A Prospective Multicenter Study on the Prevalence and Symptoms of Erosive Reflux Esophagitis in Secondary and Tertiary Hospitals in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. drbakyt@korea.ac.kr
- KMID: 1767683
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2009.53.5.283
Abstract
-
BACKGROUND/AIMS: Recent studies suggest that the prevalence of erosive esophagitis (EE) is increasing in Asia. The aims of this study were to determine the prevalence of EE among outpatients visiting gastroenterology clinics of secondary and tertiary hospitals in Korea, and to analyze their symptoms.
METHODS
From May to July 2003, outpatients undergoing their first upper gastrointestinal endoscopies after visiting gastroenterology clinics in secondary and tertiary hospitals in Korea were enrolled. Prevalence of EE was calculated from their endoscopic findings, and symptoms were analyzed from the validated symptom questionnaire.
RESULTS
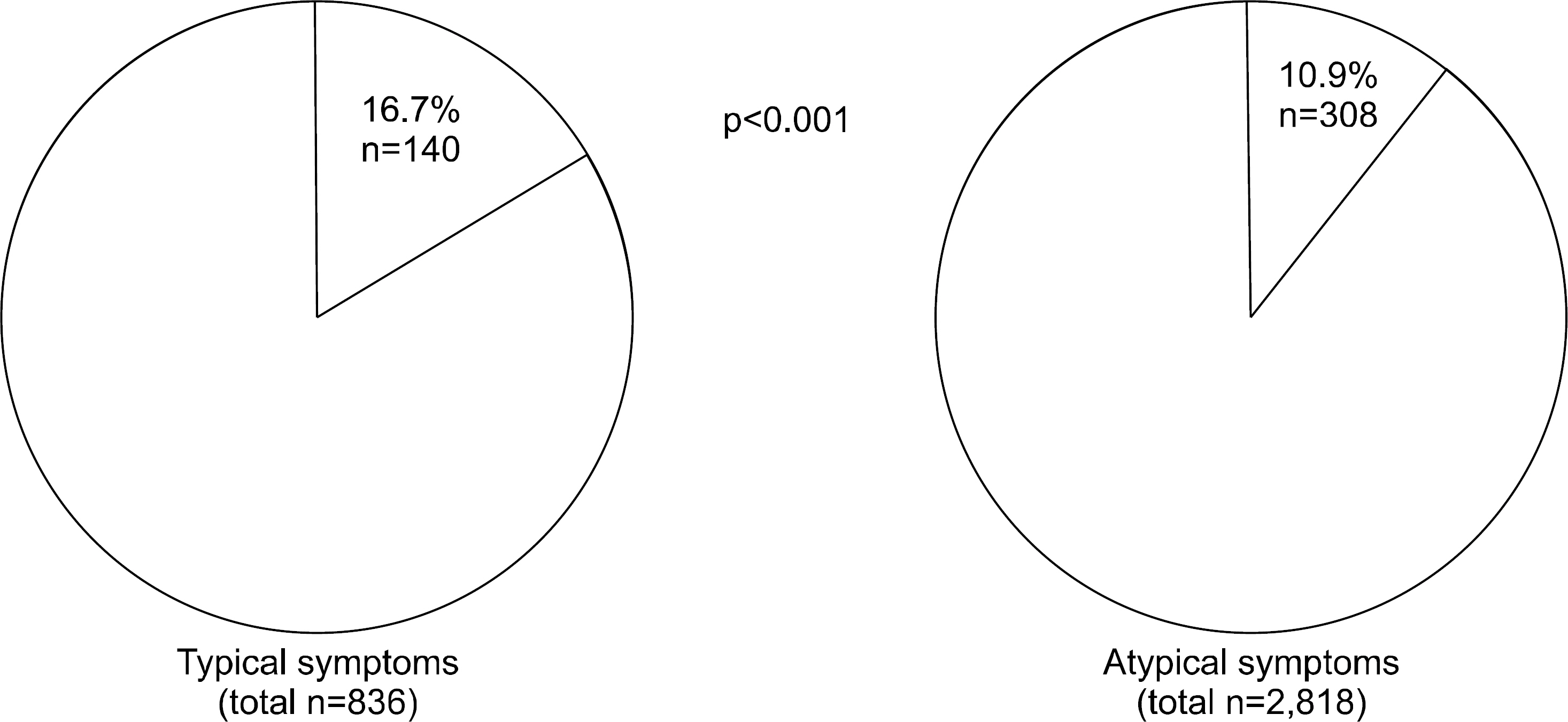
Among 4,275 cases from 24 hospitals, 506 (11.8%) had EE. Among 836 cases with predominantly typical GERD symptoms, EE was diagnosed in 140 (16.7%). Among 530 cases having predominantly typical GERD symptoms with a frequency of at least twice a week or with a significant impact on their daily lives, EE was found in 104 (19.6%). The prevalence of EE was positively associated with males irrespective of age, old aged (> or =65 years) females, predominantly typical GERD symptoms at least twice a week, and the numbers of typical GERD symptoms. The severity of GERD symptoms did not affect the prevalence of EE. The most common typical and atypical GERD symptoms in cases with EE were regurgitation and epigastric soreness, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
The prevalence of EE among outpatients visiting gastroenterology clinics in Korea was 11.8%. Independent factors associated with increased prevalence of EE were males irrespective of age, old aged (> or =65 years) females, number of typical GERD symptoms, and frequent typical GERD symptoms.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 8 articles
-
Therapeutic Response to 20 mg of Esomeprazole Twice Daily in Patients with Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease-related Non-cardiac Chest Pain: An Open-Label Randomized Pilot Study
Jae Kyun Choi, Hyun Ik Shim, Cheol Min Shin, Hyuk Yoon, Young Soo Park, Nayoung Kim, Dong Ho Lee
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2020;75(6):333-340. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2020.75.6.333.Diagnosis and Management of Barrett's Esophagus, Dysplasia and Early Esophageal Adenocarcinoma: Focusing on American and European Guidelines
Ah Young Yoo, Moon Kyung Joo
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2019;74(1):11-16. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2019.74.1.11.Gastro-Esophageal Reflux Disease in Healthy Older Children and Adolescents
Kie Young Park, Soo Hee Chang
Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2012;15(4):220-228. doi: 10.5223/pghn.2012.15.4.220.Clinical Characteristics of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease with Esophageal Injury in Korean: Focusing on Risk Factors
Seung Jun Lee, Min Kyu Jung, Sung Kook Kim, Byung Ik Jang, Si Hyung Lee, Kyeong Ok Kim, Eun Soo Kim, Kwang Bum Cho, Kyung Sik Park, Eun Young Kim, Jin Tae Jung, Joong Goo Kwon, Joong Hyun Lee, Chang Hun Yang, Chang Keun Park, Hyang Eun Seo, Seong Woo Jeon
