Korean J Pain.
2010 Jun;23(2):109-115. 10.3344/kjp.2010.23.2.109.
Central Pain from Excitotoxic Spinal Cord Injury Induced by Intraspinal NMDA Injection: A Pilot Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jgleem@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 1770542
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2010.23.2.109
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The pathophysiological and neurochemical changes following spinal injury are not yet elucidated. This study was designed to evaluate the morphological changes of the dorsal horn of the spinal cord and profiles of pain behaviors following intraspinal injection of NMDA in rats.
METHODS
Rats were randomized into three groups: a sham-operated control group and groups where the rats received 10 mM or 100 mM N-methyl-D-aspatate (NMDA) injected into their spinal dorsal horn. Following injection, hypersensitivity to cold and mechanical stimuli and excessive grooming behaviors were assessed serially for four weeks. Morphological changes of the spinal cord were evaluated four weeks after intraspinal injection.
RESULTS
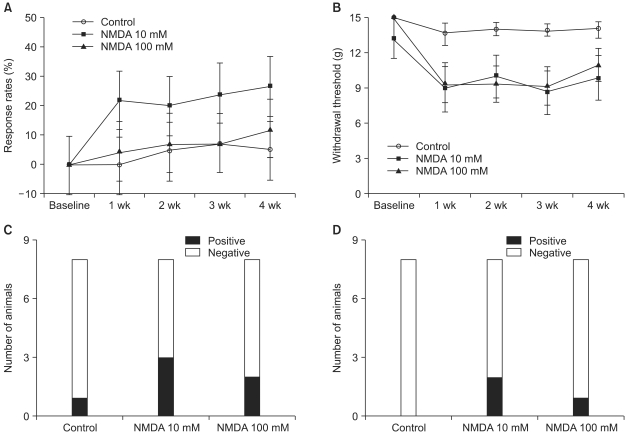
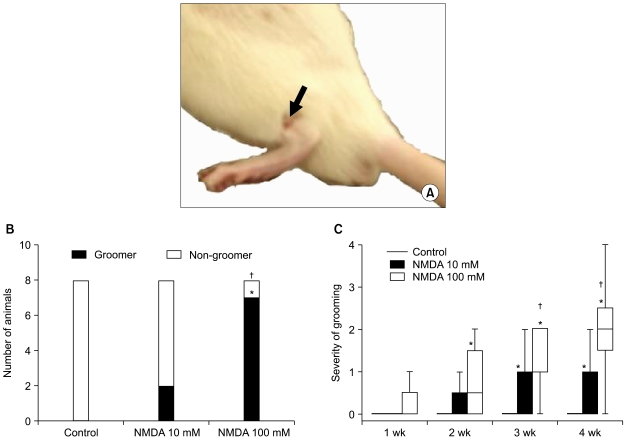
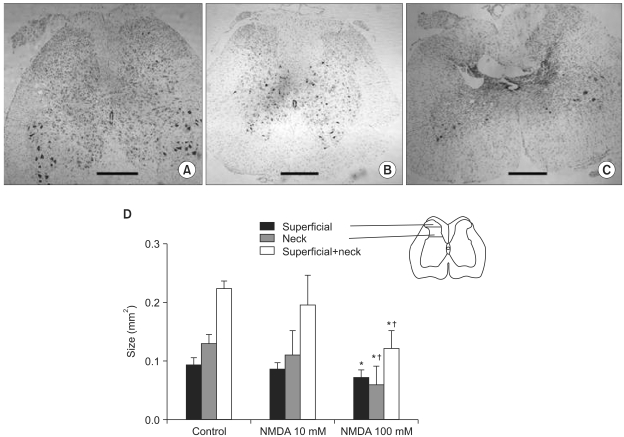
Few animals in the NMDA groups developed hypersensitivity to cold and mechanical stimuli. The number of groomers and the severity of excessive grooming were significantly higher in the 100 mM NMDA group than those values of the control and 10 mM NMDA groups. The size of the neck region (lamina III-IV) was significantly smaller in the 100 mM NMDA group than in the control and 10 mM NMDA groups.
