Effect of Perioperative Perineural Injection of Dexamethasone and Bupivacaine on a Rat Spared Nerve Injury Model
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sjinwoo@hotmail.com
- KMID: 1767872
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2010.23.3.166
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Neuropathic pain resulting from diverse causes is a chronic condition for which effective treatment is lacking. The goal of this study was to test whether dexamethasone exerts a preemptive analgesic effect with bupivacaine when injected perineurally in the spared nerve injury model.
METHODS
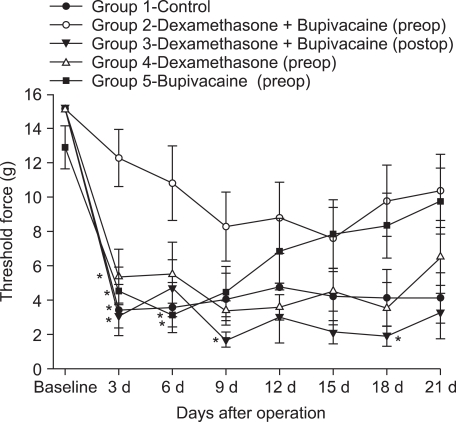
Fifty rats were randomly divided into five groups. Group 1 (control) was ligated but received no drugs. Group 2 was perineurally infiltrated (tibial and common peroneal nerves) with 0.4% bupivacaine (0.2 ml) and dexamethasone (0.8 mg) 10 minutes before surgery. Group 3 was infiltrated with 0.4% bupivacaine (0.2 ml) and dexamethasone (0.8 mg) after surgery. Group 4 was infiltrated with normal saline (0.2 ml) and dexamethasone (0.8 mg) 10 minutes before surgery. Group 5 was infiltrated with only 0.4% bupivacaine (0.2 ml) before surgery. Rat paw withdrawal thresholds were measured using the von Frey hair test before surgery as a baseline measurement and on postoperative days 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18 and 21.
RESULTS
In the group injected preoperatively with dexamethasone and bupivacaine, mechanical allodynia did not develop and mechanical threshold forces were significantly different compared with other groups, especially between postoperative days 3 and 9 (P < 0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
In conclusion, preoperative infiltration of both dexamethasone and bupivacaine showed a significantly better analgesic effect than did infiltration of bupivacaine or dexamethasone alone in the spared nerve injury model, especially early on after surgery.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, acupuncture, and spinal cord stimulation on neuropathic, inflammatory and, non-inflammatory pain in rat models
Karina Laurenti Sato, Luciana Sayuri Sanada, Morgana Duarte da Silva, Rodrigo Okubo, Kathleen A. Sluka
Korean J Pain. 2020;33(2):121-130. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2020.33.2.121.Olanzapine Attenuates Mechanical Allodynia in a Rat Model of Partial Sciatic Nerve Ligation
Taeko Fukuda, Soichiro Yamashita, Setsuji Hisano, Makoto Tanaka
Korean J Pain. 2015;28(3):185-192. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2015.28.3.185.Comparison of 4 mg dexamethasone versus 8 mg dexamethasone as an adjuvant to levobupivacaine in fascia iliaca block-a prospective study
Ranjita Acharya, Bhavna Sriramka, Sandeep Panigrahi
Korean J Pain. 2018;31(4):261-267. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2018.31.4.261.
Reference
-
1. Woolf CJ, Mannion RJ. Neuropathic pain: aetiology, symptoms, mechanisms, and management. Lancet. 1999; 353:1959–1964. PMID: 10371588.
Article2. Woolf CJ, Shortland P, Coggeshall RE. Peripheral nerve injury triggers central sprouting of myelinated afferents. Nature. 1992; 355:75–78. PMID: 1370574.
Article3. Ersayli DT, Gurbet A, Bekar A, Uckunkaya N, Bilgin H. Effects of perioperatively administered bupivacaine and bupivacaine-methylprednisolone on pain after lumbar discectomy. Spine. 2006; 31:2221–2226. PMID: 16946657.
Article4. Mirzai H, Tekin I, Alincak H. Perioperative use of corticosteroid and bupivacaine combination in lumbar disc surgery: a randomized controlled trial. Spine. 2002; 27:343–346. PMID: 11840097.
Article5. Dahl JB, Kehlet H. The value of pre-emptive analgesia in the treatment of postoperative pain. Br J Anaesth. 1993; 70:434–439. PMID: 8499204.
Article7. Cervini P, Smith LC, Urbach DR. The effect of intraoperative bupivacaine administration on parenteral narcotic use after laparoscopic appendectomy. Surg Endosc. 2002; 16:1579–1582. PMID: 12045850.
