J Korean Soc Radiol.
2013 Mar;68(3):217-219. 10.3348/jksr.2013.68.3.217.
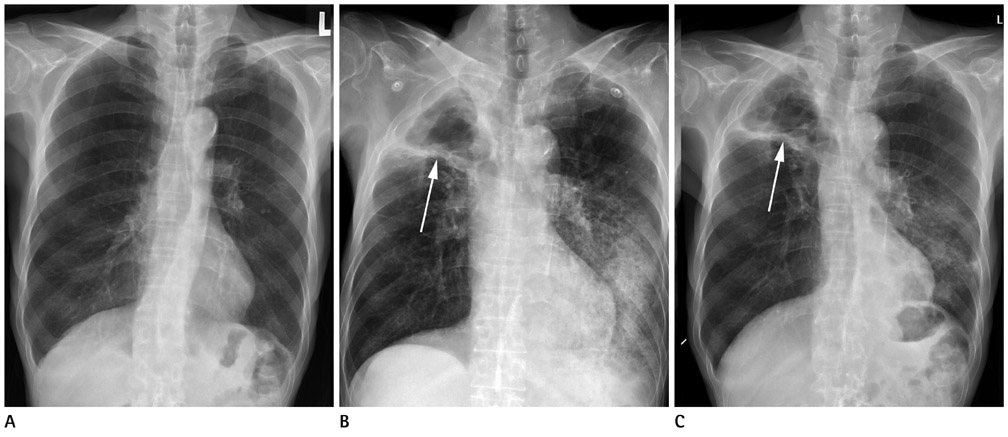
Enterobacter Asburiae Pneumonia with Cavitation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Guri Hospital, Guri, Korea. radjena@hanyang.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1748454
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2013.68.3.217
Abstract
- Enterobacter species have increasingly been identified as pathogens over the past several decades. These bacterial species have become more important because most are resistant to cephalothin and cefoxitin, and can produce extended-spectrum beta-lactamase. Enterobacter Asburiae (E. asburiae) is a gram-negative rod of the family Enterobacteriaceae, named in 1986. Since then, there has been only one clinical report of E. asburiae pneumonia. We report a case of E. asburiae pneumonia with cavitation and compare it with the previous case.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Stewart JM, Quirk JR. Community-acquired pneumonia caused by Enterobacter asburiae. Am J Med. 2001. 111:82–83.2. Brenner DJ, McWhorter AC, Kai A, Steigerwalt AG, Farmer JJ 3rd. Enterobacter asburiae sp. nov., a new species found in clinical specimens, and reassignment of Erwinia dissolvens and Erwinia nimipressuralis to the genus Enterobacter as Enterobacter dissolvens comb. nov. and Enterobacter nimipressuralis comb. nov. J Clin Microbiol. 1986. 23:1114–1120.3. Farmer JJ 3rd, Davis BR, Hickman-Brenner FW, McWhorter A, Huntley-Carter GP, Asbury MA, et al. Biochemical identification of new species and biogroups of Enterobacteriaceae isolated from clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1985. 21:46–76.4. Ehrhardt AF, Sanders CC, Thomson KS, Watanakunakorn C, Trujillano-Martin I. Emergence of resistance to imipenem in Enterobacter isolates masquerading as Klebsiella pneumoniae during therapy with imipenem/cilastatin. Clin Infect Dis. 1993. 17:120–122.5. Choi SH, Lee JE, Park SJ, Kim MN, Choo EJ, Kwak YG, et al. Prevalence, microbiology, and clinical characteristics of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacter spp., Serratia marcescens, Citrobacter freundii, and Morganella morganii in Korea. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2007. 26:557–561.6. Hansell DM, Lynch DA, McAdams HP, Bankier AA. Imaging of the diseases of the chest. 2005. Philadelphia: Elsevier Mosby.7. Sanders WE Jr, Sanders CC. Enterobacter spp.: pathogens poised to flourish at the turn of the century. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1997. 10:220–241.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Necrotizing Pneumonia: CT Findings & its Clinical Significance
- Pneumatocele Caused by Enterobacter cloacae in the Preterm Neonates
- Nosocomial pneumonia in medico-surgical intensive care unit
- Activity of cefepime against enterobacter cloacae, serratin marcesc- ens, pseudomonas aeruginosa and other aerobic gram-negative bacilli
- High-spatial-resolution, instantaneous passive cavitation imaging with temporal resolution in histotripsy: a simulation study