CONCLUSIONS
In conclusion, intraspinal injection of NMDA in rats leads to the pathological sequela in the spinal cord and to excessive grooming behavior. These results support the use of NMDA and excessive grooming behavior after excitotoxic SCI as a model to study chronic pain after SCI.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Pregabalin and gabapentin in neuropathic pain management after spinal cord injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Majid Davari, Bahman Amani, Behnam Amani, Ahmad Khanijahani, Arash Akbarzadeh, Rouhollah Shabestan
Korean J Pain. 2020;33(1):3-12. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2020.33.1.3.
Reference
-
1. Hulsebosch CE, Hains BC, Crown ED, Carlton SM. Mechanisms of chronic central neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury. Brain Res Rev. 2009; 60:202–213. PMID: 19154757.
Article2. Xu XJ, Hao JX, Aldskogius H, Seiger A, Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z. Chronic pain-related syndrome in rats after ischemic spinal cord lesion: a possible animal model for pain in patients with spinal cord injury. Pain. 1992; 48:279–290. PMID: 1589248.
Article3. Gwak YS, Crown ED, Unabia GC, Hulsebosch CE. Propentofylline attenuates allodynia, glial activation and modulates GABAergic tone after spinal cord injury in the rat. Pain. 2008; 138:410–422. PMID: 18353556.
Article4. Hulsebosch CE, Xu GY, Perez-Polo JR, Westlund KN, Taylor CP, McAdoo DJ. Rodent model of chronic central pain after spinal cord contusion injury and effects of gabapentin. J Neurotrauma. 2000; 17:1205–1217. PMID: 11186233.
Article5. Bruce JC, Oatway MA, Weaver LC. Chronic pain after clip-compression injury of the rat spinal cord. Exp Neurol. 2002; 178:33–48. PMID: 12460606.
Article6. Simpson RK Jr, Robertson CS, Goodman JC. Spinal cord ischemia-induced elevation of amino acids: extracellular measurement with microdialysis. Neurochem Res. 1990; 15:635–639. PMID: 1977091.
Article7. Liu D, Thangnipon W, McAdoo DJ. Excitatory amino acids rise to toxic levels upon impact injury to the rat spinal cord. Brain Res. 1991; 547:344–348. PMID: 1884213.
Article8. Yezierski RP, Liu S, Ruenes GL, Kajander KJ, Brewer KL. Excitotoxic spinal cord injury: behavioral and morphological characteristics of a central pain model. Pain. 1998; 75:141–155. PMID: 9539683.
Article9. Gomes-Leal W, Corkill DJ, Freire MA, Picanço-Diniz CW, Perry VH. Astrocytosis, microglia activation, oligodendrocyte degeneration, and pyknosis following acute spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol. 2004; 190:456–467. PMID: 15530884.
Article10. Gorman AL, Yu CG, Ruenes GR, Daniels L, Yezierski RP. Conditions affecting the onset, severity, and progression of a spontaneous pain-like behavior after excitotoxic spinal cord injury. J Pain. 2001; 2:229–240. PMID: 14622821.
Article11. Liu S, Ruenes GL, Yezierski RP. NMDA and non-NMDA receptor antagonists protect against excitotoxic injury in the rat spinal cord. Brain Res. 1997; 756:160–167. PMID: 9187327.
Article12. Hulsebosch CE, Hains BC, Crown ED, Carlton SM. Mechanisms of chronic central neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury. Brain Res Rev. 2009; 60:202–213. PMID: 19154757.
Article14. Iino M, Ozawa S, Tsuzuki K. Permeation of calcium through excitatory amino acid receptor channels in cultured rat hippocampal neurones. J Physiol. 1990; 424:151–165. PMID: 1697342.
Article16. Popovich PG, Guan Z, McGaughy V, Fisher L, Hickey WF, Basso DM. The neuropathological and behavioral consequences of intraspinal microglial/macrophage activation. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2002; 61:623–633. PMID: 12125741.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of the Spinal Neuropathic Pain Induced by Intraspinal Injection of N-Methyl-D-Aspartate and Quisquate in Rats
- Management of Spinal Cord Injury Pain with Small Divided Doses of Intravenous Ketamine
- The Treatment of Central Pain after Spinal Cord Injury
- Intracavernous Papaverine Injection for Erectile Impotence in Men with Spinal Cord Injury
- Microsurgical DREZotomy for treatment of intractable central pain in patient with spinal cord injury