R, Lindsay T, Walker PM. The extent and distribution of skeletal muscle necrosis after graded periods of complete ischemia. J Vasc Surg. 1987; 6:152–157.
Article23. Petrasek PF, Homer-Vanniasinkam S, Walker PM. Determinants of ischemic injury to skeletal muscle. J Vasc Surg. 1994; 19:623–631.
Article24. Heppenstall RB, Scott R, Sapega A, Park YS, Chance B. A comparative study of the tolerance of skeletal muscle to ischemia. Tourniquet application compared with acute compartment syndrome. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1986; 68:820–828.
Article25. Heppenstall RB, Sapega AA, Scott R, et al. The compartment syndrome. An experimental and clinical study of muscular energy metabolism using phosphorus nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988; (226):138–155.26. Gelberman RH. Upper extremity compartment syndromes. In : Mubarak SJ, Hargens AR, editors. Compartment syndromes and Volkmann's contracture. Philadelphia: Saunders;1981.27. Matsen FA 3rd, King RV, Krugmire RB Jr, Mowery CA, Roche T. Physiological effects of increased tissue pressure. Int Orthop. 1979; 3:237–244.
Article28. Rorabeck CH, Clarke KM. The pathophysiology of the anterior tibial compartment syndrome: an experimental investigation. J Trauma. 1978; 18:299–304.29. Bae DS, Kadiyala RK, Waters PM. Acute compartment syndrome in children: contemporary diagnosis, treatment, and outcome. J Pediatr Orthop. 2001; 21:680–688.
Article30. Olson SA, Glasgow RR. Acute compartment syndrome in lower extremity musculoskeletal trauma. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2005; 13:436–444.
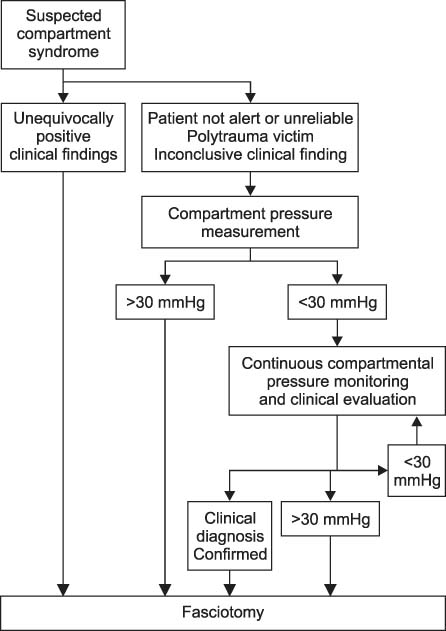
Article31. Ulmer T. The clinical diagnosis of compartment syndrome of the lower leg: are clinical findings predictive of the disorder? J Orthop Trauma. 2002; 16:572–577.
Article32. Shereff MJ. Compartment syndromes of the foot. Instr Course Lect. 1990; 39:127–132.33. Myerson MS. Management of compartment syndromes of the foot. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991; (271):239–248.
Article34. Williams J, Gibbons M, Trundle H, Murray D, Worlock P. Complications of nailing in closed tibial fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 1995; 9:476–481.
Article35. Duckworth AD, Mitchell SE, Molyneux SG, White TO, Court-Brown CM, McQueen MM. Acute compartment syndrome of the forearm. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012; 94:e63.
Article36. Schwartz JT Jr, Brumback RJ, Lakatos R, Poka A, Bathon GH, Burgess AR. Acute compartment syndrome of the thigh. A spectrum of injury. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1989; 71:392–400.
Article37. Willis RB, Rorabeck CH. Treatment of compartment syndrome in children. Orthop Clin North Am. 1990; 21:401–412.
Article38. Scholander PF, Hargens AR, Miller SL. Negative pressure in the interstitial fluid of animals. Fluid tensions are spectacular in plants; in animals they are elusively small, but just as vital. Science. 1968; 161:321–328.