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2011;57(5):281-287. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2011.57.5.281.Is There a Difference in the Prevalence of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease between Peritoneal Dialysis and Hemodialysis Patients?
Hyun Jung Song, Sun Moon Kim, Yu Mi Lee, Jung Ah Hwang, Kyung Min Moon, Chang Gi Moon, Hoon Sup Koo, Kyung Ho Song, Yong Seok Kim, Tae Hee Lee, Kyu Chan Huh, Young Woo Choi, Young Woo Kang, Won Min Hwang, Sung Ro Yun
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2013;62(4):206-212. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2013.62.4.206.Clinical Analysis of Recurrence Rate and Symptom Improvement in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Patients
You Jeong Jeong, Dong Ho Lee, Tae Hyuck Choi, Tae Jun Hwang, Byeong Hwan Lee, Jong Chon Nah, Sang Hyub Lee, Young Soo Park, Jin-Hyok Hwang, Jin-Wook Kim, Sook-Hyang Jeong, Nayoung Kim, Hyun Chae Jung, In Sung Song
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2010;55(2):100-108. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2010.55.2.100.Diagnosis of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: a Systematic Review
Yu Kyung Cho, Gwang Ha Kim, Jeong Hwan Kim, Hwoon-Yong Jung, Joon Seong Lee, Nayoung Kim
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2010;55(5):279-295. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2010.55.5.279.Diagnosis and Treatment of GastroEsophageal Reflux Disease at the Primary Health Care Clinics in Korea
Young Sun Kim, Dong Hoon Kang, Hyun Chul Park, Tae Hoon Oh, Yong Sik Kim
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2023;82(4):180-189. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2023.032.
Reference
-
1. Fock KM, Talley NJ, Fass R, et al. Asia-Pacific consensus on the management of gastroesophageal reflux disease: update. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008; 23:8–22.
Article2. Wiklund I. Review of the quality of life and burden of illness in gastroesophageal reflux disease. Dig Dis. 2004; 22:108–114.
Article3. Locke GR 3rd, Talley NJ, Fett SL, Zinsmeister AR, Melton LJ 3rd. Prevalence and clinical spectrum of gastroesophageal reflux: a population-based study in Olmsted County, Minne-sota. Gastroenterology. 1997; 112:1448–1456.
Article4. Cho YS, Choi MG, Jeong JJ, et al. Prevalence and clinical spectrum of gastroesophageal reflux: a population-based study in Asan-si, Korea. Am J Gastroenterol. 2005; 100:747–753.
Article5. Yang SY, Lee OY, Bak YT, et al. Prevalence of gastroesophageal reflux disease symptoms and uninvestigated dyspepsia in Korea: a population-based study. Dig Dis Sci. 2008; 53:188–193.
Article6. Jeon SG, Sohn CI, Kim JE, et al. Prevalence of gastroesophageal reflux in routine check-up subjects. Korean J Med. 2000; 58:145–151.7. Oh JH, Choi MG, Kim HR, et al. Clinical spectrum of endoscopic reflux esophagitis in routine check-up subjects in Korea. Korean J Gastrointest Motil. 2006; 12:12–18.8. Na IK, Jung JI, Pard HS. The prevalence and associated factors of reflux esophagitis in routine check-up subjects. J Korean Acad Fam Med. 2001; 22:1647–1655.9. Yoo SS, Lee WH, Ha J, et al. The prevalence of esophageal disorders in the subjects examined for health screening. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2007; 50:306–312.10. Kim N, Lee SW, Cho SI, et al. The prevalence of and risk factors for erosive oesophagitis and non-erosive reflux disease: a nationwide multicentre prospective study in Korea. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2008; 27:173–185.
