Clin Orthop Surg.
2014 Mar;6(1):103-109. 10.4055/cios.2014.6.1.103.
How to Do Random Allocation (Randomization)
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Seoul Sacred Heart General Hospital, Seoul, Korea. kjhnav@naver.com
- KMID: 1737639
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2014.6.1.103
Abstract
- PURPOSE
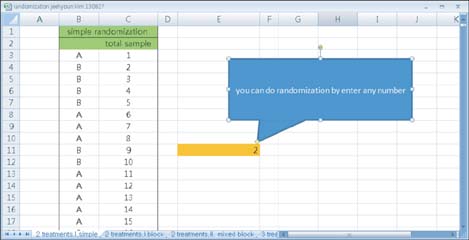
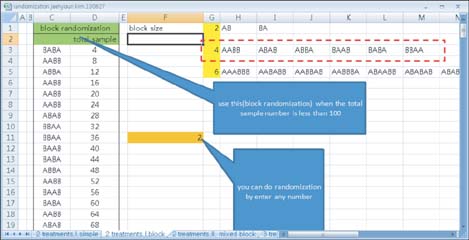
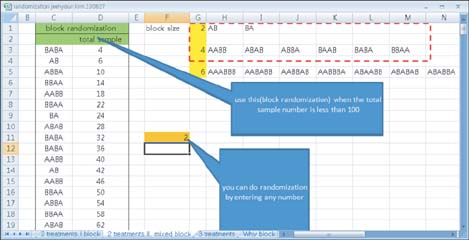
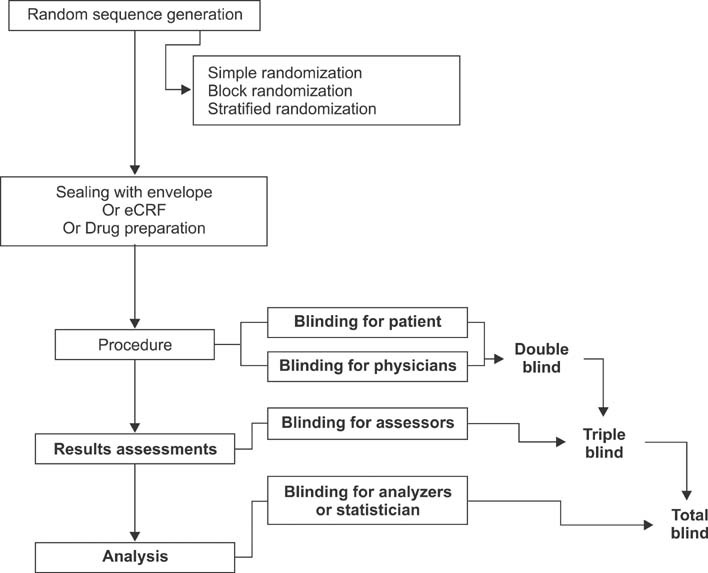
To explain the concept and procedure of random allocation as used in a randomized controlled study.
METHODS
We explain the general concept of random allocation and demonstrate how to perform the procedure easily and how to report it in a paper.
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Concealing Block Sizes Is Not Sufficient
Vance W. Berger, Xin He
Clin Orthop Surg. 2015;7(3):422-423. doi: 10.4055/cios.2015.7.3.422.Introduction of a pilot study
Junyong In
Korean J Anesthesiol. 2017;70(6):601-605. doi: 10.4097/kjae.2017.70.6.601.Effectiveness of continuous hypertonic saline infusion with an automated infusion pump for decompressive neuroplasty: a randomized clinical trial
Ho-Jin Lee, Jaewoo Lee, Yeon wook Park, Ho Young Gil, Eunjoo Choi, Francis Sahngun Nahm, Pyung Bok Lee
Korean J Pain. 2019;32(3):196-205. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2019.32.3.196.
Reference
-
1. Bhandari M, Richards RR, Sprague S, Schemitsch EH. The quality of reporting of randomized trials in the Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery from 1988 through 2000. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002; 84(3):388–396.2. Montané E, Vallano A, Vidal X, Aguilera C, Laporte JR. Reporting randomised clinical trials of analgesics after traumatic or orthopaedic surgery is inadequate: a systematic review. BMC Clin Pharmacol. 2010; 10:2.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Random allocation and dynamic allocation randomization
- Randomization in clinical studies
- Randomization, What is the Proper Method?
- Comparison of Efficiency between Individual Randomization and Cluster Randomization in the Field Trial
- A Quality Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials about Erectile Dysfunction