Article39. Rorabeck CH, Castle GSP, Lugan J. The slit catheter: a new device for measuring intracompartmental pressure. Surg Forum. 1980; 31:513.40. McQueen MM, Court-Brown CM. Compartment monitoring in tibial fractures. The pressure threshold for decompression. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1996; 78:99–104.41. Whitesides TE, Haney TC, Morimoto K, Harada H. Tissue pressure measurements as a determinant for the need of fasciotomy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1975; (113):43–51.
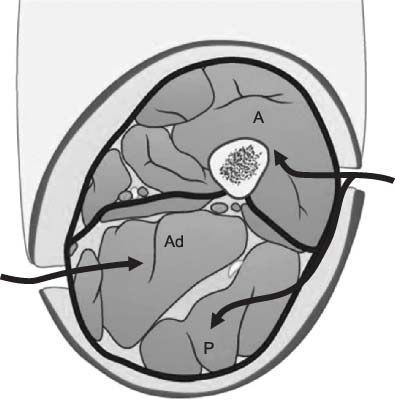
Article42. Frink M, Hildebrand F, Krettek C, Brand J, Hankemeier S. Compartment syndrome of the lower leg and foot. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010; 468:940–950.
Article43. Oh CW, Lee HJ. Acute compartment syndrome after trauma. J Korean Fract Soc. 2010; 23:399–403.
Article44. Better OS, Zinman C, Reis DN, Har-Shai Y, Rubinstein I, Abassi Z. Hypertonic mannitol ameliorates intracompartmental tamponade in model compartment syndrome in the dog. Nephron. 1991; 58:344–346.
Article45. Odland R, Schmidt AH, Hunter B, et al. Use of tissue ultrafiltration for treatment of compartment syndrome: a pilot study using porcine hindlimbs. J Orthop Trauma. 2005; 19:267–275.46. Bourne RB, Rorabeck CH. Compartment syndromes of the lower leg. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989; (240):97–104.
Article47. McQueen MM, Christie J, Court-Brown CM. Acute compartment syndrome in tibial diaphyseal fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1996; 78:95–98.
Article48. Cooper GG. A method of single-incision, four compartment fasciotomy of the leg. Eur J Vasc Surg. 1992; 6:659–661.
Article49. Maheshwari R, Taitsman LA, Barei DP. Single-incision fasciotomy for compartmental syndrome of the leg in patients with diaphyseal tibial fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2008; 22:723–730.
Article50. Mubarak SJ, Owen CA. Double-incision fasciotomy of the leg for decompression in compartment syndromes. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1977; 59:184–187.
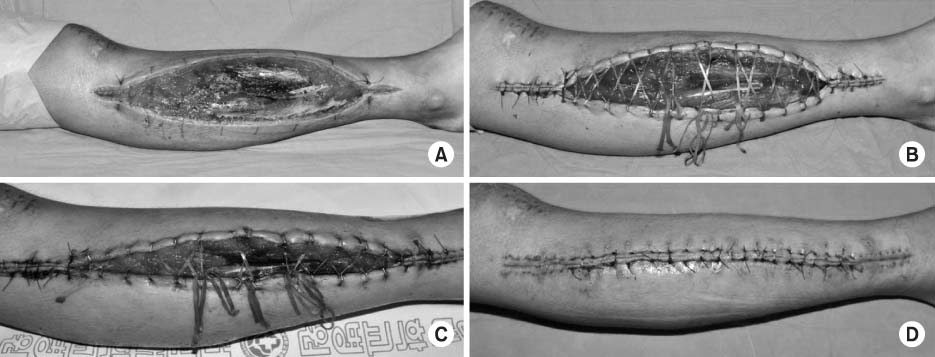
Article51. Wilkin G, Khogali S, Garbedian S, et al. Negative-pressure wound therapy after fasciotomy reduces muscle-fiber regeneration in a pig model. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014; 96:1378–1385.
Article52. Kakagia D, Karadimas EJ, Drosos G, Ververidis A, Trypsiannis G, Verettas D. Wound closure of leg fasciotomy: comparison of vacuum-assisted closure versus shoelace technique. A randomised study. Injury. 2014; 45:890–893.
Article53. Moed BR, Strom DE. Compartment syndrome after closed intramedullary nailing of the tibia: a canine model and report of two cases. J Orthop Trauma. 1991; 5:71–77.