Article8. Turner GA, Chalkiadis G. Comparison of preoperative with postoperative lignocaine infiltration on postoperative analgesic requirements. Br J Anaesth. 1994; 72:541–543. PMID: 8198905.
Article9. Dierking GW, Dahl JB, Kanstrup J, Dahl A, Kehlet H. Effect of pre- vs postoperative inguinal field block on postoperative pain after herniorrhaphy. Br J Anaesth. 1992; 68:344–348. PMID: 1642910.
Article10. Dahl JB, Hansen BL, Hjortsø NC, Erichsen CJ, Møiniche S, Kehlet H. Influence of timing on the effect of continuous extradural analgesia with bupivacaine and morphine after major abdominal surgery. Br J Anaesth. 1992; 69:4–8. PMID: 1637601.
Article11. Skjelbred P, Løkken P. Post-operative pain and inflammatory reaction reduced by injection of a corticosteroid. A controlled trial in bilateral oral surgery. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1982; 21:391–396. PMID: 7042372.
Article12. Holte K, Kehlet H. Perioperative single-dose glucocorticoid administration: pathophysiologic effects and clinical implications. J Am Coll Surg. 2002; 195:694–712. PMID: 12437261.
Article13. Bisgaard T, Klarskov B, Kehlet H, Rosenberg J. Preoperative dexamethasone improves surgical outcome after laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Ann Surg. 2003; 238:651–660. PMID: 14578725.
Article14. Castillo J, Curley J, Hotz J, Uezono M, Tigner J, Chasin M, et al. Glucocorticoids prolong rat sciatic nerve blockade in vivo from bupivacaine microspheres. Anesthesiology. 1996; 85:1157–1166. PMID: 8916834.
Article15. Dräger C, Benziger D, Gao F, Berde CB. Prolonged intercostal nerve blockade in sheep using controlled-release of bupivacaine and dexamethasone from polymer microspheres. Anesthesiology. 1998; 89:969–979. PMID: 9778015.
Article16. Kopacz DJ, Lacouture PG, Wu D, Nandy P, Swanton R, Landau C. The dose response and effects of dexamethasone on bupivacaine microcapsules for intercostal blockade (T9 to T11) in healthy volunteers. Anesth Analg. 2003; 96:576–582. PMID: 12538215.
Article17. Stan T, Goodman EJ, Bravo-Fernandez C, Holbrook CR. Adding methylprednisolone to local anesthetic increases the duration of axillary block. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2004; 29:380–381. PMID: 15305267.
Article18. Kelly DJ, Ahmad M, Brull SJ. Preemptive analgesia I: physiological pathways and pharmacological modalities. Can J Anaesth. 2001; 48:1000–1010. PMID: 11698320.
Article19. Decosterd I, Woolf CJ. Spared nerve injury: an animal model of persistent peripheral neuropathic pain. Pain. 2000; 87:149–158. PMID: 10924808.
Article20. Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, Chung JM, Yaksh TL. Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J Neurosci Methods. 1994; 53:55–63. PMID: 7990513.
Article21. Devor M, Wall PD, Catalan N. Systemic lidocaine silences ectopic neuroma and DRG discharge without blocking nerve conduction. Pain. 1992; 48:261–268. PMID: 1589245.
Article22. Kingery WS, Vallin JA. The development of chronic mechanical hyperalgesia, autotomy and collateral sprouting following sciatic nerve section in rat. Pain. 1989; 38:321–332. PMID: 2812843.
Article23. Woolf CJ. Evidence for a central component of post-injury pain hypersensitivity. Nature. 1983; 306:686–688. PMID: 6656869.
Article24. Woolf CJ, Wall PD. Chronic peripheral nerve section diminishes the primary afferent A-fibre mediated inhibition of rat dorsal horn neurones. Brain Res. 1982; 242:77–85. PMID: 7104735.
Article25. Tverskoy M, Cozacov C, Ayache M, Bradley EL Jr, Kissin I. Postoperative pain after inguinal herniorrhaphy with different types of anesthesia. Anesth Analg. 1990; 70:29–35. PMID: 2297102.
Article26. Jebeles JA, Reilly JS, Gutierrez JF, Bradley EL Jr, Kissin I. The effect of pre-incisional infiltration of tonsils with bupivacaine on the pain following tonsillectomy under general anesthesia. Pain. 1991; 47:305–308. PMID: 1784501.
Article27. Kato J, Ogawa S, Katz J, Nagai H, Kashiwazaki M, Saeki H, et al. Effects of presurgical local infiltration of bupivacaine in the surgical field on postsurgical wound pain in laparoscopic gynecologic examinations: a possible preemptive analgesic effect. Clin J Pain. 2000; 16:12–17. PMID: 10741813.
