Korean J Pain.
2010 Sep;23(3):211-214. 10.3344/kjp.2010.23.3.211.
Spontaneous Retropharyngeal Hematoma: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kmshin1@yahoo.co.kr
- 2Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Hallym University College of Medicine, Anyang, Korea.
- KMID: 1767887
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2010.23.3.211
Abstract
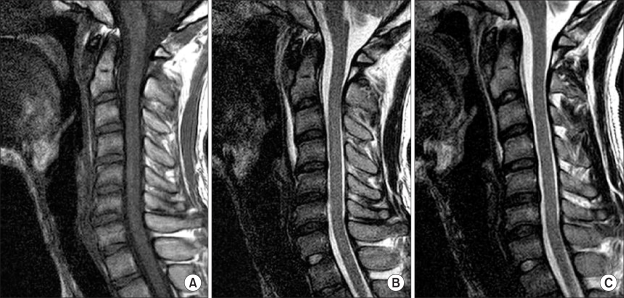
- Spontaneous retropharyngeal hematoma is rare and difficult to diagnosis early. A 23-year-old male spontaneously developed acute onset of neck pain, limitation of neck motion, and mild dysphagia. Magnetic resonance imaging demonstrated blood products in prevertebral space from C2 to C4, suggesting a diagnosis of retropharyngeal hematoma. We report a rare case of spontaneous retropharyngeal hematoma causing neck pain.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chin KW, Sercarz JA, Wang MB, Andrews R. Spontaneous cervical hemorrhage with near-complete airway obstruction. Head Neck. 1998; 20:350–353. PMID: 9588708.
Article2. Bloom DC, Haegen T, Keefe MA. Anticoagulation and spontaneous retropharyngeal hematoma. J Emerg Med. 2003; 24:389–394. PMID: 12745040.
Article3. DiFrancesco RC, Escamilla JS, Sennes LU, Voegles RL, Tsuji DH. Spontaneous cervical hematoma: a report of two cases. Ear Nose Throat J. 1999; 78:168. 171. 175. PMID: 10188353.
Article4. Muñoz A, Fischbein NJ, de Vergas J, Crespo J, Alvarez-Vincent J. Spontaneous retropharyngeal hematoma: diagnosis by MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001; 22:1209–1211. PMID: 11415922.5. Sandor F, Cooke RT. Spontaneous cervico-mediastinal haematoma. Br J Surg. 1964; 51:682–686. PMID: 14222573.
Article6. Higa K, Hirata K, Hirota K, Nitahara K, Shono S. Retropharyngeal hematoma after stellate ganglion block: analysis of 27 patients reported in the literature. Anesthesiology. 2006; 105:1238–1245. PMID: 17122587.7. Lazott LW, Ponzo JA, Puana RB, Artz KS, Ciceri DP, Culp WC Jr. Severe upper airway obstruction due to delayed retropharyngeal hematoma formation following blunt cervical trauma. BMC Anesthesiol. 2007; 7:2. PMID: 17352800.
Article8. Penning L. Prevertebral hematoma in cervical spine injury: incidence and etiologic significance. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1981; 136:553–561. PMID: 6781295.
Article9. Rojas CA, Vermess D, Bertozzi JC, Whitlow J, Guidi C, Martinez CR. Normal thickness and appearance of the prevertebral soft tissues on multidetector CT. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009; 30:136–141. PMID: 19001541.
Article10. Haun CL. Retropharyngeal tendinitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1978; 130:1137–1140. PMID: 418653.
Article11. Eastwood JD, Hudgins PA, Malone D. Retropharyngeal effusion in acute calcific prevertebral tendinitis: diagnosis with CT and MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1998; 19:1789–1792. PMID: 9802506.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Spontaneous Retropharyngeal Hematoma: A Case Report and Literature Overview
- Acute Airway Obstruction by a Retropharyngeal Hematoma when Performing Internal Jugular Vein Cannulation in a Patient with HELLP Syndrome: A case report
- A Clinical Review on Four Cases of the Retropharyngeal Hematoma
- Cervical Prevertebral Hematoma - a Rare Complication of Acupuncture Therapy: A Case Report
- Traumatic Retropharyngeal Hematoma following Cervical Vascular Injury: A Case Report