Article11. Cho SH, Kim CW. The relationship between obesity and reflux esophagitis in health check-up subjects. Korean J Obes. 2007; 16:58–64.12. Armstrong D, Bennett JR, Blum AL, et al. The endoscopic assessment of esophagitis: a progress report on observer agreement. Gastroenterology. 1996; 111:85–92.
Article13. Kim BC, Yoon YH, Jyung HS, et al. Clinical characteristics of gastroesophageal reflux diseases and association with Helicobacter pylori infection. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2006; 47:363–369.14. Jeon SG, Rhee PL, Shin MH, et al. The prevalence and risk factors of reflux esophagitis in routine check-up subjects. Korean J Gastroenterol. 1998; 32:701–708.15. Pilotto A, Franceschi M, Leandro G, et al. Clinical features of reflux esophagitis in older people: a study of 840 consec-utive patients. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2006; 54:1537–1542.
Article16. Castell DO. The esophagus. 2nd ed.Boston: Little Brown and Company;1995.17. Amano K, Adachi K, Katsube T, Watanabe M, Kinoshita Y. Role of hiatus hernia and gastric mucosal atrophy in the development of reflux esophagitis in the elderly. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2001; 16:132–136.
Article18. Inamori M, Togawa J, Nagase H, et al. Clinical characteristics of Japanese reflux esophagitis patients as determined by Los Angeles classification. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2003; 18:172–176.
Article19. Furukawa N, Iwakiri R, Koyama T, et al. Proportion of reflux esophagitis in 6010 Japanese adults: prospective evaluation by endoscopy. J Gastroenterol. 1999; 34:441–444.
Article20. Okamoto K, Iwakiri R, Mori M, et al. Clinical symptoms in endoscopic reflux esophagitis: evaluation in 8031 adult subjects. Dig Dis Sci. 2003; 48:2237–2241.
Article21. Hung CS, Lee CL, Yang JN, et al. Clinical application of Carlsson's questionnaire to predict erosive GERD among healthy Chinese. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005; 20:1900–1905.
Article22. Chen TS, Chang FY. The prevalence and risk factors of reflux esophagitis among adult Chinese population in Taiwan. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2007; 41:819–822.
Article23. Rosaida MS, Goh KL. Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease, reflux oesophagitis and non-erosive reflux disease in a multi-racial Asian population: a prospective, endoscopy based study. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004; 16:495–501.24. Wong BCY, Kinoshita Y. Systematic review on epidemiology of gastroesophageal reflux disease in Asia. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006; 4:398–407.
Article25. Kawanishi M. Will symptomatic gastroesophageal reflux disease develop into reflux esophagitis? J Gastroenterol. 2006; 41:440–443.
Article26. Labenz J, Nocon M, Lind T, et al. Prospective follow-up data from the ProGERD study suggest that GERD is not a catego-rial disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006; 101:2457–2462.
Article27. Faybush EM, Fass R. Gastroesophageal reflux disease in non-cardiac chest pain. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2004; 33:41–54.
Article28. Wong WM, Lai KC, Lau CP, et al. Upper gastrointestinal evaluation of Chinese patients with non-cardiac chest pain. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2002; 16:465–471.
Article29. Vakil N, van Zanten SV, Kahrilas P, Dent J, Jones R. The Montreal definition and classification of gastroesophageal reflux disease: a global evidence-based consensus. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006; 101:1900–1920.
Article30. Dent J, Armstrong D, Delaney B, Moayyedi P, Talley NJ, Vakil N. Symptom evaluation in reflux disease: workshop background, processes, terminology, recommendations, and discussion outputs. Gut. 2004; 53(Suppl 4):iv1–24.
Article31. Kim JH, Rhee PL, Park EH, Son HJ, Kim JJ, Rhee JC. Clinical usefulness of subgrouping of patients with non-cardiac chest pain according to characteristic symptoms in Korea. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007; 22:320–325.
Article32. Galmiche JP. Endoscopy-negative reflux disease: part of the spectrum of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease or a separate disorder? Implications for treatment. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2005; 21(Suppl 1):9–10.33. Smout AJ, Geus WP, Mulder PG, Stockbrugger RW, Lamers CB. Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in The Netherlands. Results of a multicentre pH study. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1996; 31:10–15.
Article34. Lee JH, Lee JS, Rhee PL, et al. Interobserver variation in the endoscopic diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 2006; 33:197–203.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Spectrum of Endoscopic Reflux Esophagitis in Routine Check-Up Subjects in Korea
- Atypical Symptoms in Patients With Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
- Minimal Change Esophagitis
- A Case of Barrett Esophagus Associated with Erosive Reflux Esophagitis in a Patient with Hiatal Hernia
- Gastro-Esophageal Reflux Disease in Healthy Older Children and Adolescents