Yonsei Med J.
2009 Aug;50(4):505-511. 10.3349/ymj.2009.50.4.505.
Direct Immunofluorescence in Behcet's Disease: A Controlled Study with 108 Cases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Istanbul Medical Faculty, Istanbul University, Istanbul, Turkey. akose@istanbul.edu.tr
- KMID: 1758608
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2009.50.4.505
Abstract
- PURPOSE
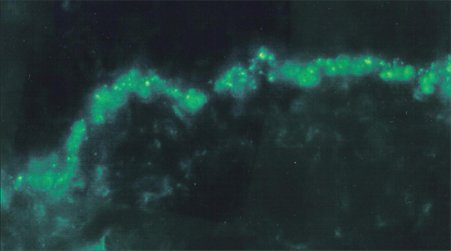
Behcet's disease (BD) is a disease of unknown etiology, which has multisystemic involvement. This multisystemic involvement might be the clue for an autoimmune pathogenesis. In order to evaluate an autoimmune pathogenesis, we examined immunoreactans depositions in the skin of BD patients. MATERIALS AND METHODS: The skin samples of 108 BD patients (28 perilesional skin, 44 positive pathergy test site, 22 negative pathergy test site, 14 normal skin) were examined for the depositions of immunoglobulin (Ig)M, IgG, IgA, complement 3 (C3), and fibrinogen (F) using direct immunofluorescence (DIF). The data were statistically compared to the DIF of 36 systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients and 20 healthy controls using chi-square Fisher exact test. RESULTS: Highly significant immunoreactans depositions were obtained in BD (deposition rates: IgM 70.3%, IgG 0%, IgA 20.3%, C3 62.9%, F 83.3%). The comparison with SLE revealed no differences in IgM, IgA, and C3. However, IgG deposition was higher in SLE while F deposition was higher in BD. In both BD and SLE, the Ig depositions were highly significant when the data were compared with the healthy controls. CONCLUSION: The significant deposition of immunoreactans in BD, especially in the negative pathergy and the normal skin sites, were observed. This study is the first controlled study revealing positive Ig depositions in BD, and it is expected to help us to reconsider the autoimmune pathogenesis in BD.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Yazıcı H, Fresko I, Tunç R, Melikoglu M. Ball GV, Bridges SL, editors. Behçet's syndrome: pathogenesis, clinical manifestations and treatment. Vasculitis. 2002. New York: Oxford University Press;406–432.2. Laskaris G, Sklavounou A, Angelopoulos A. Direct immunofluorescence in oral lichen planus. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1982. 53:483–487.
Article3. Provost TT, Reichlin M. Immunopathologic studies of cutaneous lupus erythematosus. J Clin Immunol. 1988. 8:223–233.
Article4. Kulthanan K, Roongphiboolsopit P, Chanjanakijskul S, Kullavanijaya P. Chronic discoid lupus erythematosus in Thailand: direct immunofluorescence study. Int J Dermatol. 1996. 35:711–714.
Article5. Helm KF, Peters MS. Deposition of membrane attack complex in cutaneous lesions of lupus erythematosus. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993. 28:687–691.
Article6. Wojnarowska F, Bhogal B, Black MM. The significance of an IgM band at the dermo-epidermal junction. J Cutan Pathol. 1986. 13:359–362.
Article7. Laskaris G. Oral pemphigus vulgaris: an immunofluorescent study of fifty-eight cases. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1981. 51:626–631.
Article8. Haim S, Sobel JD, Friedman-Birnbaum R, Lichtig C. Histohogical and direct immunofluorescence study of cutaneous hyperreactivity in Behçet's disease. Br J Dermatol. 1976. 95:631–636.
Article9. Azizlerli G, Saylan T, Cologlu AS, Bozan G, Urgancioglu M. Major immunoglobulins in Behçet's disease and a study with direct and indirect immunofluorescent methods. Excepta Medica. 1977. 232–235. International Congress Series.10. Luderschmidt C, Wolff HH, Scherer R. [Apthae: histologic, immunofluorescent and immuno--electron microscopy study of their pathogenesis.]. Hautarzt. 1981. 32:364–369.11. Reimer G, Luckner L, Hornstein OP. Direct immunofluorescence in recurrent aphthous ulcers and Behçet's disease. Dermatologica. 1983. 167:293–298.
Article12. Akdag Kose A, Sarica R, Azizlerli G, Ovül C, et al. Gunes AT, Avcı O, Ozkan S, Fetil , editors. Behçet hastalarında Pategy pozitif, negative, lezyonlu ve lezyonsuz deride histopatolojik ve immunfloresan bulguların karsilastirilması. XV. National Dermatology Congres-III. Internatıonal TURKOD Kurultayi (31.10-4.11.1994 Izmir). 1996. Izmir: Bildiri Kitabı;190–193.13. International Study Group for Behçet's Disease. Criteria for the diagnosis of Behçet's disease. Lancet. 1990. 335:1078–1080.14. Akdag KOSE A, Sarica R, Azizlerli G, Ozturk AS, Balcıoglu G, Sur H. The importance of direct immunofluorescence in the diagnosis of lupus erythematosus. Turkderm. 1997. 31:114–116.15. Weigand DA. Lupus band test: anatomic regional variations in discoid lupus erythematosus. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1986. 14:426–428.
Article16. Williams RE, Mackie RM, O'Keefe R, Thomson W. The contribution of direct immunofluorescence to the diagnosis of lupus erythematosus. J Cutan Pathol. 1989. 16:122–125.
Article17. Amital H, Shoenfeld Y. Autoimmunity and autoimmune disease such as systemic lupus erythematosus. 1999. San Diego: Academic Press;1–16.18. Sontheimer RD. Lahita RG, editor. Systemic lupus erythematosus and the skin. Systemic lupus erythematosus. 1999. San Diego: Academic Press;631–656.19. Rowell NR, Goolfield MJD. Champion RH, Burton JL, Burns DA, Breathach SM, editors. The connective tissue disease. Textbook of dermatology. 1998. London: Blackwell Science Press;2437–2575.20. Dahl MV. Usefulness of direct immunofluorescence in patients with lupus erythematosus. Arch Dermatol. 1983. 119:1010–1017.
Article21. Beutner EH, Chorzelski TP, Jablonska S. Immunufluorescence test. Clinical significance of sera and skin in bullous disease. Int J Dermatol. 1985. 24:405–421.22. Bhogal B, Wojnarowska F, Black MM, Xu W, Levene GM. The distribution of immunoglobulins and the C3 component of complement in multiple biopsies from the uninvolved and perilesional skin in pemphigus. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1986. 11:49–53.
Article23. Alpsoy E, Uzun S, Akman A, Acar MA, Memişoglu HR, Başaran E. Histological and immunofluorescence findings of non-follicular papulopustular lesions in patients with Behçet's disease. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2003. 17:521–524.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Humoral Immunity of Each Subgroup in Behcet's Syndrome
- Antinuclear Antibodies in Patients with Behcet's Disease
- A Case of Behcet's Disease Associated with Pyoderma Gangrenosum
- Treatment of Behcet's Disease: 4 Cases of the Behcet's Disease Treated with Chlorambucil
- Diagnostic criteria of Behcet's disease: problems and suggestions