Article28. Hannibal K, Galatius H, Hansen A, Obel E, Ejlersen E. Preoperative wound infiltration with bupivacaine reduces early and late opioid requirement after hysterectomy. Anesth Analg. 1996; 83:376–381. PMID: 8694322.
Article29. McQuay HJ, Carroll D, Moore RA. Postoperative orthopaedic pain--the effect of opiate premedication and local anesthetic blocks. Pain. 1988; 33:291–295. PMID: 3419836.
Article30. Gordon SM, Dionne RA, Brahim J, Jabir F, Dubner R. Blockade of peripheral neuronal barrage reduces postoperative pain. Pain. 1997; 70:209–215. PMID: 9150295.
Article31. Roberge CW, McEwen M. The effects of local anesthetics on postoperative pain. AORN J. 1998; 68:1003–1012. PMID: 9864591.
Article32. Kissin I, Lee SS. Effects of long-term nerve blockade in the spared nerve injury model. Anesthesiology. 2004; 101:806–807. PMID: 15329619.
Article33. Ririe DG, Barclay D, Prout H, Tong C, Tobin JR, Eisenach JC. Preoperative sciatic nerve block decreases mechanical allodynia more in young rats: is preemptive analgesia developmentally modulated? Anesth Analg. 2004; 99:140–145. PMID: 15281520.
Article34. Suter MR, Papaloïzos M, Berde CB, Woolf CJ, Gilliard N, Spahn DR, et al. Development of neuropathic pain in the rat spared nerve injury model is not prevented by a peripheral nerve block. Anesthesiology. 2003; 99:1402–1408. PMID: 14639156.
Article35. Manchikanti L. Role of neuraxial steroids in interventional pain management. Pain Physician. 2002; 5:182–199. PMID: 16902669.
Article36. Baxendale BR, Vater M, Lavery KM. Dexamethasone reduces pain and swelling following extraction of third molar teeth. Anaesthesia. 1993; 48:961–964. PMID: 8250191.
Article37. Giannoni C, White S, Enneking FK. Does dexamethasone with preemptive analgesia improve pediatric tonsillectomy pain? Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2002; 126:307–315. PMID: 11956540.
Article38. Lee C, Kim TY. The effect of preoperative dexamethasone administration, according to age and gender on postoperative pain in patients who undergo laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Korean J Pain. 2008; 21:51–56.
Article39. Tom LW, Templeton JJ, Thompson ME, Marsh RR. Dexamethasone in adenotonsillectomy. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 1996; 37:115–120. PMID: 8894809.
Article40. Movafegh A, Razazian M, Hajimaohamadi F, Meysamie A. Dexamethasone added to lidocaine prolongs axillary brachial plexus blockade. Anesth Analg. 2006; 102:263–267. PMID: 16368840.
Article41. Devor M, Govrin-Lippmann R, Raber P. Corticosteroids suppress ectopic neural discharge originating in experimental neuromas. Pain. 1985; 22:127–137. PMID: 4047699.
Article42. Christensen K, Jensen EM, Noer I. The reflex dystrophy syndrome response to treatment with systemic corticosteroids. Acta Chir Scand. 1982; 148:653–655. PMID: 6763435.43. Kozin F, McCarty DJ, Sims J, Genant H. The reflex sympathetic dystrophy syndrome. I. Clinical and histologic studies: evidence for bilaterality, response to corticosteroids and articular involvement. Am J Med. 1976; 60:321–331. PMID: 56891.44. Kingery WS, Agashe GS, Sawamura S, Davies MF, Clark JD, Maze M. Glucocorticoid inhibition of neuropathic hyperalgesia and spinal Fos expression. Anesth Analg. 2001; 92:476–482. PMID: 11159254.
Article45. Xie W, Luo S, Xuan H, Chou C, Song G, Lv R, et al. Betamethasone affects cerebral expressions of NF-kappaB and cytokines that correlate with pain behavior in a rat model of neuropathy. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2006; 36:39–46. PMID: 16501235.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Efficacy of perineural versus intravenous dexamethasone in prolonging the duration of analgesia when administered with peripheral nerve blocks: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Peripheral Nerve Injury Alters Excitatory and Inhibitory Synaptic Transmission in Rat Spinal Cord Substantia Gelatinosa
- An Experimental Study of Local Anesthetic Injection Injury to Peripheral Nerves
- Comparative Study of Scar Formation at the Site of Sciatic Nerve Repair in Rats
- Effect of the Preoperative Intercostal Nerve Block in a Rat Model of Postthoracotomy Pain